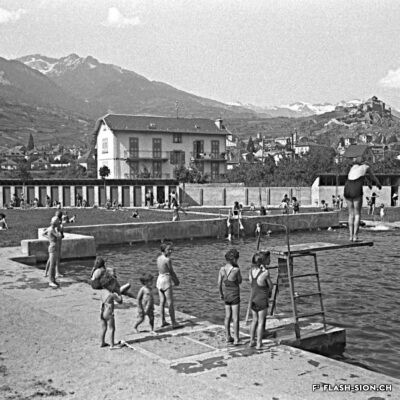
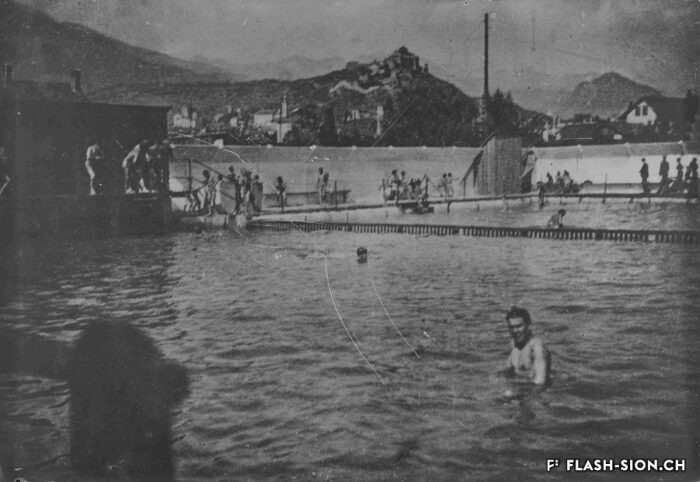
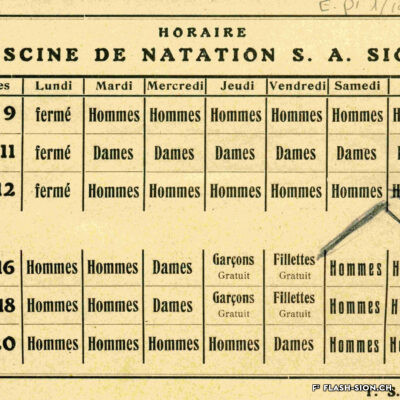
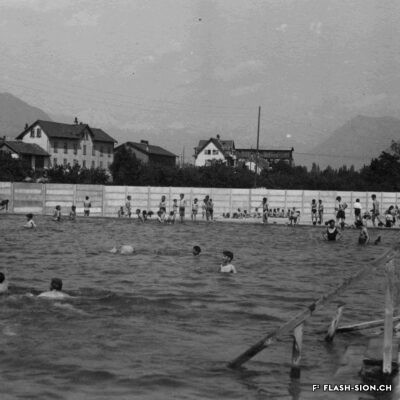La piscine, entre première cantonale et pudeur locale
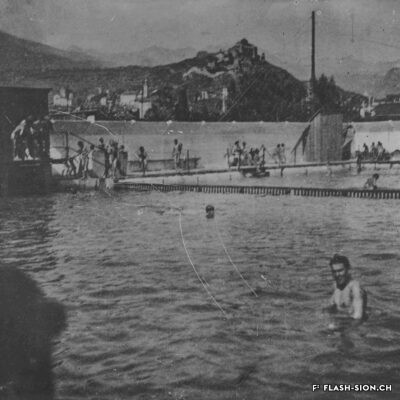
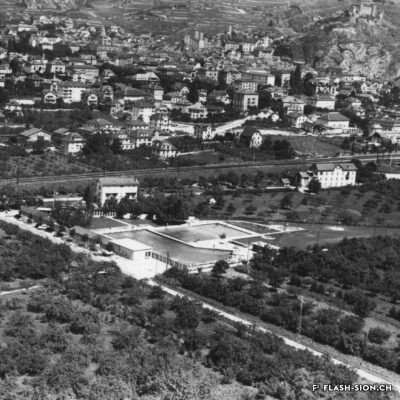
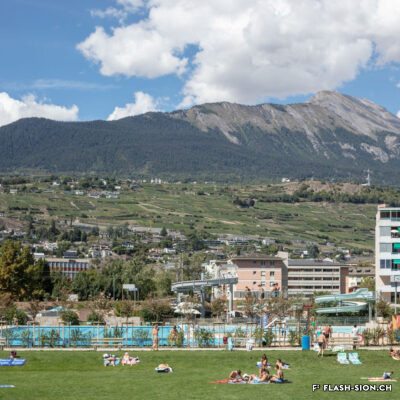
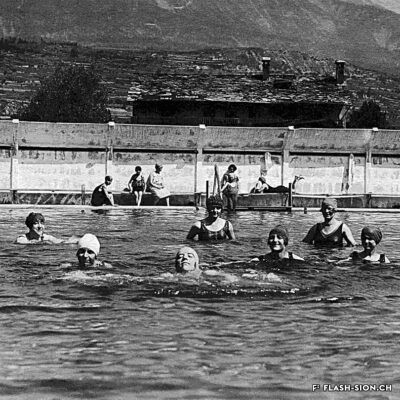
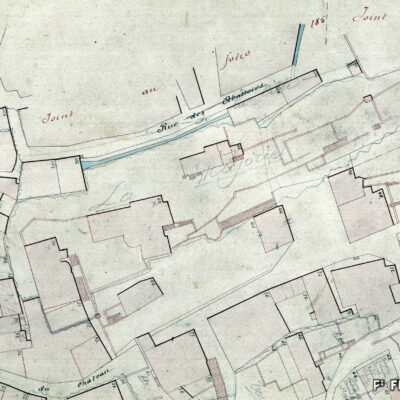
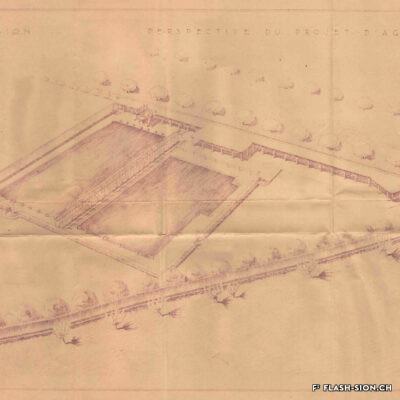
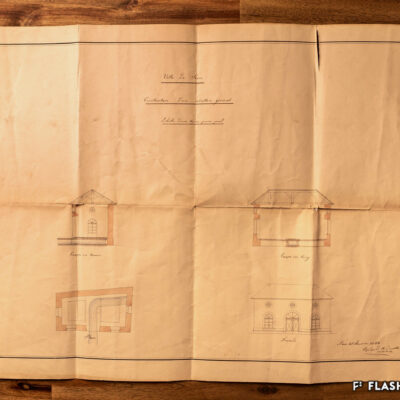
Construite en 1922 en bordure de ville mais à l’abri des regards, la piscine de la Blancherie est la première piscine publique de Sion, mais également du canton. Le projet est initié par une société privée. Sa construction est loin d’être un fleuve tranquille. Les déboires financiers poursuivent longtemps l’établissement, jusqu’à sa reprise par la Ville. Malgré des débuts chaotiques, la piscine trouve rapidement son public et joue un rôle social important dans la communauté sédunoise. Cependant, un point de discorde, et non des moindres, marque l’histoire de l’établissement et concerne sans surprise la mixité. En effet, l’accès à la piscine était initialement réservé aux hommes ou aux femmes selon des horaires bien séparés. Elle ne devient ouverte à tous simultanément que progressivement au début des années 1930, non sans heurts et polémiques…
Freibad Sitten, zwischen kantonaler Premiere und lokaler Prüderie
1922 entsteht am Stadtrand von Sitten, aber dennoch gut verborgen vor begehrlichen Blicken, das Schwimmbad La Blancherie. Es ist das erste öffentliche Freibad der Stadt Sitten aber auch des ganzen Kantons Wallis. Auf Initiative einer privaten Gesellschaft angeregt, stellen sich Bau und Betrieb der Badeanstalt jedoch als alles andere als ein ruhiger Fluss heraus. Finanzielle Schwierigkeiten stehen an der Tagesordnung, bis das Freibad schliesslich von der Stadt übernommen wird. Trotz der schwierigen Ausgangslage erfreut sich das Schwimmbad rasch grosser Beliebtheit und spielt eine wichtige soziale Rolle in der Bevölkerung von Sitten. Ein nicht unwesentlicher Streitpunkt prägt jedoch die Geschichte der Einrichtung und betrifft, wie könnte es anders sein, die Geschlechtertrennung. Tatsächlich war der Zugang zum Schwimmbad ursprünglich Männern oder Frauen nach klar getrennten Zeiten vorbehalten. Erst Anfang der 1930er Jahre wurden die nach Geschlechtern getrennten Öffnungszeiten nach und nach abgeschafft, was bisweilen für erheblichen Zündstoff sorgt…
The swimming pool, a mixture between cantonal premiere and local prudishness
Built in 1922 on the edge of town but hidden from public view, the Blancherie swimming pool was the first public pool in Sion, and of the canton as well. The project was launched by a private company. The history of how it got built was not a smooth process : the institution had to deal continuously with financial setbacks until the commune took over the case. Despite a chaotic start, the pool quickly found its audience and played an important social role in Sion’s community. However, one crucial point of contention marks the history of the institution, which without great surprise, concerns gender mixing. Initially, men and women had access to the swimming pool at separate time slots. It was only gradually opened up to everyone at the same time in the early 1930s, and not without controversy…
La piscina, tra primato cantonale e pudicizia locale
Costruita nel 1922 ai margini della città, ma al riparo dagli sguardi, la piscina della Blancherie è la prima piscina pubblica di Sion, ma anche del Cantone. Il progetto fu avviato da una società privata. La sua costruzione è lungi dall’essere un lungo fiume tranquillo. Le difficoltà finanziarie perseguitarono a lungo la struttura, finché non fu ripresa dalla città. Nonostante gli inizi caotici, la piscina trovò rapidamente il suo pubblico e svolse un importante ruolo sociale nella comunità di Sion. Tuttavia, un punto di contesa, non di minore importanza, ha segnato la storia della struttura e riguardava ovviamente la coesistenza. Inizialmente, l’accesso alla piscina era riservato a uomini e donne in orari separati. Solo all’inizio degli anni ’30 fu progressivamente aperto a tutti, non senza scontri e polemiche …
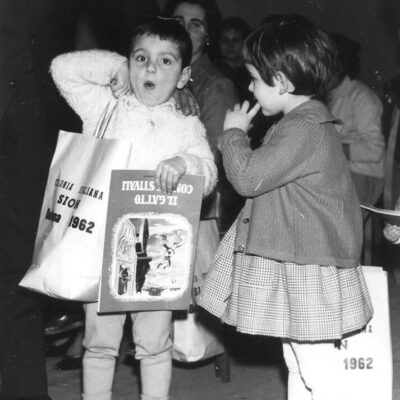
Un point de rencontre italo-sédunois
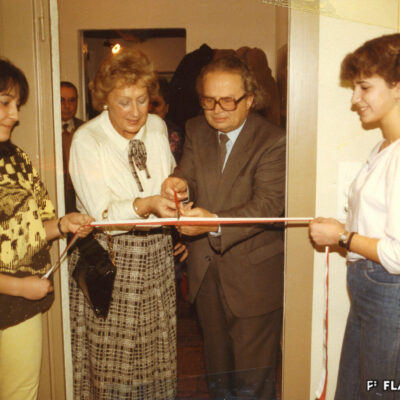
Institution historique et lieu de rassemblement, la Colonia Italiana réunit la communauté des Italiens de Sion dans son bâtiment de la rue de la Majorie depuis plus de soixante ans. Le foyer italien est fondé en 1958 sous l’impulsion de groupes actifs sur les plans sportif et artistique. Leur souhait est de disposer d’un lieu pour se réunir et partager leurs traditions. Rencontres culinaires, expositions, animations culturelles et autres activités rythment depuis lors la vie de ce lieu italo-sédunois.
Begegnungsort der Italienischen und Sittener Gemeinde
Seit mehr als 60 Jahren versammelt sich die italienische Gemeinde in der Colonia Italiana an der Rue de la Majorie. Die geschichtsträchtige Institution und der Treffpunkt von Italienern und Italienerinnen aus Sitten wurde 1958 auf Anregung verschiedener in Sport und Kultur tätigen Gruppen gegründet. Sie hatten das Bedürfnis einen Begegnungsort zu schaffen, wo sie sich treffen und austauschen konnten. Kulinarische Anlässe, Ausstellungen, kulturelle Veranstaltungen sowie weitere Aktivitäten prägen seither das Leben des “Italo-Sittener” Vereinslokals.
Where Italy meets Sion
The Colonia Italiana building in Rue de la Majorie is a historic institution where Sion’s Italian community has gathered together for over 60 years. This Italian centre was founded in 1958 at the initiative of various groups involved in sports and the arts. They wanted a place to meet and share their traditions. This venue where Italy meets Sion stages a regular programme of culinary events, exhibitions, cultural entertainment and other activities.
Un punto di ritrovo italo-sedunese
Istituzione storica e luogo di ritrovo, la Colonia italiana raduna la comunità degli Italiani di Sion nell’edificio in “rue de la Majorie” da oltre sessant’anni. Il focolare italiano è stato fondato nel 1958 sotto l’impulso di gruppi attivi nel campo sportivo e artistico. Il loro intento è quello di disporre di un luogo per riunirsi e condividere le proprie tradizioni. Incontri culinari, mostre, animazioni culturali e altre attività scandiscono da quel momento la vita di questo luogo italo-sedunese.
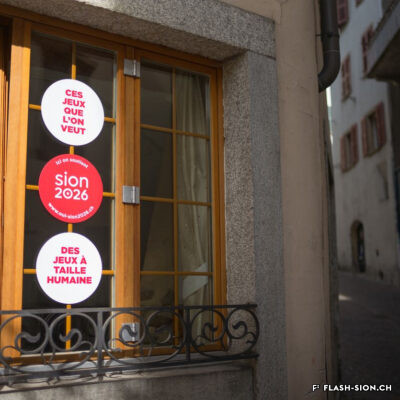
L’impossible histoire des JO à Sion ?
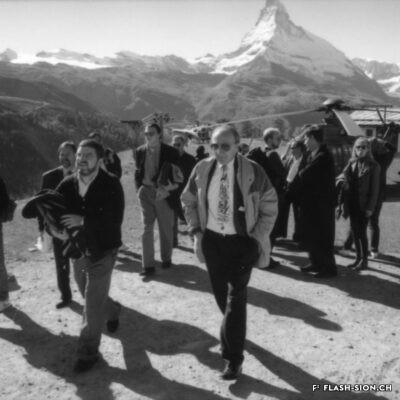
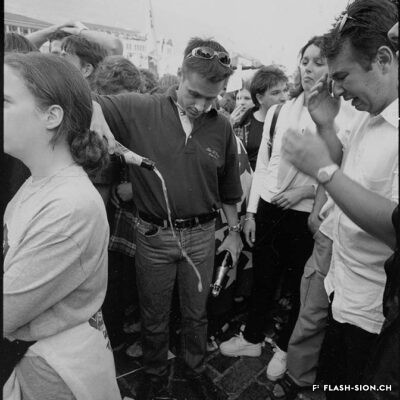
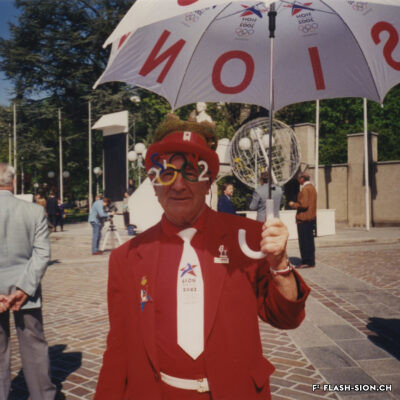
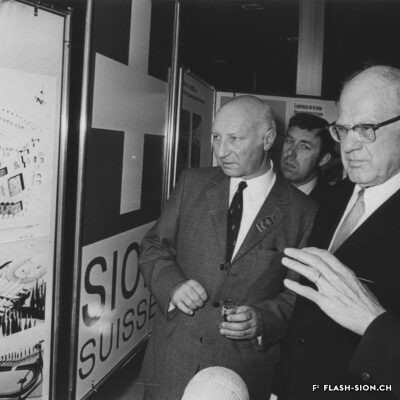
Printemps 1960, un comité étudie pour la première fois la possibilité d’accueillir les Jeux Olympiques d’hiver (JO) à Sion en 1968. La population vote pourtant en 1963 contre le crédit prévu pour cette entreprise. Malgré un premier échec, des candidatures sont officiellement lancées pour les JO 1976, 2002, 2006 et 2026. Le refus provient tantôt du Comité International Olympique (CIO), par ailleurs accusé de corruption, tantôt des autorités communales, refusant de porter le projet sans l’appui financier du Canton et de la Confédération. Les citoyens valaisans, pour leur part, indignés de voir l’argent public investi dans un tel projet et pas ailleurs, craignent de devoir éponger un éventuel déficit. Alors que les candidatures de 2002 et 2006 font rêver une majorité de Valaisans, celle de 2026 a plutôt suscité les dissensions et mis en lumière le décalage entre les ambitions des promoteurs du projet et les préoccupations écologistes grandissantes au sein de la population. Malgré tout, l’idée d’une candidature est émise pour 2030, mais n’aboutit pas. Sion poursuivra-t-elle son rêve olympique à l’heure d’une possible candidature suisse pour 2030 ?
Die unmögliche Geschichte der Olympischen Spiele in Sitten
Im Frühjahr 1960 prüft ein Komitee erstmals die Möglichkeit zur Austragung von Olympischen Winterspielen 1968 in Sitten. Die Bevölkerung lehnt den vorgesehenen Kredit für das Vorhaben jedoch 1963 ab. Trotz dieser Abfuhr werden 1976, 2002, 2006 und 2026 weitere Olympia-Kandidaturen lanciert. Die Ablehnung der Bewerbungen ist einmal auf das damals der Korruption bezichtigte Olympische Komitee (IOC) zurückzuführen, ein andermal auf die Gemeindebehörden, die das Projekt nicht ohne finanzielle Absicherung durch Kanton und Bund zu tragen bereit sind. Die Walliser Bevölkerung wiederum zeigt sich empört darüber, dass öffentliche Gelder nicht besser investiert werden, und befürchtet, dass der Ausgleich eines allfälligen Defizits auf sie zurückfällt. Während bei den Olympia-Kandidaturen von 2002 und 2006 noch eine Mehrheit der Walliser Bevölkerung mitfiebert, führt die Bewerbung für die Spiele von 2026 eher zu Meinungsverschiedenheiten und zeigt eine zunehmende Diskrepanz zwischen den Ambitionen der Befürwortenden und dem wachsenden ökologischen Bewusstsein in der Bevölkerung auf. Dennoch wird eine Walliser Kandidatur 2030 nochmals in Erwägung gezogen, bevor diese kurz darauf fallen gelassen wird. Ob sich Sittens Olympia-Traum über die aktuellen Bestrebungen für eine Schweizer Kandidatur 2030 doch noch verwirklichen lässt, bleibt dahingestellt.
The impossible tale of the Olympic Games in Sion?
In the spring of 1960, for the first time, a committee studied the possibility of hosting the 1968 Winter Olympic Games in Sion. However, in 1963, the population voted against funding this project. Despite this initial defeat, bids were officially submitted for the 1976, 2002, 2006 and 2026 Olympic Games. The opposition came either from the International Olympic Committee (IOC), incidentally accused of corruption or from the local authorities, who refused to support a project without the financial support of the Canton and the Confederation. The local population, outraged to see public money being invested in such a project and not elsewhere, feared that they would have to cover any potential deficit. While the 2002 and 2006 bids revealed a united and utopic Valais, the 2026 bid sparked divisions and highlighted the gap between the ambition of the promoters of the project and the growing environmental concerns of the population. The idea of another bid for 2030 has nonetheless been issued but did not come to fruition. Will Sion pursue its olympic ambition despite Switzerland becoming a potential candidate for 2030?
La storia impossibile dei Giochi Olimpici a Sion?
Nella primavera del 1960, un comitato studiò per la prima volta la possibilità di ospitare le Olimpiadi invernali a Sion del 1968. Tuttavia, nel 1963 la popolazione votò contro il credito previsto per questo progetto. Nonostante un iniziale insuccesso, furono lanciate ufficialmente le candidature per i Giochi Olimpici del 1976, 2002, 2006 e 2026. Il rifiuto arrivò sia dal Comitato Olimpico Internazionale (CIO), accusato inoltre di corruzione, e dalle autorità comunali, che si sono rifiutate di sostenere il progetto senza l’appoggio finanziario del Cantone e della Confederazione. I vallesani, dal canto loro, indignati nel vedere il denaro pubblico investito in un progetto del genere e non altrove, temono di dover coprire un eventuale deficit. Mentre le candidature del 2002 e del 2006 rappresentano il sogno della maggioranza dei vallesani, quella del 2026 è stata più che altro fonte di dissenso, evidenziando la discrepanza tra le ambizioni dei promotori del progetto e le crescenti preoccupazioni ecologiche della popolazione. Tuttavia, l’idea di una candidatura vallesana è stata avanzata per il 2030, ma non è stata realizzata. Sion perseguirà il suo sogno olimpico in vista di una possibile candidatura svizzera per il 2030?