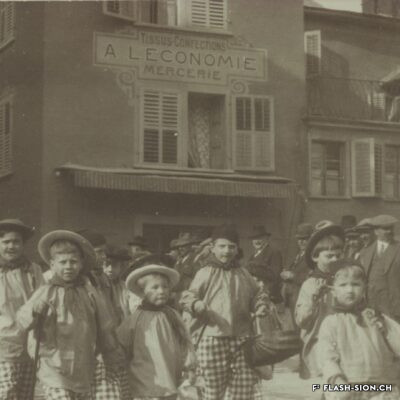
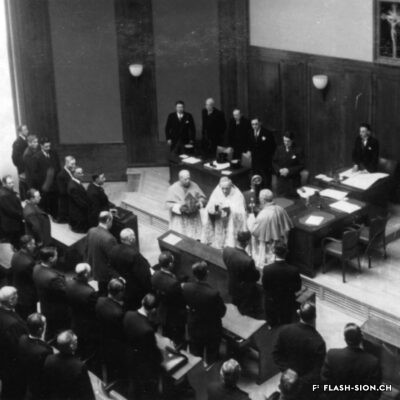
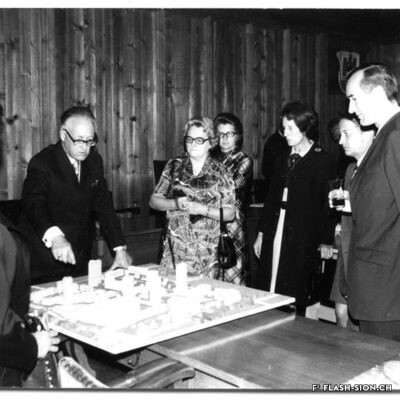
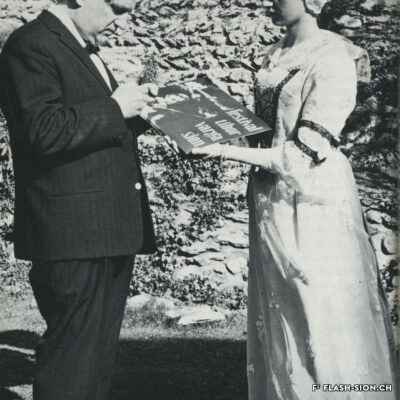
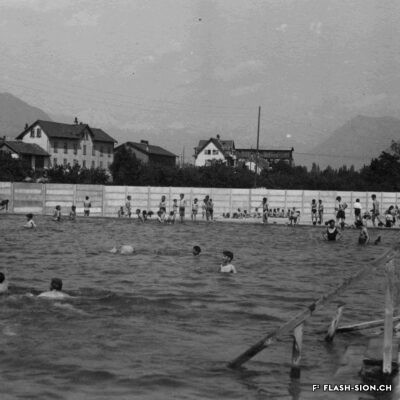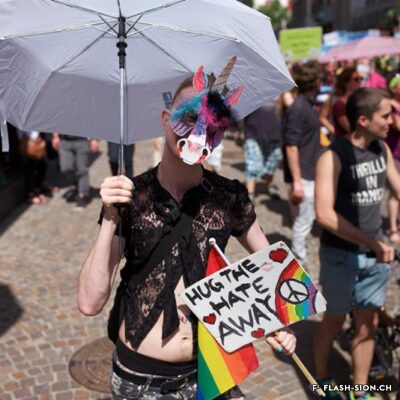Des jeux de société aux jeux politiques
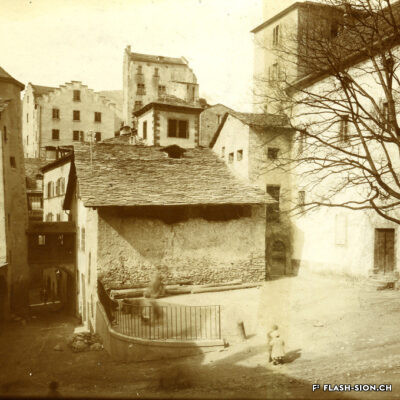
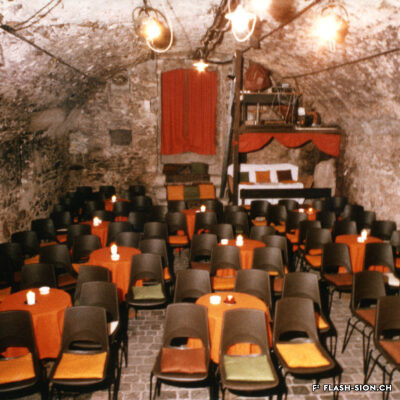
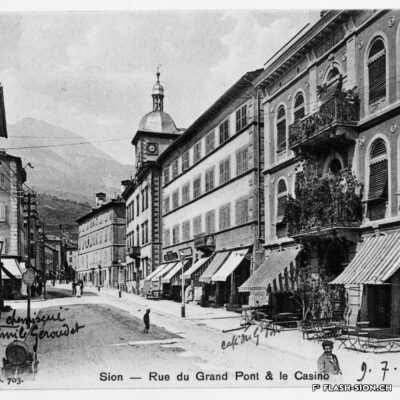
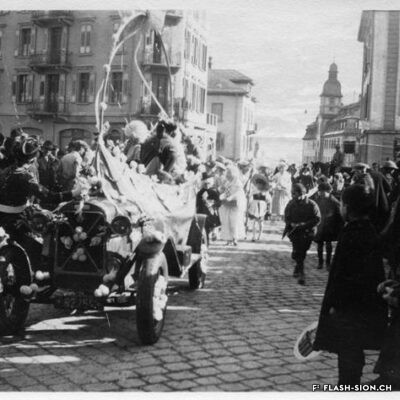
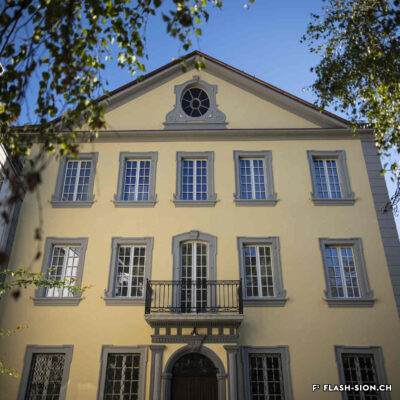
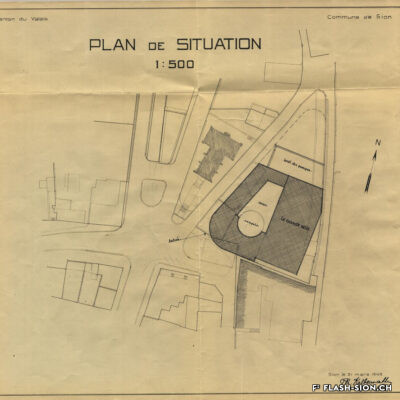
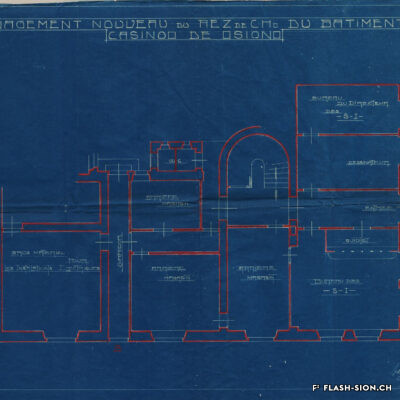
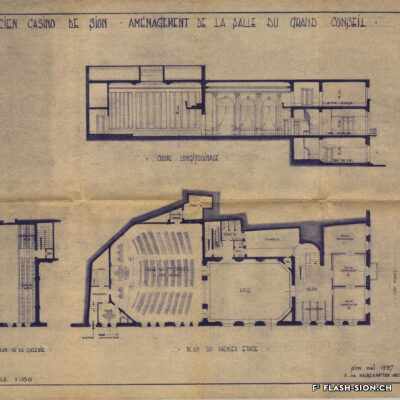
Contrairement à ce que son nom pourrait suggérer, le Casino de Sion n’a jamais hébergé de jeux de hasard sous son toit. Destiné à resserrer les liens de la société sédunoise, l’établissement, représentatif de l’architecte Emile Vuilloud, est construit en 1861 sur décision de la Bourgeoisie de Sion. L’édifice, avec sa grande salle de fête et les différents salons de lecture et de jeux de société, est inauguré en 1865. Parallèlement, la Société du Casino est constituée et un règlement de police strict est adopté. Après presque 40 ans d’existence, la société rencontre de plus en plus de difficultés à rassembler des membres. Elle est dissoute en 1904 et le bâtiment est racheté en 1912 par la Municipalité. En 1924, pour éviter de devoir mettre à disposition, à ses frais, des locaux plus spacieux pour les séances du Parlement valaisan, le conseil communal autorise le Grand Conseil à siéger, à bien plaire, dans la salle du Casino. Rénové et agrandi de 1938 à 1939, le Casino devient le siège permanent du Grand Conseil, excluant définitivement son utilisation parallèle comme salle de fête.
Von Gesellschaftsspielen zu politischen Spielchen
Entgegen seinem Namen sind im Casino von Sitten nie Glücksspiele angeboten worden. Der repräsentative Bau des Architekten Emile Vuilloud ist vielmehr dazu bestimmt, den gesellschaftlichen Zusammenhalt unter den Sittener Bürgern zu festigen und zu pflegen. 1861 beschliesst die Burgergemeinde von Sitten die Errichtung des Gebäudes. Die Einweihung des Casinos mit seinem großen Festsaal und den verschiedenen Salons zum Lesen und für Gesellschaftsspiele findet 1865 statt. Gleichzeitig erfolgt die Gründung der Société du Casino, welche ein strenges Polizeireglement für das Casino verabschiedet. Knapp 40 Jahre nach der Gründung verzeichnet die Gesellschaft jedoch zunehmend Schwierigkeiten, Mitglieder zu werben. Sie wird 1904 aufgelöst und das Gebäude 1912 von der Gemeinde aufgekauft. Um nicht auf eigene Kosten größere Räumlichkeiten für das Walliser Parlament zur Verfügung stellen zu müssen, kommt der Gemeinderat 1924 schliesslich dem Großen Rat entgegen und gestattet ihm, vorübergehend im Saal des Casinos zu tagen. Nach den Renovierungs- und Ausbauarbeiten zwischen 1938 und 1939 wird das Casino schliesslich zum ständigen Sitz des Großen Rates – eine parallele Nutzung als Festsaal wird damit endgültig ausgeschlossen.
From society games to political games
Contrary to what one might think of when considering its name, the Casino of Sion never hosted any gambling activities. The building was erected in 1861 upon approval of the Bourgeoisie of Sion. Well represeting the works of Emile Vuilloud, it aimed at reinforcing the bounds within the community members of Sion. The building was inaugurated in 1865 and consists of a huge hall for celebrations and several salons for reading and playing board games.
The ‘‘Société du Casino’’ was established concurrently and strict police regulations were enforced. Nearly 40 years later it was becoming harder and harder for the society to attract members, so it was dissolved in 1904 and the Municipality bought the building in 1912. In 1924, the town council -to avoid the costs that would have been encured by renting rooms more spacious for the meetings of the Parlement of Valais- gave the Grand Conseil the permission to sit ‘‘à bien plaire’’ (temporarily, so long as the Conseil approves of it) in the hall oft he Casino. It was renovated and extended between 1938 and 1939 and became the permanent seat of the Great Conseil, thus definitely excluding the possibilities to concurrently use it as a banquet hall.
Dai giochi di società ai giochi politici
Contrariamente a quanto potrebbe suggerire il nome, il Casinò di Sion non ha mai ospitato i giochi d’azzardo sotto il suo tetto. Destinato a rafforzare i legami della società di Sion, l’edificio rappresentativo dell’epoca, fu progettato dall’architetto Emile Vuilloud nel 1861 per decisione della borghesia di Sion. L’edificio con il grande salone delle feste e le varie sale di lettura e di giochi da tavolo, venne inaugurato nel 1865. Allo stesso tempo venne costituita la “Società del Casinò” e furono adottati severi regolamenti di polizia. Dopo quasi 40 anni di esistenza, la società trova sempre più difficoltà a riunire i membri. Fu sciolta nel 1904 e l’edificio fu acquistato nel 1912 dal Comune. Nel 1924, per evitare di dover fornire, a proprie spese, locali più spaziosi per le sedute del Parlamento vallesano, il Consiglio comunale autorizzò il Gran Consiglio a riunirsi, a suo piacimento, nella sala del Casinò. Ristrutturato e ampliato dal 1938 al 1939, il Casinò divenne la sede permanente del Gran Consiglio, escludendo definitivamente il suo utilizzo parallelo come salone delle feste.
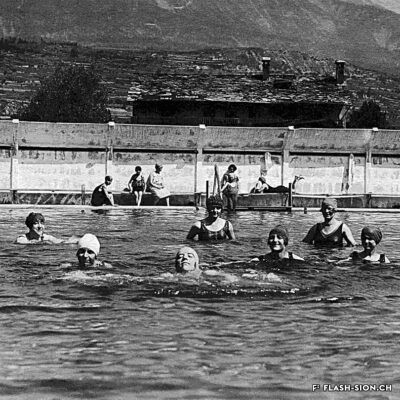
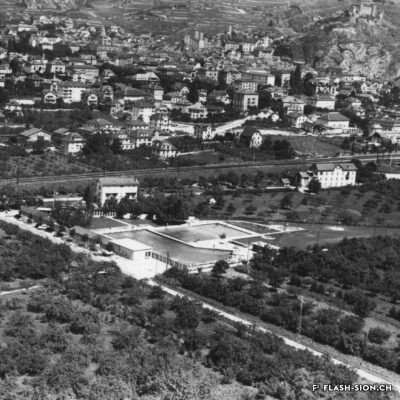
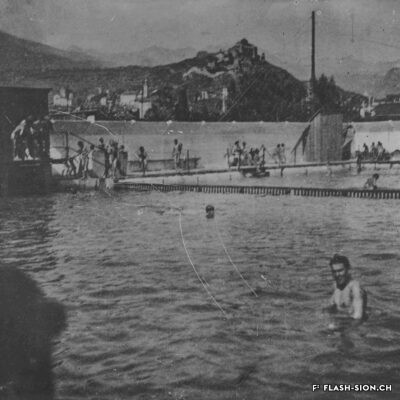
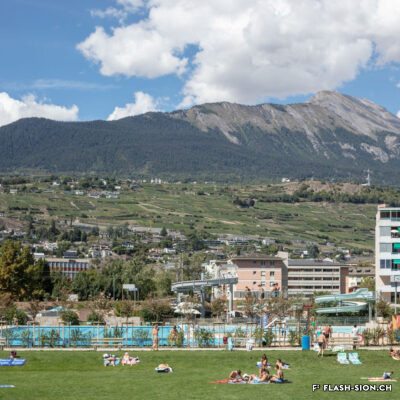
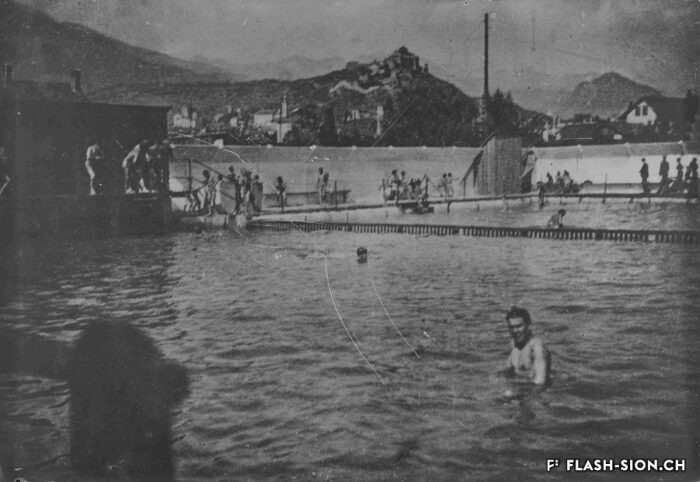
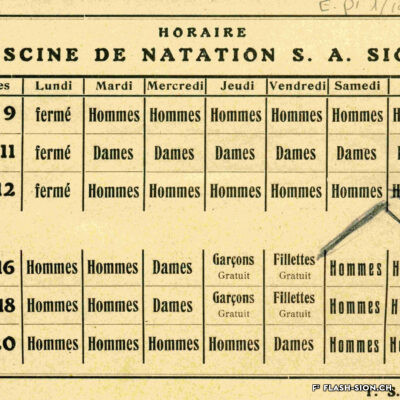
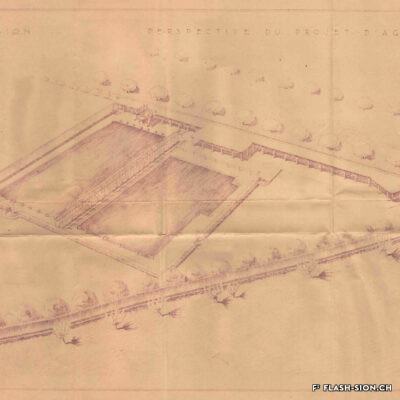
La piscine, entre première cantonale et pudeur locale
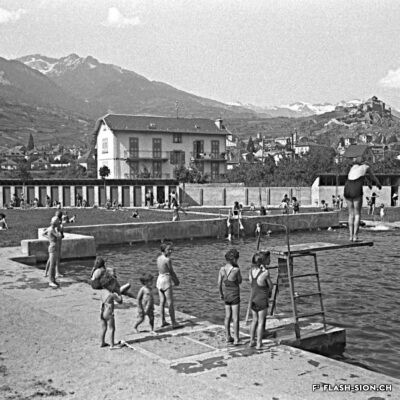
Construite en 1922 en bordure de ville mais à l’abri des regards, la piscine de la Blancherie est la première piscine publique de Sion, mais également du canton. Le projet est initié par une société privée. Sa construction est loin d’être un fleuve tranquille. Les déboires financiers poursuivent longtemps l’établissement, jusqu’à sa reprise par la Ville. Malgré des débuts chaotiques, la piscine trouve rapidement son public et joue un rôle social important dans la communauté sédunoise. Cependant, un point de discorde, et non des moindres, marque l’histoire de l’établissement et concerne sans surprise la mixité. En effet, l’accès à la piscine était initialement réservé aux hommes ou aux femmes selon des horaires bien séparés. Elle ne devient ouverte à tous simultanément que progressivement au début des années 1930, non sans heurts et polémiques…
Freibad Sitten, zwischen kantonaler Premiere und lokaler Prüderie
1922 entsteht am Stadtrand von Sitten, aber dennoch gut verborgen vor begehrlichen Blicken, das Schwimmbad La Blancherie. Es ist das erste öffentliche Freibad der Stadt Sitten aber auch des ganzen Kantons Wallis. Auf Initiative einer privaten Gesellschaft angeregt, stellen sich Bau und Betrieb der Badeanstalt jedoch als alles andere als ein ruhiger Fluss heraus. Finanzielle Schwierigkeiten stehen an der Tagesordnung, bis das Freibad schliesslich von der Stadt übernommen wird. Trotz der schwierigen Ausgangslage erfreut sich das Schwimmbad rasch grosser Beliebtheit und spielt eine wichtige soziale Rolle in der Bevölkerung von Sitten. Ein nicht unwesentlicher Streitpunkt prägt jedoch die Geschichte der Einrichtung und betrifft, wie könnte es anders sein, die Geschlechtertrennung. Tatsächlich war der Zugang zum Schwimmbad ursprünglich Männern oder Frauen nach klar getrennten Zeiten vorbehalten. Erst Anfang der 1930er Jahre wurden die nach Geschlechtern getrennten Öffnungszeiten nach und nach abgeschafft, was bisweilen für erheblichen Zündstoff sorgt…
The swimming pool, a mixture between cantonal premiere and local prudishness
Built in 1922 on the edge of town but hidden from public view, the Blancherie swimming pool was the first public pool in Sion, and of the canton as well. The project was launched by a private company. The history of how it got built was not a smooth process : the institution had to deal continuously with financial setbacks until the commune took over the case. Despite a chaotic start, the pool quickly found its audience and played an important social role in Sion’s community. However, one crucial point of contention marks the history of the institution, which without great surprise, concerns gender mixing. Initially, men and women had access to the swimming pool at separate time slots. It was only gradually opened up to everyone at the same time in the early 1930s, and not without controversy…
La piscina, tra primato cantonale e pudicizia locale
Costruita nel 1922 ai margini della città, ma al riparo dagli sguardi, la piscina della Blancherie è la prima piscina pubblica di Sion, ma anche del Cantone. Il progetto fu avviato da una società privata. La sua costruzione è lungi dall’essere un lungo fiume tranquillo. Le difficoltà finanziarie perseguitarono a lungo la struttura, finché non fu ripresa dalla città. Nonostante gli inizi caotici, la piscina trovò rapidamente il suo pubblico e svolse un importante ruolo sociale nella comunità di Sion. Tuttavia, un punto di contesa, non di minore importanza, ha segnato la storia della struttura e riguardava ovviamente la coesistenza. Inizialmente, l’accesso alla piscina era riservato a uomini e donne in orari separati. Solo all’inizio degli anni ’30 fu progressivamente aperto a tutti, non senza scontri e polemiche …
Danses interdites à la Matze
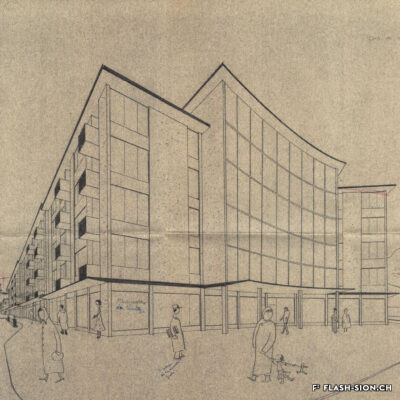
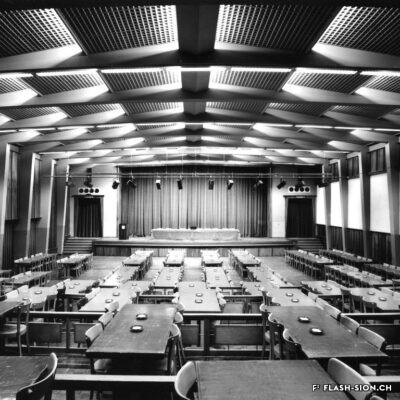
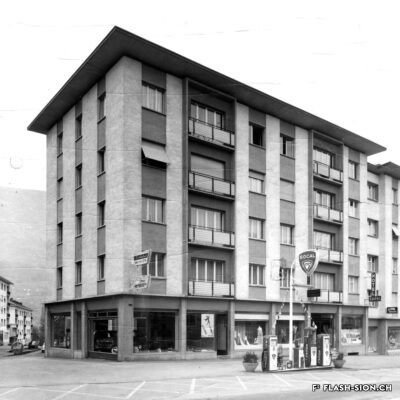
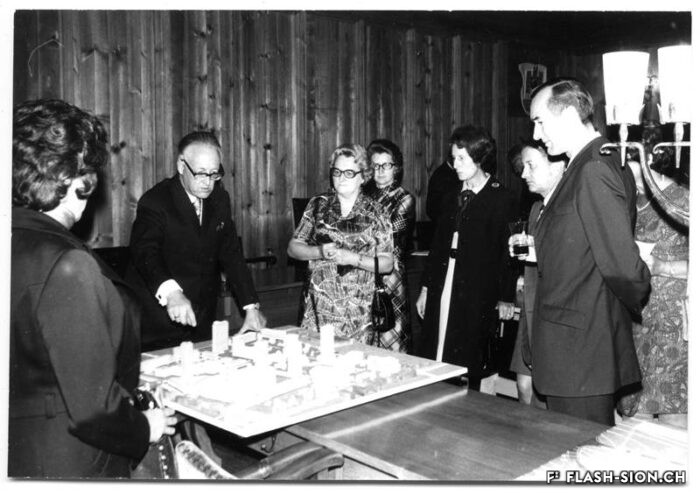
Au milieu des années 1950, le complexe de la Matze introduit une nouvelle échelle et manière de penser la ville dans un quartier encore marqué par des vergers. C’est le Groupement Artisanal, fondé par les frères Raymond, Marcel et Pierre Kamerzin et Armand Varone, qui porte et finance le projet dessiné par l’architecte Robert Tronchet. Avec ses 13 commerces de première nécessité, un hôtel, un restaurant-bar et 87 appartements à loyer modéré, il constitue jusqu’à sa démolition en 2014 une véritable petite cité à lui seul. La légendaire Salle de la Matze, avec ses 800 places assises, reste longtemps la plus grande salle de spectacle du canton. Elle ouvre en 1959, après d’âpres négociations qui ont conduit les promoteurs à accepter l’inscription d’une servitude en faveur de la Municipalité. Quant au premier dancing de plaine, perçu comme un lieu de « débauche dangereux » et refusé par la Ville, il reçoit finalement l’approbation de l’évêque… sous conditions de fermetures temporaires obligatoires durant les périodes de l’Avent et du Carême.
Verbotene Tänze in der Matze
Mitte der 1950er Jahre setzt die Grossüberbauung der Matze in einem von Obstgärten geprägten Quartier einen neuen Maßstab und Ansatz der Stadtplanung. Das Projekt des Architekten Robert Tronchet wird vom Groupement Artisanal der Gebrüder Raymond, Marcel und Pierre Kamerzin sowie Armand Varone getragen und finanziert. Mit seinen 13 Geschäften für den täglichen Bedarf, einem Hotel, einem Restaurant-Bar und 87 Wohnungen mit erschwinglichen Mieten bildet der Komplex bis zu seinem Abriss im Jahr 2014 eine kleine Stadt in sich. Der legendäre Saal der Matze mit seinen 800 Sitzplätzen bleibt lange Zeit der größte Veranstaltungssaal des Kantons. Er wird nach zähen Verhandlungen, in deren Verlauf die Bauherren zur Eintragung einer Grunddienstbarkeit zugunsten der Gemeinde verpflichtet werden, 1959 eröffnet. Das erste Tanzlokal in der Talebene hingegen wird als Ort “gefährlicher Ausschweifungen” wahrgenommen und von der Stadt vorerst abgelehnt. Schliesslich erhält das Lokal die Genehmigung des Bischofs … unter der Bedingung, dass das Dancing während der Advents- und Fastenzeit geschlossen bleibt.
Forbidden dancing at la Matze
By the mid-50’s, the building complex of la Matze was a pionneer reference in terms of scale and way of conceiving the town in an area still imprinted by orchards. The Raymond brothers together with Marcel and Pierre Kamerzin and Armand Varone founded the Groupement Artisanal (craftsmen union), which was supporting and funding the project drafted by the architect Robert Tronchet: 13 basic goods shops, a hotel, a bar-restaurant and 87 moderate rental price flats. Until 2014 -when it was pulled down- it stood as a shear little town per se. The legendary hall la Matze -with a capacity of 800 seats- remained the biggest hall of the canton for quite a while. Its was opened in 1959 following up fierce negociations, among which promoters came to agree upon a right of way in favour of the Municipality. As to the first dancing ever existing in the plain it was looked upon as a ‘‘dangerous’’ place of ‘‘debauchery’’. First turned down by the Town, it was finally approved by the bishop… under the conditions of temporarily and compulsorily closing down during the Advent and Lent.
Danze proibite alla Matze
A metà degli anni Cinquanta, il complesso della Matze introdusse una nuova scala e un modo di pensare la città in un quartiere ancora dominato dai frutteti. Fu il raggruppamento artigianale “Groupement Artisanal”, fondato dai fratelli Raymond, Marcel e Pierre Kamerzin e da Armand Varone, che sviluppa e finanzia il progetto dell’architetto Robert Tronchet. Con 13 commerci essenziali, un hotel, un ristorante-bar e 87 appartamenti a basso costo, costituiva una vera e propria piccola città a sé stante, fino alla sua demolizione nel 2014. La leggendaria Salle della Matze, con i suoi 800 posti a sedere, è rimasta a lungo la più grande sala da spettacolo del Cantone. Fu inaugurata nel 1959, dopo dure trattative che portarono i promotori ad accettare l’iscrizione di una servitù a favore del Comune. Quanto alla prima sala da ballo della pianura, percepita come luogo di “pericolosa dissolutezza” e rifiutata dalla città, riceve finalmente l’approvazione del vescovo… con l’obbligo di chiusura temporanea durante i periodi di Avvento e Quaresima.
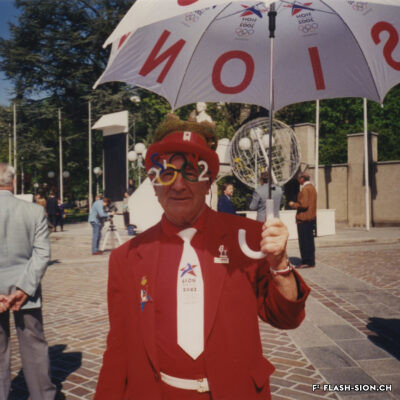
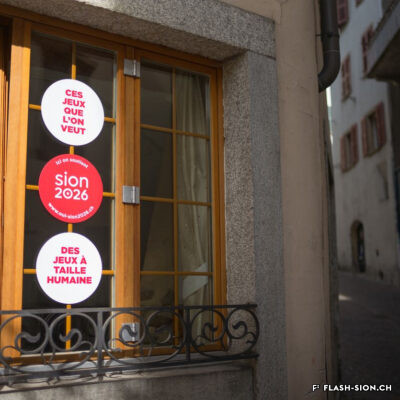
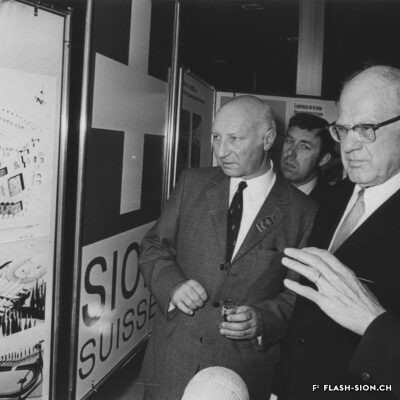
L’impossible histoire des JO à Sion ?
Printemps 1960, un comité étudie pour la première fois la possibilité d’accueillir les Jeux Olympiques d’hiver (JO) à Sion en 1968. La population vote pourtant en 1963 contre le crédit prévu pour cette entreprise. Malgré un premier échec, des candidatures sont officiellement lancées pour les JO 1976, 2002, 2006 et 2026. Le refus provient tantôt du Comité International Olympique (CIO), par ailleurs accusé de corruption, tantôt des autorités communales, refusant de porter le projet sans l’appui financier du Canton et de la Confédération. Les citoyens valaisans, pour leur part, indignés de voir l’argent public investi dans un tel projet et pas ailleurs, craignent de devoir éponger un éventuel déficit. Alors que les candidatures de 2002 et 2006 font rêver une majorité de Valaisans, celle de 2026 a plutôt suscité les dissensions et mis en lumière le décalage entre les ambitions des promoteurs du projet et les préoccupations écologistes grandissantes au sein de la population. Malgré tout, l’idée d’une candidature est émise pour 2030, mais n’aboutit pas. Sion poursuivra-t-elle son rêve olympique à l’heure d’une possible candidature suisse pour 2030 ?
Die unmögliche Geschichte der Olympischen Spiele in Sitten
Im Frühjahr 1960 prüft ein Komitee erstmals die Möglichkeit zur Austragung von Olympischen Winterspielen 1968 in Sitten. Die Bevölkerung lehnt den vorgesehenen Kredit für das Vorhaben jedoch 1963 ab. Trotz dieser Abfuhr werden 1976, 2002, 2006 und 2026 weitere Olympia-Kandidaturen lanciert. Die Ablehnung der Bewerbungen ist einmal auf das damals der Korruption bezichtigte Olympische Komitee (IOC) zurückzuführen, ein andermal auf die Gemeindebehörden, die das Projekt nicht ohne finanzielle Absicherung durch Kanton und Bund zu tragen bereit sind. Die Walliser Bevölkerung wiederum zeigt sich empört darüber, dass öffentliche Gelder nicht besser investiert werden, und befürchtet, dass der Ausgleich eines allfälligen Defizits auf sie zurückfällt. Während bei den Olympia-Kandidaturen von 2002 und 2006 noch eine Mehrheit der Walliser Bevölkerung mitfiebert, führt die Bewerbung für die Spiele von 2026 eher zu Meinungsverschiedenheiten und zeigt eine zunehmende Diskrepanz zwischen den Ambitionen der Befürwortenden und dem wachsenden ökologischen Bewusstsein in der Bevölkerung auf. Dennoch wird eine Walliser Kandidatur 2030 nochmals in Erwägung gezogen, bevor diese kurz darauf fallen gelassen wird. Ob sich Sittens Olympia-Traum über die aktuellen Bestrebungen für eine Schweizer Kandidatur 2030 doch noch verwirklichen lässt, bleibt dahingestellt.
The impossible tale of the Olympic Games in Sion?
In the spring of 1960, for the first time, a committee studied the possibility of hosting the 1968 Winter Olympic Games in Sion. However, in 1963, the population voted against funding this project. Despite this initial defeat, bids were officially submitted for the 1976, 2002, 2006 and 2026 Olympic Games. The opposition came either from the International Olympic Committee (IOC), incidentally accused of corruption or from the local authorities, who refused to support a project without the financial support of the Canton and the Confederation. The local population, outraged to see public money being invested in such a project and not elsewhere, feared that they would have to cover any potential deficit. While the 2002 and 2006 bids revealed a united and utopic Valais, the 2026 bid sparked divisions and highlighted the gap between the ambition of the promoters of the project and the growing environmental concerns of the population. The idea of another bid for 2030 has nonetheless been issued but did not come to fruition. Will Sion pursue its olympic ambition despite Switzerland becoming a potential candidate for 2030?
La storia impossibile dei Giochi Olimpici a Sion?
Nella primavera del 1960, un comitato studiò per la prima volta la possibilità di ospitare le Olimpiadi invernali a Sion del 1968. Tuttavia, nel 1963 la popolazione votò contro il credito previsto per questo progetto. Nonostante un iniziale insuccesso, furono lanciate ufficialmente le candidature per i Giochi Olimpici del 1976, 2002, 2006 e 2026. Il rifiuto arrivò sia dal Comitato Olimpico Internazionale (CIO), accusato inoltre di corruzione, e dalle autorità comunali, che si sono rifiutate di sostenere il progetto senza l’appoggio finanziario del Cantone e della Confederazione. I vallesani, dal canto loro, indignati nel vedere il denaro pubblico investito in un progetto del genere e non altrove, temono di dover coprire un eventuale deficit. Mentre le candidature del 2002 e del 2006 rappresentano il sogno della maggioranza dei vallesani, quella del 2026 è stata più che altro fonte di dissenso, evidenziando la discrepanza tra le ambizioni dei promotori del progetto e le crescenti preoccupazioni ecologiche della popolazione. Tuttavia, l’idea di una candidatura vallesana è stata avanzata per il 2030, ma non è stata realizzata. Sion perseguirà il suo sogno olimpico in vista di una possibile candidatura svizzera per il 2030?
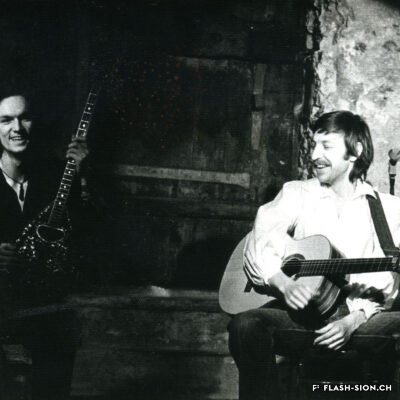
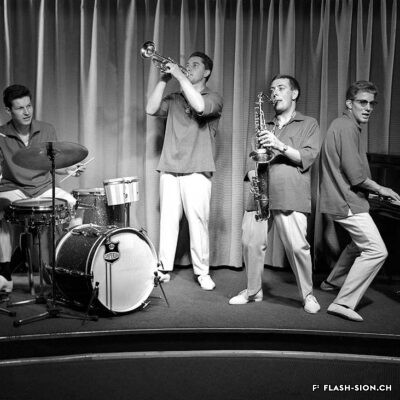
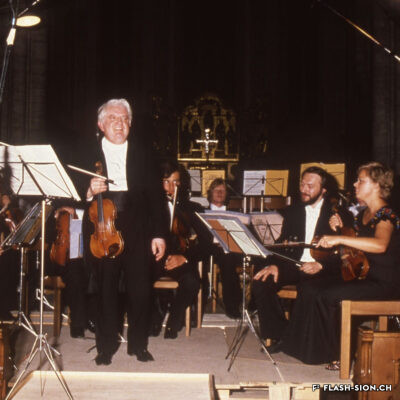
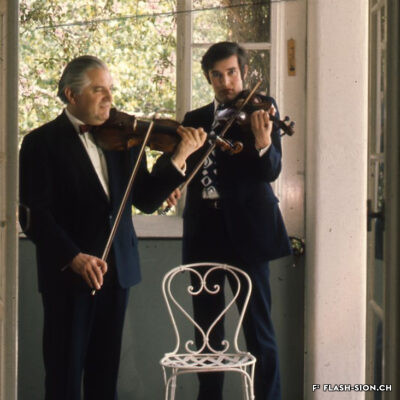
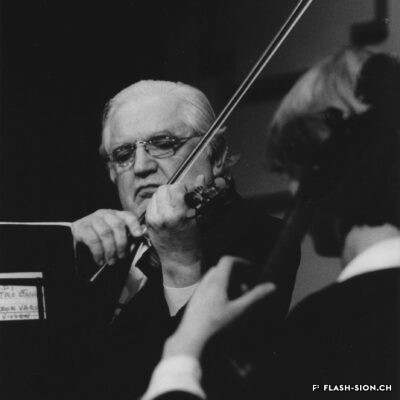
L’homme qui a fait de Sion la capitale du violon
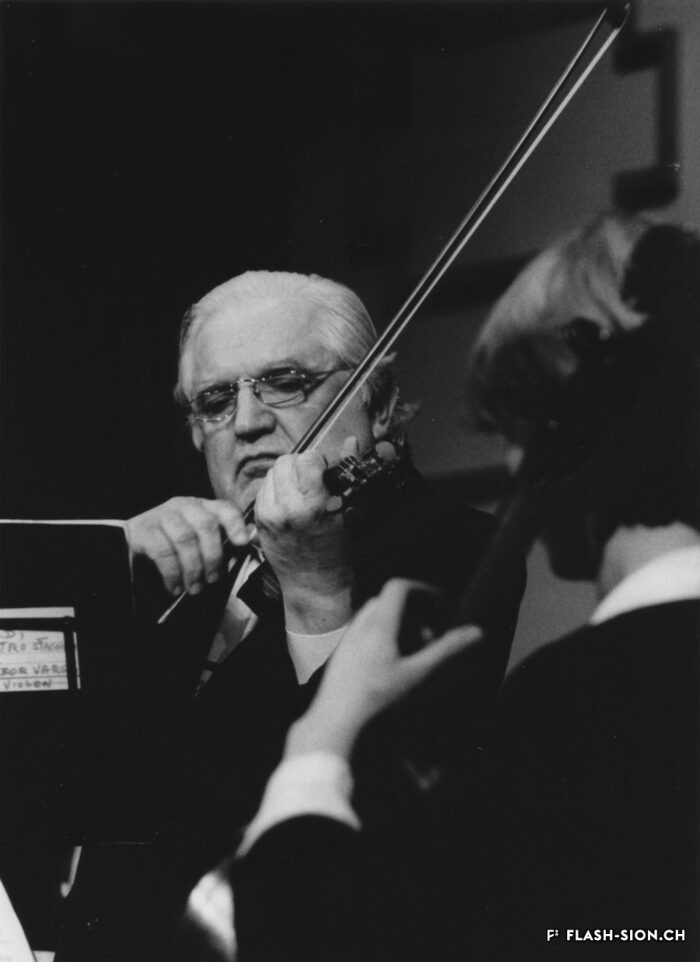
Originaire de Györ en Hongrie, Tibor Varga (1921-2003) se consacre dès son plus jeune âge au violon. En 1956, la famille Varga s’installe près de Sion pour soigner leur fils. Désormais au cœur de l’Europe, Tibor Varga peut facilement voyager pour sa musique. Six ans après son arrivée, Georges Haenni, directeur du Conservatoire de Sion, et Judith Szava, première épouse de Varga, le convainquent enfin d’y donner des cours d’été. L’Académie Tibor Varga voit ainsi le jour et un festival de musique est lancé en 1964. Au pays des fanfares, il faut cependant du temps au festival pour faire sa place. Heureusement, la renommée de Varga ainsi que les efforts de ses partenaires assurent la venue de musiciens de qualité à Sion. Au fil du temps, le succès étant toujours au rendez-vous, Varga décide de consolider son œuvre à travers la création d’une association pour gérer le festival, d’un concours international de violon, d’une fondation à son nom ainsi que d’une école supérieure de musique. Sa contribution à la professionnalisation de la musique marque encore aujourd’hui le Valais.
Der Mann, der Sitten zur Violine-Hauptstadt machte
Der aus Györ in Ungarn stammende Tibor Varga (1921-2003) widmet sich bereits in jungen Jahren dem Geigenspiel. 1956 lässt sich die Familie Varga in der Nähe von Sitten nieder, um ihren Sohn zu pflegen. Die strategische Lage im Herzen Europas ist idealer Ausgangspunkt für Tibor Vargas ausgedehnte Konzertreisen. Sechs Jahre nach seiner Niederlassung in der Schweiz bewegen Georges Haenni, Direktor des Konservatoriums von Sitten, und Judith Szava, Vargas erste Frau, ihn schließlich dazu, in Sitten Sommerkurse auszuschreiben. Damit ist die Sommerakademie Tibor-Varga ins Leben gerufen. Ab 1964 ergänzt ein Musikfestival das Angebot. Im Land der Blasmusiken hat das Festival vorerst einen schweren Stand, kann sich aber nach und nach etablieren. Vargas Bekanntheitsgrad und die Bemühungen seiner Partner sorgen dafür, dass erstklassige Musiker engagiert werden können. Der wachsende Erfolg bewegt Varga schliesslich dazu, sein Werk durch die Gründung eines Vereins zur Verwaltung des Musikfestivals, des internationalen Violinwettbewerbs, einer nach ihm benannten Stiftung sowie einer Musikhochschule zu konsolidieren. Damit leistet er einen bedeutenden und bis heute spürbaren Beitrag zur Professionalisierung der Musik im Wallis.
The man who made Sion the capital of the violin
Born in Györ, Hungary, Tibor Varga (1921-2003) started playing the violin at a very young age. In 1956, the Varga family moved near Sion so their son’s health can be cared for. Being by then in the middle of Europe, Tibor could easily travel anywhere for his music. Six years after his arrival, Georges Haenni -director of the conservatory in Sion – and Judith Svaza -Varga’s first wife-, finally persuaded him to give lessons there during the summer. The Tibor Varga music academy was thus created. Its success spawned the launch of a festival in 1964. In a canton where classical music was not really recognized, it took time to persuade the population of Valais of the necessity of music and a festival. Fortunately, Varga’s renown and his partners’ efforts brought musicians of quality to Sion. As time passed his activities were still crowned with success, so Varga decided to consolidate his work by creating an association to manage the festival, an international violin competition, a foundation in his name and a music academy. His contribution to the professionalization of music ist still impacting.
L’uomo che ha fatto di Sion la capitale del violino
Originario di Györ in Ungheria, Tibor Varga (1921-2003) si dedicò al violino fin dalla tenera età. Nel 1956, la famiglia Varga si stabilisce vicino a Sion per prendersi cura del loro figlio. Stando nel cuore dell’Europa, Tibor Varga poteva facilmente viaggiare per la sua musica. Sei anni dopo il suo arrivo, Georges Haenni, direttore del Conservatorio di Sion, e Judith Szava, la prima moglie di Varga, lo convinsero finalmente di impartire dei corsi estivi. Nacque così l’Accademia Tibor Varga e nel 1964 fu lanciato un festival musicale. Nella terra delle bande di ottoni, tuttavia, ci volle del tempo prima che il festival si affermasse. Fortunatamente, la reputazione di Varga e gli sforzi dei suoi partner fecero sì che a Sion arrivassero musicisti di qualità. Con il passare del tempo e il continuo successo del festival, Varga decise di consolidare la sua opera attraverso la creazione di un’associazione per la gestione del festival, di un concorso internazionale di violino, di una fondazione a suo nome e di una scuola superiore di musica. Il suo contributo alla professionalizzazione della musica caratterizza ancora oggi il Vallese.
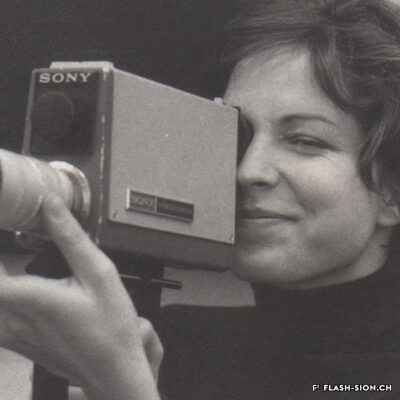
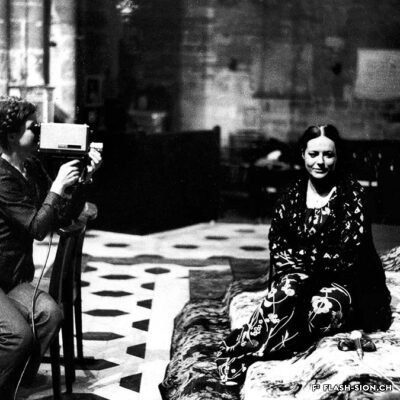
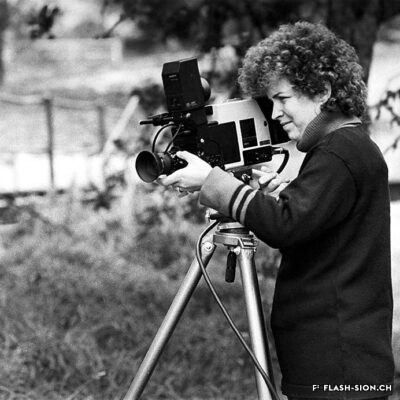
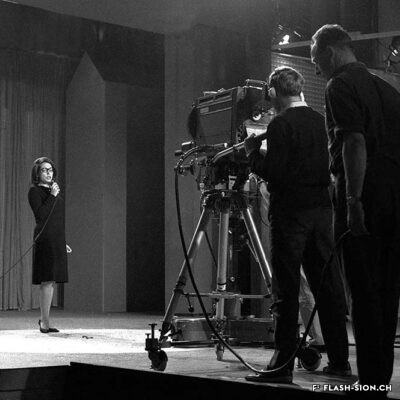
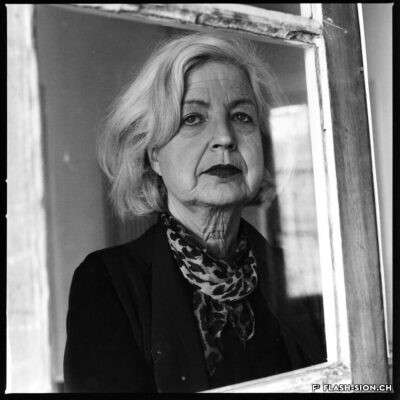
Carole Roussopoulos, vidéaste citoyenne
Née de Kalbermatten, Carole Roussopoulos (1945-2009), voit le jour à Sion, petite ville de 20 000 habitants où les jeunes n’ont pas accès au cinéma avant leurs 18 ans. Élevée dans un milieu bourgeois plutôt cadré, la jeune femme découvre à 22 ans la « vidéo légère » et Paris, en pleine émulation des années 1968. Cette période extrêmement stimulante éveille la passion de celle qui deviendra une réalisatrice féministe et engagée. Son credo ? Donner la parole aux « sans voix », aux minorités qu’on écoute pas. Son moteur ? La colère envers les injustices. Durant sa carrière, elle tourne aussi bien en France et en Suisse qu’ailleurs dans le monde. Très attachée à sa ville natale, elle reviendra en 1992 s’établir à Molignon et continuera de couvrir des sujets de société, souvent difficiles et délicats, mais nécessaires au changement des mentalités. Avec plus de 120 films à son actif, elle se positionne, presque malgré elle, en véritable pionnière du film documentaire.
Carole Roussopoulos, Videoaktivistin
Carole Roussopoulos (1945-2009), geborene de Kalbermatten, verbringt ihre Kindheit in der Kleinstadt Sitten, die damals 20 000 Einwohner zählt und Jugendlichen unter 18 Jahren den Zutritt ins Kino untersagt. Sie wächst in einem streng bürgerlichen Umfeld auf und entdeckt mit 22 Jahren, auf dem Höhepunkt der Jugendbewegungen der 1968er Jahre, die Videotechnik und Paris. Diese stimulierende Zeit weckt die Leidenschaft der feministischen und engagierten Videoschaffenden. Ihr Leitsatz? Minderheiten eine Stimme geben. Ihr Antrieb? Die Wut über Ungerechtigkeiten. Im Laufe ihrer Karriere dreht sie in Frankreich und der Schweiz, aber auch in anderen Teilen der Welt. Ihrer Heimatstadt bleibt sie verbunden und kehrt 1992 nach Molignon zurück. Von hier aus berichtet sie weiterhin über schwierige und heikle gesellschaftliche Themen, um den notwendigen Mentalitätswandel herbeizuführen. Mit ihren über 120 Videofilmen wird sie, fast unfreiwillig, zu einer anerkannten Pionierin des Dokumentarfilms.
Carole Roussopoulos, a civic videographer
Carole Roussopoulos (1945-2009), née de Kalbermatten, was born in Sion, a small town of 20’000 inhabitants, where young people weren’t allowed in cinemas until the age of 18. Raised in a rather strict bourgeois environment, the 22-year-old discovers “light video” and Paris at the height of the 1968 movements. This extremely stimulating period awakened the future feminist and militant director’s passion. Her credo? Give a voice to the voiceless, to the minorities no one listens to. Her driving force? Anger at injustice. During her career, she filmed both in France and Switzerland as well as abroad. Very fond of her hometown, she came back to settle in Molignon in 1992 and continued to cover social issues, which are often difficult and sensitive, but necessary for the changing of mentalities. With more than 120 films to her credit, she earned her position, almost in spite of herself, as a true pioneer of documentary film.
Carole Roussopoulos, videografa cittadina
Nata de Kalbermatten, Carole Roussopoulos (1945-2009) viene alla luce a Sion, una cittadina di 20.000 abitanti dove i giovani non hanno accesso al cinema prima dei 18 anni. Cresciuta in un ambiente borghese piuttosto strutturato, all’età di 22 anni, la giovane donna scopre il “video leggero” e Parigi, in piena emulazione degli anni 1968. Questo periodo estremamente stimolante risveglia la passione di colei che diventerà una regista femminista e impegnata. Il suo credo? è dare la voce ai “senza voce”, alle minoranze che non vengono ascoltate. La sua forza motrice? La rabbia per le ingiustizie. Nel corso della sua carriera ha girato in Francia, in Svizzera e in altre parti del mondo. Molto legata alla sua città natale, si è trasferita a Molignon nel 1992 e continua ad occuparsi di temi sociali, spesso difficili e delicati, ma necessari per cambiare la mentalità. Con più di 120 film al suo attivo, si posiziona, quasi suo malgrado, come una vera pioniera del cinema documentario.
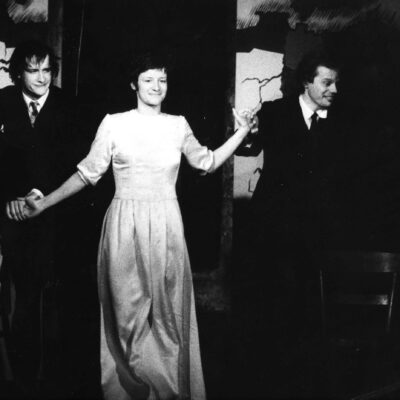
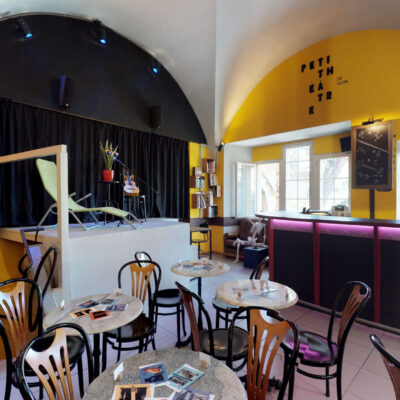
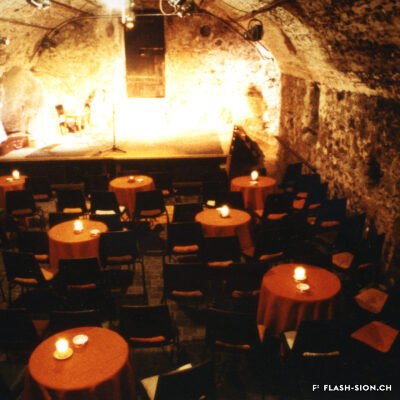
Une pièce en 3 actes pour le théâtre de poche
Sous l’impulsion de privés, soutenus par la Bourgeoisie et la Ville, un théâtre de poche se créée par et pour la jeunesse locale en 1975, dans une cave voûtée de la rue du Vieux-Collège. Dès la naissance du Petithéâtre, les fondateurs dessinent une ligne théâtrale plus jeune et moins classique que les spectacles présentés au Théâtre de Valère, alors fermé durant quelques années pour rénovation. Avec un budget modeste, le comité de gestion et les bénévoles ne ménagent pas leur temps pour tenir un rythme soutenu en termes de représentations et d’animations. Après 15 ans d’existence, le Petithéâtre déménage juste en face, dans l’ancienne petite Chancellerie, bâtiment entièrement réhabilité pour l’accueillir dignement. Tout en gardant son identité, le Petithéâtre entame en 2022 un troisième chapitre de sa vie, grâce à la nouvelle dynamique apportée par la restructuration des théâtres sous une même bannière : le Spot (Sion Pôles des Théâtres).
Ein Stück in drei Akten für eine Kleinbühne
1975 wird in einem Gewölbekeller der rue du Vieux-Collège ein Kellertheater von und für die lokale Jugend eingerichtet, angeregt von Privatpersonen und unterstützt von Burgergemeinde und Stadt Sitten.
Seit Beginn bieten die Gründungsmitglieder des Petithéâtre eine jüngere und weniger klassische Theaterlinie an als die Stücke, welche im damals aufgrund von Renovierungsarbeiten für einige Jahre geschlossenen Théâtre de Valère zur Aufführung kamen. Trotz bescheidenen Mitteln scheuen die Verwaltungsmitglieder und ehrenamtlichen Mitarbeitenden keine Mühen, um dem Publikum jährlich einen vielfältigen und umfangreichen Spielplan zu präsentieren. Zum 15-jährigen Bestehen siedelt das Petithéatre in die gegenüberliegende alte, kleine Kanzlei über, die speziell für die Bedürfnisse des Kleintheaters umgebaut worden war.
Im Jahr 2022, beginnt dank der Dynamik, die die Umstrukturierung der Sittener Theater unter einem einzigen Banner, dem sogenannten Spot (Sion Pôles des Théâtres) mit sich zieht, ein drittes Kapitel in der Geschichte des Petithéâtre.
A three-act play for the black box theatre
Under the initiative of private parties, with the support of the bourgeoisie and the commune, a black box theatre was founded by and for the local youth in 1975, in a vaulted cellar on Vieux-Collège Street. From the outset, the founders of the Petithéâtre pursued a more youthful and less classical theatrical line than the shows presented at the Théâtre de Valère, closed by then for several years for renovations. Having only a small budget, the management committee and the volunteers worked countless hours to sustain a steady pace of performances and events. 15 years later, the Petithéâtre moved across the street, to a fully renovated former petite Chancellerie, where it was welcomed with dignity. Whilst keeping its identity, the Petithéâtre started the third chapter of its life in 2022, thanks to a new dynamics brought by the restructuring of the theatres under the same banner Spot (Sion Pôle des Théâtres).
Commedia in 3 atti per il teatro tascabile
Sotto l’impulso di privati, con il sostegno della borghesia e della città, nel 1975 è stato creato un teatro tascabile da e per i giovani locali, in una cantina a volta della rue du Vieux-Collège. Fin dalla nascita del Petithéâtre, i fondatori tracciano uno stile teatrale più giovane e meno classico rispetto agli spettacoli presentati al Théâtre de Valère, chiuso per alcuni anni per ristrutturazione. Con un budget modesto, il comitato di gestione e i volontari non risparmiano tempo per mantenere un ritmo sostenuto in termini di spettacoli ed eventi. Dopo 15 anni di esistenza, il Petithéâtre si trasferisce proprio di fronte, nell’ex piccola Cancelleria, un edificio che è stato completamente ristrutturato per accoglierlo con dignità. Pur mantenendo la sua identità, il Petithéâtre inizia un terzo capitolo della sua vita nel 2022, grazie alla nuova dinamica portata dalla ristrutturazione dei teatri sotto un’unica insegna: lo Spot (Sion Pôles des Théâtres).
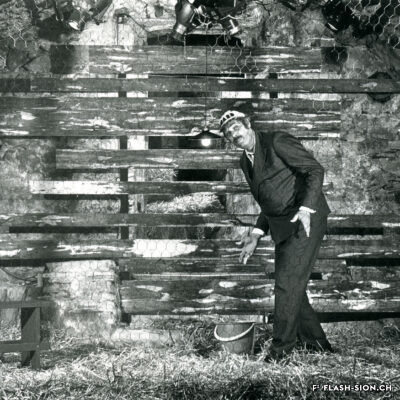
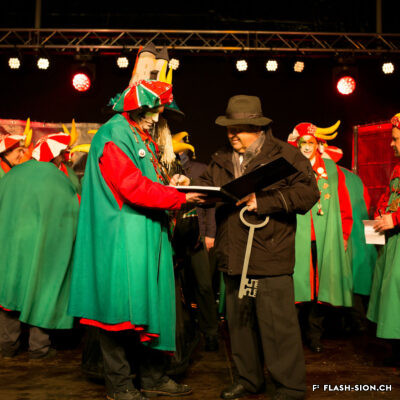
Le carnaval de Sion, entre subversion et respect de l’ordre
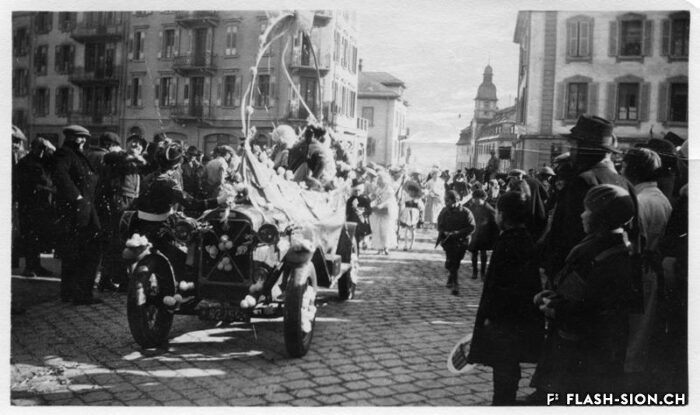
Les origines du carnaval sont assez floues, mais son étymologie « Carnelevare » qui signifie « enlever la viande », le lie au Carême chrétien. Le carnaval, période de festivités, de joie et d’excès avant la privation, laisse place à l’imaginaire. A travers les masques et les déguisements, la population peut se jouer de l’ordre social établi pendant un laps de temps bien défini. Pour éviter les débordements, les autorités religieuses et politiques imposent des règles à cette fête. Sion ne fait pas exception. En 1849, le président de la Ville fait édicter un règlement pour que bals et travestissements soient soumis à son autorisation. Plus tard, cette prérogative passera dans les mains de la police communale. Durant le carnaval, des bals masqués, des représentations théâtrales ainsi que des cortèges sont organisés à Sion. Pour rendre ces festivités plus acceptables, une partie des recettes récoltées est remise à des œuvres de charité. Aujourd’hui, les carnavals modernes doivent donc jongler entre l’agitation inhérente à la fête et les règles à respecter. Depuis 1975, l’association du Carnaval de Sion s’occupe de relever ce défi.
Der Karneval von Sitten, zwischen Subversion und Ordnungsliebe
Der Ursprung des Karnevals ist nicht eindeutig geklärt, “Carnelevare” bedeutet jedoch so viel wie “das Fleisch wegnehmen», was auf die christliche Fastenzeit hinweist. Der Karneval, eine Zeit der Ausgelassenheit, Freude und Exzesse vor der Entbehrung, lässt Raum für Fantasie. Dank Masken und Verkleidung kann die etablierte soziale Ordnung während einer genau festgelegten Zeitspanne auf den Kopf gestellt werden. Um während dieser Zeit der Narrenfreiheit Ausschreitungen zu vermeiden, erlassen religiöse und politische Behörden entsprechende Vorschriften. Sitten bildet in diesem Zusammenhang keine Ausnahme. So unterstellt der Stadtpräsident 1849 Fastnachtsbälle und Crossdressing einer Genehmigung. Später wird die Verantwortung für die Einhaltung der Ordnung der Gemeindepolizei übertragen. Während der Karnevalszeit finden in Sitten Maskenbälle, Theateraufführungen und Umzüge statt. Um dem bunten Treiben eine akzeptable Note zu verleihen, wird ein Teil der Einnahmen an wohltätige Organisationen gespendet. Seit 1975 stellt sich der Karnevalsverein von Sitten alljährlich der Herausforderung, die typische Ausgelassenheit des Festes mit der Einhaltung der gültigen Vorschriften in Einklang zu bringen.
The carnival in Sion, a mix between subversivness and respecting public order
The origins of carnival are rather unclear, but its etymology “Carnelevare”, meaning “to remove meat”, links it to Christian Lent. Carnival, a time of festivities, joy and extravagance before deprivation, lets imagination run wild. Through the use of masks and disguises, people can make fun of the existing social order for a well-defined period of time. To avoid any excess, religious and political authorities used to enforce rules around this celebration. Sion is no exception. In 1849, president of the town issued rules requiring his personal authorization for balls and masquerades. This prerogative was later transferred to the local police. During Carnival, masked balls, theatrical performances and parades were organised in Sion. To make those festivities more acceptable, a part of the incomes was donated to charities. Today, modern carnivals therefore have to balance the excitement inherent to festivities with the rules that have to be respected. The Sion Carnival Association has been meeting this challenge since 1975.
Il carnevale di Sion, tra sovversione e rispetto dell’ordine
Le origini del carnevale sono piuttosto vaghe, ma la sua etimologia, “Carnelevare” che significa “togliere la carne”, lo collega alla Quaresima cristiana. Il Carnevale, periodo di festeggiamenti, di gioia e di eccessi prima delle privazioni, lascia spazio all’immaginazione. Attraverso maschere e travestimenti, la popolazione può giocare con l’ordine sociale costituito per un periodo di tempo ben definito. Per evitare eccessi, le autorità religiose e politiche impongono delle regole a questa festa. Sion non fa eccezione. Nel 1849, il presidente della città emanò un regolamento affinché i balli e i travestimenti fossero soggetti alla sua autorizzazione. Successivamente tale prerogativa passerà nelle mani della polizia municipale. Durante il Carnevale a Sion vengono organizzati balli in maschera, spettacoli teatrali e cortei. Per rendere più gradite queste festività, parte del ricavato raccolto viene devoluto in beneficenza. Oggi i carnevali moderni devono quindi destreggiarsi tra la frenesia dei festeggiamenti e le regole da rispettare. È dal 1975, che l’associazione del Carnevale di Sion affronta questa sfida.
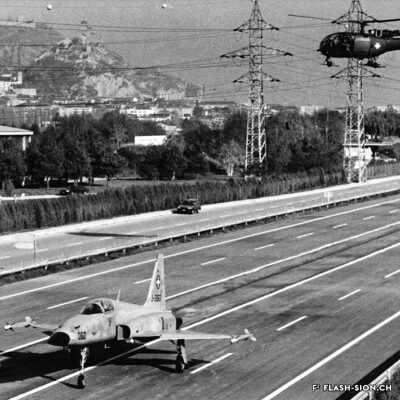
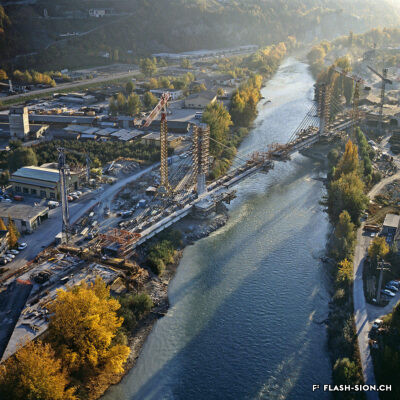
Roulez dans la paix du Christ !
Près d’un quart de siècle après l’approbation du premier projet d’autoroute en Valais, l’évitement de la capitale sera terminé en 1991. Sous la pression de différents mouvements d’opposition, le projet initial est entièrement revu par la commission Bovy. Celle-ci renonce à la traversée de la ville sur pilotis au profit d’une solution enterrée. Ainsi, le 16 décembre 1991, sous la bénédiction du cardinal Henri Schwery, le conseiller d’état Bernard Bornet et le conseiller fédéral Adolf Ogi inaugurent le tronçon Sion-Ouest Sion-Est de l’A9 d’une longueur de 3km et d’un coût total de 158 millions de francs. L’espace de la tranchée couverte de 710 mètres, baptisé Cours Roger-Bonvin, est devenu depuis un véritable trait d’union verdoyant entre les quartiers de Vissigen et de Champsec en plein développement.
Fahret hin in Frieden !
Knapp ein Vierteljahrhundert nach der Genehmigung des ersten Autobahnprojekts im Wallis wird die Umfahrung von Sitten 1991 fertiggestellt. Unter dem Druck verschiedener Autobahngegnerbewegungen wird das ursprüngliche Projekt von der speziell einberufenen Kommission Bovy komplett überarbeitet. Diese verzichtet auf die ursprünglich geplante Durchquerung der Stadt Sitten auf Pfeilern und ersetzt diese durch eine unterirdische Lösung. Am 16. Dezember 1991 weihen Staatsrat Bernard Bornet und Bundesrat Adolf Ogi unter dem Segen von Kardinal Henry Schwéry den Abschnitt Sion-Ouest Sion-Est der A9 ein. Der 3 km lange Abschnitt kostet 158 Millionen Franken. Der «Cours Roger Bonvin», der 710 Meter lange gedeckte Einschnitt, ist zu einem willkommenen grünen Bindeglied zwischen den sich stark entwickelnden Quartieren von Vissigen und Champsec geworden.
Drive in the peace of Christ !
Nearly a quarter of century after the first highway project in Valais was approved of, the project circumventing the capital was completed in 1991. Under the pressure of several movements opposing the early project, it was fully reviewed by the Bovy commission: it renounced going across the town on a road suspended on stilts, but chose instead to bury the construction. Thus, on 16 December 1991 –with the blessing of cardinal Henri Schwery- both the state councillor Bernard Bornet and the federal councillor Adolf Ogi inaugurated the Sion-West Sion-East section of Highway A9. It was 3km long and cost 158 million francs. The trench-like 710-meters wide space named Cours Roger-Bonvin has become since then a real lushfull place connecting area between the district of Vissigen and the currently developping district of Champsec.
Guidare nella pace di Cristo !
Quasi un quarto di secolo dopo l’approvazione del primo progetto autostradale nel Vallese, la circonvallazione della capitale sarà completata nel 1991. Sotto la pressione di diversi movimenti di opposizione, il progetto iniziale viene completamente rivisto dalla commissione Bovy. Si rinuncia ad attraversare la città sulle palafitte a favore di una soluzione sotterranea. Il 16 dicembre 1991, sotto la benedizione del cardinale Henri Schwery, il consigliere di Stato Bernard Bornet e il consigliere federale Adolf Ogi inaugurarono il tratto di 3 km Sion-Ouest-Sion-Est della A9, per un costo totale di 158 milioni di franchi svizzeri. Lo spazio coperto della trincea di 710 metri, chiamato Cours Roger-Bonvin, è da allora diventato un vero e proprio collegamento verde tra i quartieri in rapido sviluppo di Vissigen e Champsec.
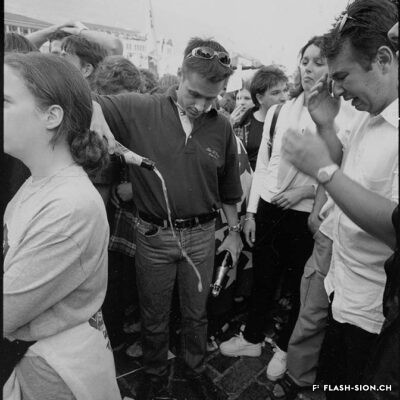
Sion aux couleurs de l’arc-en-ciel
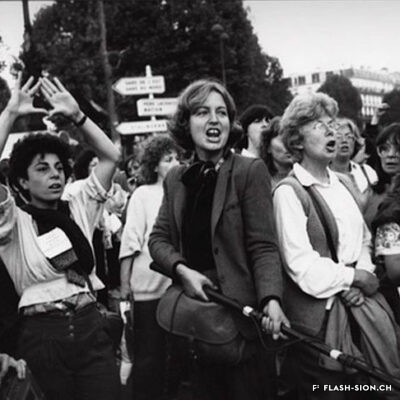
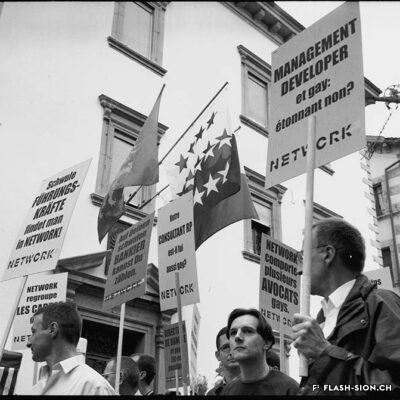
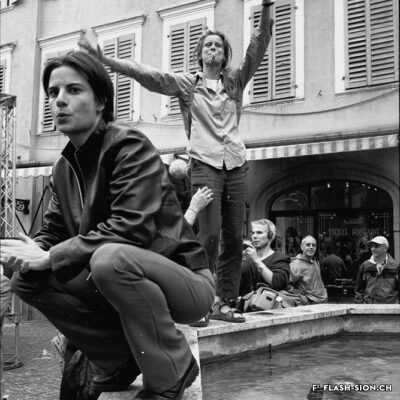
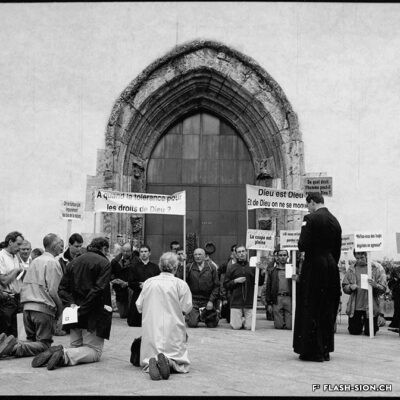
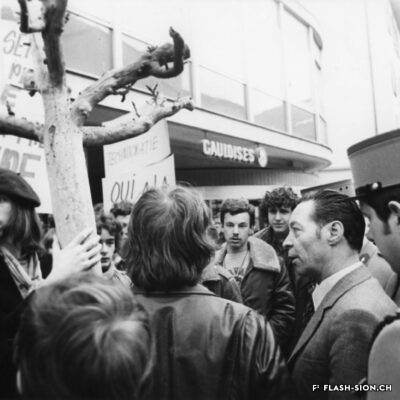
Fin 2000, un comité mené par Marianne Bruchez se lance dans la courageuse organisation d’une Lesbian and Gay Pride & Friends à Sion, au grand dam des milieux conservateurs. Majoritairement défavorable à la tenue de la manifestation, le conseil municipal ne peut formellement l’interdire et appelle les organisateurs à y renoncer. Ces derniers maintiennent pourtant leur position. La tension s’installe et l’opinion publique s’agite. L’Evêque dénonce un jeu diabolique. Une page publicitaire contre la Pride, accompagnée d’une pétition, est publiée dans la presse et vient mettre le feu aux poudres. Le débat s’enflamme, les articles de presse déferlent, les critiques s’additionnent, jusqu’au jour J, montrant d’autant plus l’importance de l’évènement face à l’intolérance et aux attaques homophobes. En mars, à l’unanimité, et afin de respecter le droit constitutionnel, le conseil municipal autorise la tenue de la manifestation. Grâce à la persévérance de sa coordinatrice, la « première Gay Pride romande du 21e siècle » aura bien lieu, le 7 juillet 2001, sans débordements, réunissant plus de 15 000 personnes dans l’amour et le respect de tous-tes.
Sitten in den Farben des Regenbogens
Unter der Leitung von Marianne Bruchez wagt ein Komitee Ende 2000 den mutigen Schritt, eine «Lesbian and Gay Pride & Friends» in Sitten zu organisieren, dies zum grossen Missfallen der konservativen Kreise. Der Stadtrat, dessen Mehrheit sich gegen die Parade ausspricht, kann diese jedoch nicht formell verbieten und fordert somit die Organisierenden zu einem Verzicht der Veranstaltung auf. Diese wiederum halten an ihrer Position fest. So kommt es zu unvermeidbaren Spannungen und die öffentliche Meinung schlägt hohe Wellen. Der Bischof bezeichnet die Veranstaltung als ein Spiel mit dem Teufel. Eine Werbekampagne begleitet von einer Petition gegen die Pride erscheint in der lokalen Presse und führt zu weiterem Zündstoff. Die Debatte entflammt, die Presse überschlägt sich, die Kritik häuft sich bis zum Austragungstag und zeigt, welche Bedeutung die Veranstaltung angesichts der Intoleranz und der homophoben Angriffe einnimmt. Im März genehmigt der Stadtrat schliesslich einstimmig die Veranstaltung, um das Verfassungsrecht zu respektieren. Dank dem Durchhaltewillen der Koordinatorin findet am 7. Juli 2001 die “erste Westschweizer Gay Pride des 21. Jahrhunderts” ohne jegliche Ausschreitungen statt. Sie verbindet mehr als 15’000 Teilnehmende in Liebe und gegenseitigem Respekt.
A rainbow coloured Sion
At the end of 2000, a committee led by Marianne Bruchez bravely set out to organize a Lesbian and Gay Pride & Friends in Sion, much to the displeasure of conservative sectors. Most of the city council declared itself against this event, but could not formally ban it. Although the committee was suggested to give up, the latter maintained its position. Tension arose and public opinion grew agitated. The bishop condemned what he called a demonic game. An advertisement against the event, accompanied by a petition, published in the press, sparked things off. The debate became heated, press articles poured in and criticism grew up until D-Day, demonstrating all the more the importance of the event in the face of intolerance and homophobic attacks. In March, the council finally unanimously approved the event. Thanks to the perseverance of its coordinator, the “first Gay Pride in French-speaking Switzerland in the 21st century” took place on 7 July 2001, without any incidents, bringing 15’000 people together in a spirit of love and respect for everyone.
Sion nei colori dell’arcobaleno
Alla fine del 2000, un comitato guidato da Marianne Bruchez si è lanciato nella coraggiosa organizzazione di un Lesbian and Gay Pride & Friends a Sion, con grande dispiacere degli ambienti conservatori. Sebbene la maggioranza del consiglio comunale fosse contraria all’evento, non riuscì a vietarlo formalmente e invitò il comitato a ritirarsi. Tuttavia, quest’ultimo mantiene la sua posizione. La tensione cresce e l’opinione pubblica è agitata. Il Vescovo denuncia un gioco diabolico. Una pagina pubblicitaria contro il Pride, accompagnata da una petizione, viene pubblicata nella stampa e da fuoco alle polveri. Il dibattito si accende, gli articoli di stampa aumentano, le critiche si accumulano, fino al D-day, dimostrando ancora di più l’importanza dell’evento di fronte all’intolleranza e agli attacchi omofobi. A marzo, all’unanimità e nel rispetto della legge costituzionale, il Consiglio comunale ha autorizzato lo svolgimento della manifestazione. Grazie alla perseveranza della sua coordinatrice, il “primo Gay Pride francofono del 21e secolo” si svolgerà il 7 luglio 2001, senza eccessi, riunendo più di 15.000 persone nell’amore e nel rispetto di tutti.