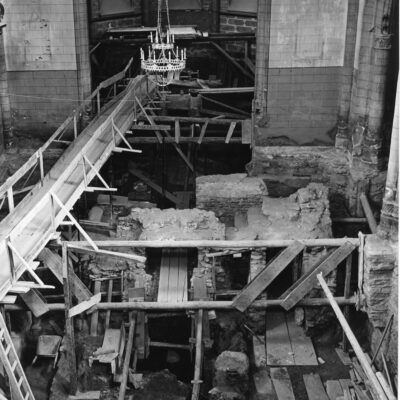
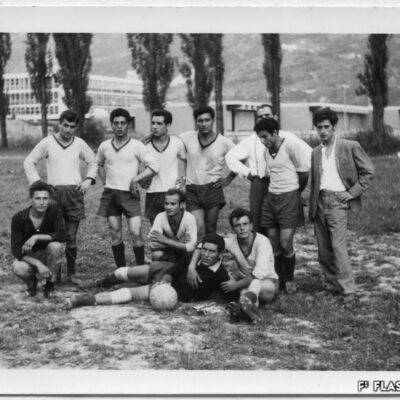
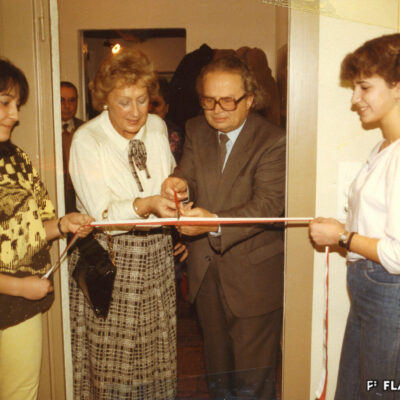
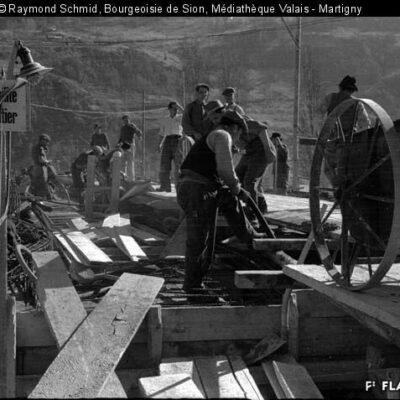
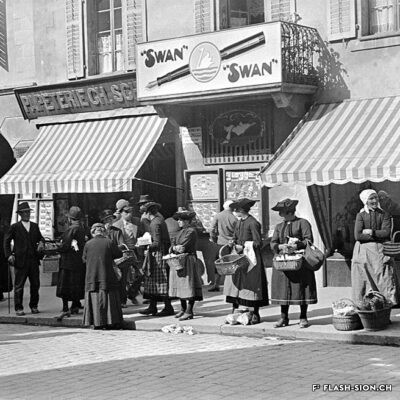
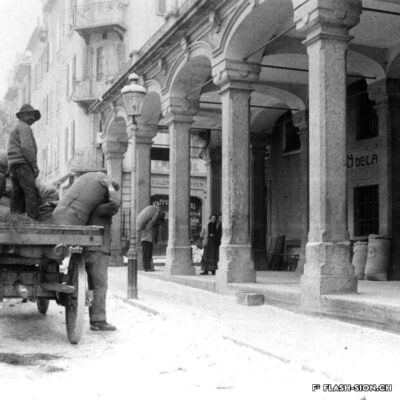
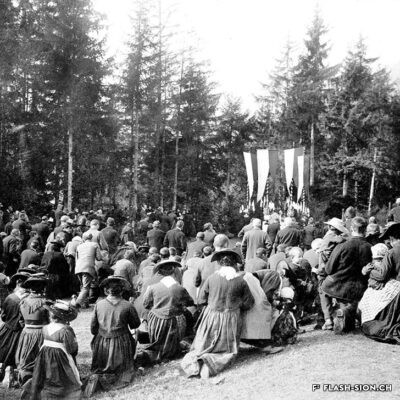
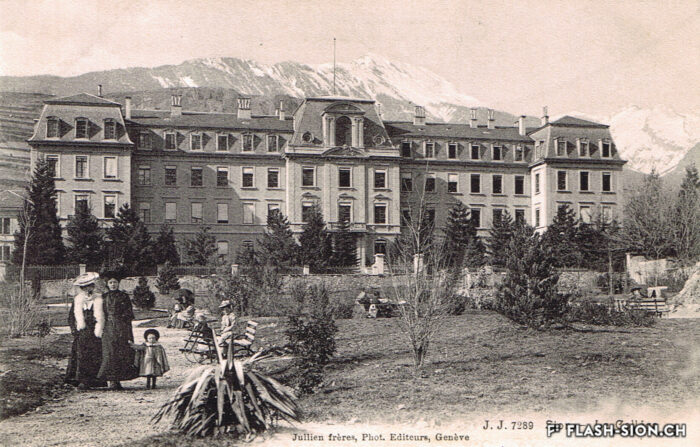
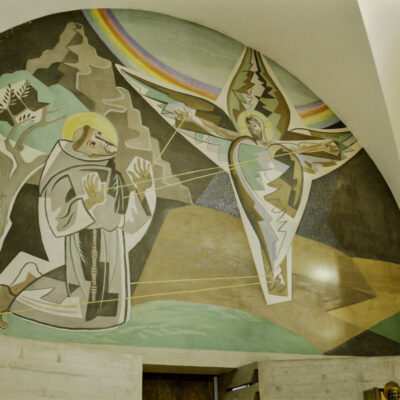Du culte du corps aux lieux de culte
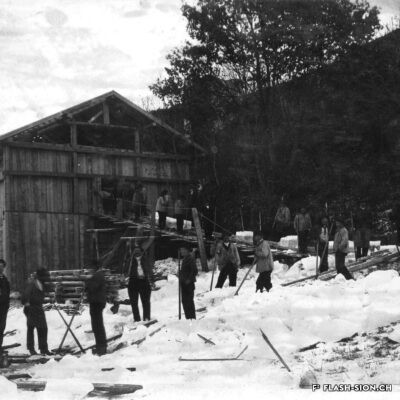
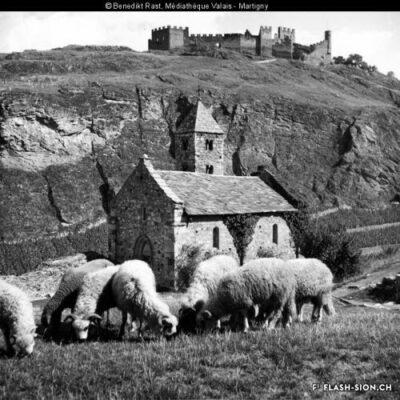
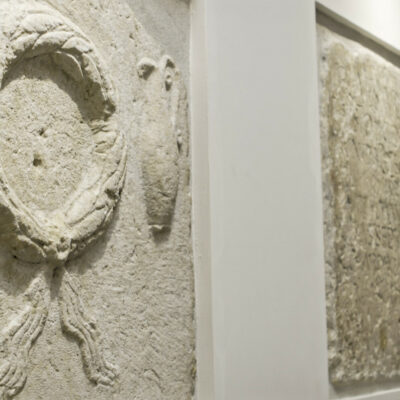
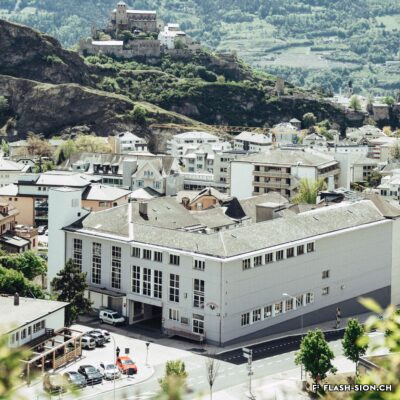
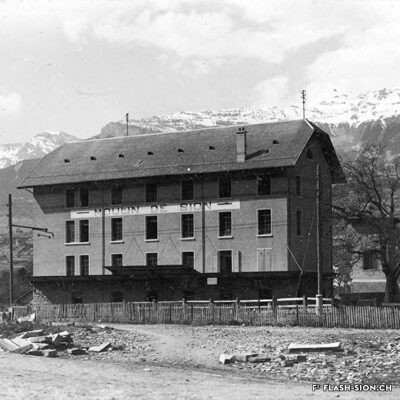
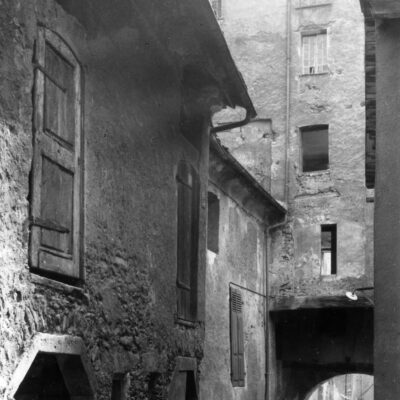
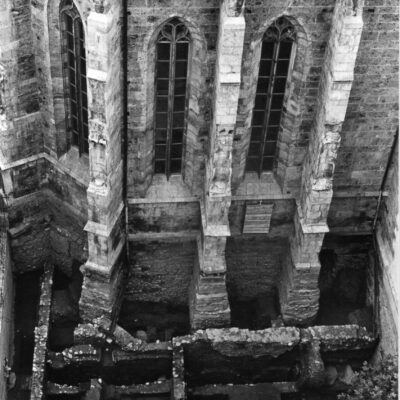
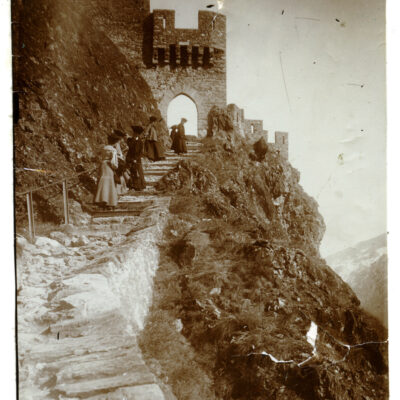
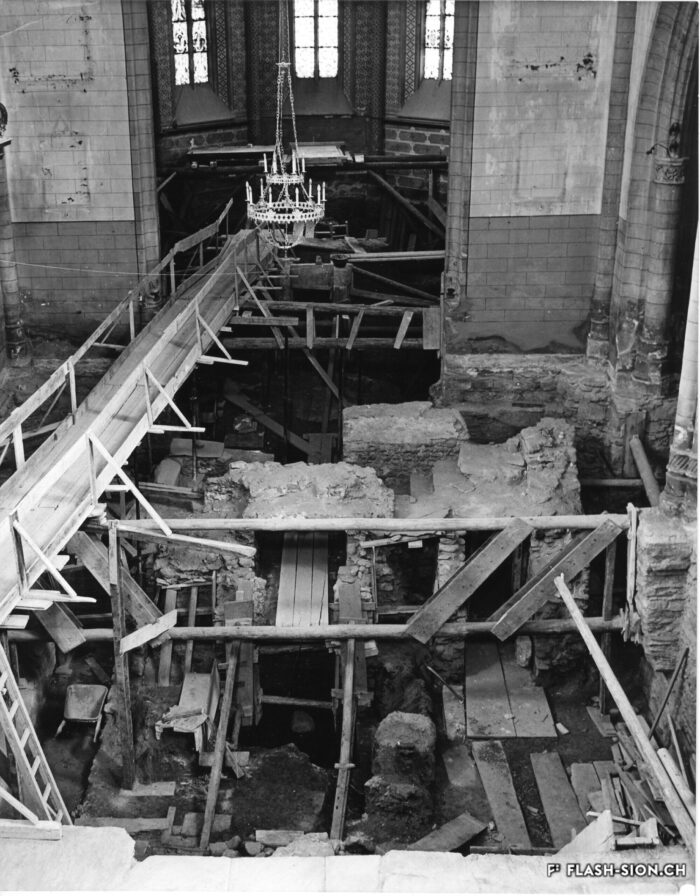
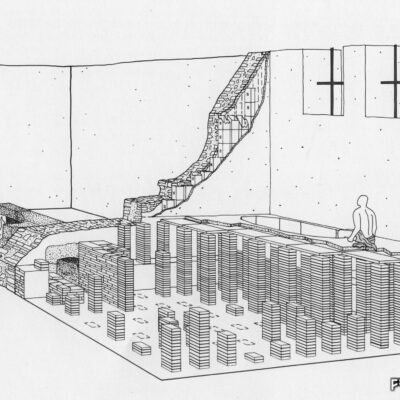
Les fouilles archéologiques de St-Théodule au début des années 1960 révèlent une surprise de taille ! Sous l’église gothique actuelle, œuvre de reconstruction inachevée de l’illustre maître-maçon transalpin Ulrich Ruffiner, les archéologues découvrent non seulement les ruines de trois édifices religieux antérieurs, mais également les vestiges de thermes romains. Infrastructure balnéaire caractéristique de la vie sociale de la Rome antique, les thermes publics étaient placés à côté du forum. Ainsi, l’hypothèse de la présence d’une place publique au Glarier sous l’Empire romain est aujourd’hui avancée par les spécialistes.
Vom Köperkult zum Kultort
Die archäologischen Ausgrabungen von St.Theodul Anfang der 1960er Jahre hielten eine grosse Überraschung bereit! Unter den Mauern der bestehenden gotischen Kirche, die auf ein unvollendetes Projekt des berühmten Maurermeisters Ulrich Ruffiner zurückführt, entdeckten Archäologen nicht nur die Ruinen von drei früheren Sakralbauten, sondern auch Überreste einer römischen Therme. Die für das gesellschaftliche Leben im alten Rom charakteristische Badeinfrastruktur befand sich gewöhnlich neben dem Forum. So vertreten Wissenschaftler heute die Hypothese, dass während des römischen Reichs das Zentrum der Siedlung in Glarier gelegen haben könnte.
Cleanliness is next to godliness
The archaeological excavations at the church of St. Theodulus in the early 1960s uncovered a major surprise! Beneath the present-day Gothic church (an unfinished reconstruction by the renowned Italian master mason Ulrich Ruffiner), the archaeologists discovered not only the ruins of three earlier religious buildings, but also the remains of Roman baths. The public baths were a typical feature of social life in ancient Rome, and they were usually located beside the forum. This discovery has now prompted experts to suggest that there was a public square in Sion’s Glarier district under the Roman Empire.
Dal culto del corpo ai luoghi di culto
Gli scavi archeologici presso St-Théodule, all’inizio degli anni 60, svelano una sorpresa notevole! Sotto la chiesa gotica attuale, opera di ricostruzione incompiuta dell’illustre capomastro transalpino Ulrich Ruffiner, gli archeologi scoprono non solamente le rovine di tre edifici religiosi antecedenti ma anche vestigi di terme romane. Infrastruttura balneare caratteristica della vita sociale della Roma antica, le terme pubbliche erano collocate accanto al foro. Pertanto, oggi gli specialisti avanzano l’ipotesi della presenza di una piazza pubblica al Glarier sotto l’Impero Romano.
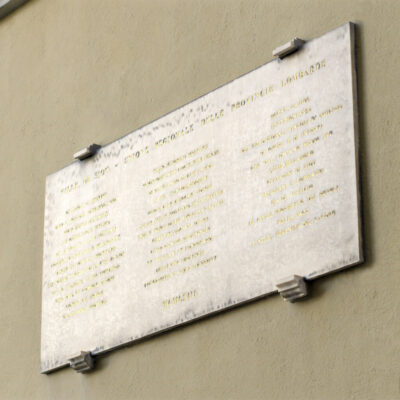
Des Lombards à Sion
A Sion, la présence de Lombards est attestée dès le 13e siècle. Actifs dans la banque et le commerce, ils prennent part au développement de la vie économique et politique sédunoise. Pourtant, la mention du quartier « en Lombardie » n’apparaît dans les écrits qu’à partir du 17e siècle, soit plusieurs siècles après leur installation. La rue qui porte leur nom est un hommage tardif. Une plaque commémorative posée au début de la rue de la Lombardie renforce encore ce souvenir des liens qui unissent le Valais et la Lombardie.
Lombarden in Sitten
In Sitten ist die Präsenz von Lombarden ab dem 13. Jahrhundert belegt. Sie betätigten sich als Kaufleute und Bankiers und waren massgeblich an der politischen und wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung der Stadt beteiligt. Der Name des Stadtteils “en Lombardie” tritt jedoch erst im 17. Jahrhundert in den Schriften auf. Die Strasse, die heute ihren Namen trägt, ist eine späte Hommage. Am Anfang der Rue de la Lombardie erinnert eine Gedenktafel an die Beziehungen zwischen der Lombardei und dem Wallis.
Lombards in Sion
There is evidence that Lombards were present in Sion from the 13th century onwards. They played an active part in banking and commerce, and they contributed to the development of Sion’s economic and political life. However, the city district known as “en Lombardie” is not mentioned in documentation until the 17th century – several centuries after the Lombards settled here. The street that bears their name is a belated tribute. A commemorative plaque installed at the start of Rue de la Lombardie is another reminder of the bonds that link Valais and Lombardy.
I lombardi a Sion
A Sion, la presenza dei lombardi è confermata dal 13° secolo. Attivi nel settore bancario e commerciale, prendono parte allo sviluppo della vita economica e politica di Sion.
Ciò nonostante, la menzione del quartiere “in Lombardia” appare negli scritti solo dal 17° secolo, ossia molti secoli dopo il loro insediamento. La via, che porta il loro nome, è un omaggio tardivo. Una targa commemorativa installata all’inizio della via “rue de la Lombardie” rafforza maggiormente il ricordo dei legami tra il Vallese e la Lombardia.
Un évêque valdôtain
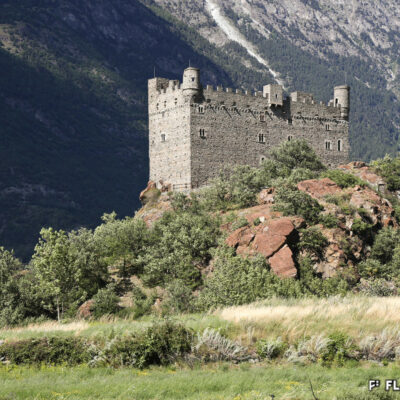
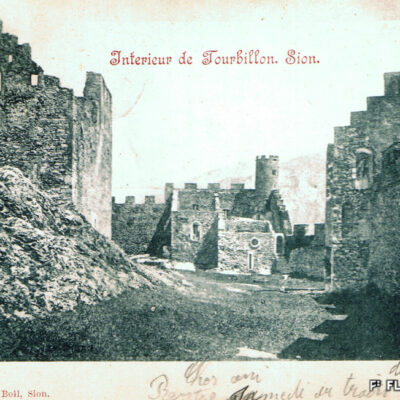
Boniface de Challant, évêque de Sion de 1290 à 1308, est originaire de l’une des familles les plus puissantes du Val d’Aoste. Sachant manier avec énergie et fermeté la crosse et l’épée, il commandite la construction du château de Tourbillon, érigé au tournant du 13e siècle. Il s’inscrit ainsi dans la tradition familiale de « bâtisseurs de châteaux-forts », les Challant ayant déjà fait édifier de nombreuses forteresses dans leur vallée d’origine.
Ein Bischof aus dem Aostatal
Der zwischen 1290 und 1308 als Bischof von Sitten amtierende Bonifaz de Challant stammte aus einer der einflussreichsten Familien des Aostatals. Er handhabte Bischofsstab wie Schwert mit Tatkraft und Entschlossenheit und blieb der Familientradition der “Burgenbauer” treu. Gelten doch die Challants als Auftraggeber zahlreicher Festungen in ihrer Heimatregion. Der Bau der Burganlage von Tourbillon, die um die Wende des 13. Jahrhunderts entstanden ist, wird allgemein Bonifaz de Challant zugeschrieben.
A bishop from Val d’Aosta
Boniface de Challant, Bishop of Sion from 1290 to 1308, came from one of the most powerful families in Val d’Aosta. As a vigorous and resolute wielder of the crook and the sword, he sponsored the construction of Tourbillon Castle, built at the turn of the 13th century. In so doing, he followed the family tradition of “builders of fortified castles”: the Challant family had already commissioned many fortresses in their home valley.
Un vescovo valdostano
Bonifacio di Challant, vescovo di Sion dal 1290 al 1308, proviene da una delle famiglie più potenti della Valle d’Aosta. Sapendo maneggiare con forza e fermezza il pastorale e la spada, commissiona la costruzione del castello di Tourbillon, eretto al volgere del 13° secolo. S’iscrive così a pieno titolo nella tradizione familiare dei “costruttori di fortezze”, visto che gli Challant avevano già fatto edificare numerose fortezze nella loro valle d’origine.
Le parfum du sud
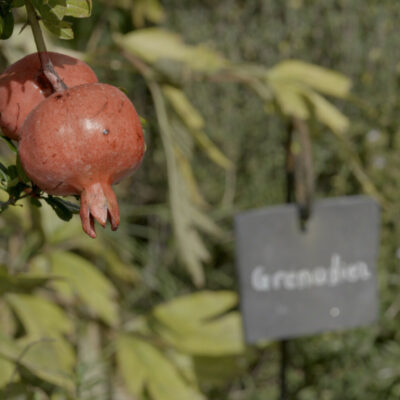
Région la plus sèche de Suisse, le Valais central et la station météorologique de Sion enregistrent régulièrement des températures record. Sur les collines de Valère et Tourbillon, une végétation caractéristique des steppes continentales, mêlée à quelques espèces typiquement méditerranéennes, reflètent le climat d’une vallée intra-alpine. Dès le 16e siècle déjà, la faune et la flore exceptionnelles du site des collines suscitent l’intérêt des scientifiques et la valeur importante de ces milieux refuges demande aujourd’hui toute notre attention. Ponctuée par le chant des cigales en été, la présence d’espèces cultivées comme l’amandier, le figuier ou encore le grenadier, ajoute à l’agréable souvenir du Sud qui s’en dégage.
Der Duft des Südens
Als trockenste Region der Schweiz bekannt, verzeichnen das Zentralwallis und die Wetterstation von Sitten regelmässig Rekordtemperaturen. Auf den Felshügeln von Valeria und Tourbillon repräsentiert eine von mediterranen Arten durchzogene Steppenvegetation das kontinentale Klima eines inneralpinen Tales. Bereits seit dem 16. Jahrhundert wecken die aussergewöhnliche Fauna und Flora der Burghügel von Sitten das Interesse der Wissenschaftler. Die grosse Bedeutung als Zufluchtsort seltener Arten verlangt heute eine spezielle Rücksichtsname. Im Sommer haftet dem Ort durch den Gesang der Zikaden und Kulturpflanzen wie Mandel-, Feigen- und Granatapfelbaum eine angenehm südliche Note an.
Fragrances of the South
Central Valais is Switzerland’s driest region, and Sion’s meteorological station regularly registers record temperatures. On the Valère and Tourbillon hills, the climate of an inner Alpine valley fosters characteristic continental steppe vegetation mixed with some typically Mediterranean species. From the 16th century onwards, the interest of scientists was already aroused by the unusual fauna and flora present on these hills; nowadays too, these valuable and important refuge habitats merit our fullest attention. Pleasant memories of the South abound here, as the cicadas sing during summer amid cultivated species such as almond, fig and even pomegranate trees.
Il profumo del Sud
Considerata la regione più secca della Svizzera, il Vallese centrale e la stazione meteorologica di Sion registrano regolarmente delle temperature record. Sulle colline di Valère e Tourbillon, una vegetazione caratteristica delle steppe continentali, mischiata ad alcune specie tipiche della vegetazione mediterranea, rispecchia il clima di una valle intra-alpina. Già dal 16°secolo, la fauna e la flora eccezionali del sito delle colline suscitano l’interesse degli scienziati e il valore importante di questi luoghi, considerati come rifugio, richiede oggi tutta la nostra attenzione. Scandita dal canto delle cicale nel periodo estivo, la presenza di specie coltivate come il mandorlo, l’albero di fico o ancora il melograno, riportano la memoria alle terre del Sud.
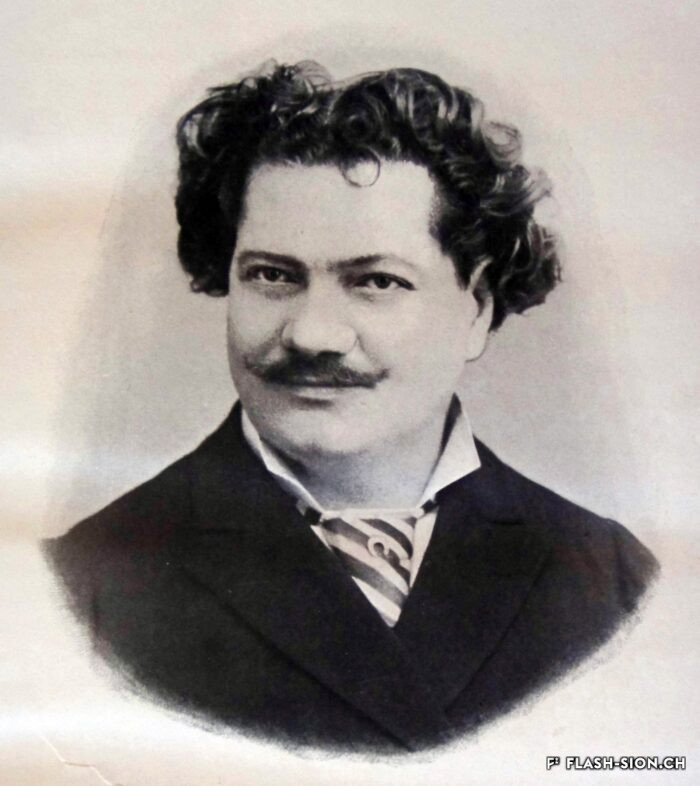
De Jean-Baptiste à Marguerite
Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia ou Garbazzia (1790-1865) s’établit à Sion en tant que maître-maçon au début du 19e siècle. Piémontais originaire de Varallo, il fait de nombreux dons aux pauvres de la cité ainsi qu’aux établissements de charité. Cet homme généreux lègue également à la Municipalité divers bâtiments, dont l’imposante maison en bas de la ruelle qui porte aujourd’hui son nom. Démolie en 1954, cette bâtisse, un temps mise à la disposition des assistés, a laissé place à un espace baptisé en hommage à l’artiste et écrivaine Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
Von Jean-Baptiste zu Marguerite
Der Maurermeister Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia oder Garbazzia (1790-1865) siedelte sich Anfang des 19. Jahrhunderts in Sitten an. Der gebürtige Piemonteser aus Varallo zeichnete sich durch zahlreiche Spenden zu Gunsten von Mittellosen und Wohltätigkeitseinrichtungen der Stadt aus. Der grosszügige Bürger hinterliess der Gemeinde verschiedene Immobilien, darunter das imposante Haus in der Gasse, die heute seinen Namen trägt. Dieses diente einige Zeit als Unterkunft für Unterstützungsbedürftige der Stadt. Es wurde 1954 abgerissen und wich so einem Platz zu Ehren der Schriftstellerin Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
From Jean-Baptiste to Marguerite
Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia or Garbazzia (1790-1865) set up his business as a master mason in Sion at the start of the 19th century. This native of Varallo in Piedmont bestowed many gifts on the city’s poor and its charitable institutions. He also showed his generosity by bequeathing various buildings to the Municipality, including the impressive house at the bottom of the street that now bears his name. This building was placed at the disposal of people in need of social assistance before it was demolished in 1954; it made way for a space named in honour of Marguerite Burnat-Provins, the artist and writer.
Da Giovanni Battista a Marguerite
Giovanni Battista Garbaccia o Garbazzia (1790-1865) si stabilisce a Sion come capomastro all’inizio del 19° secolo. Piemontese, originario di Varallo, fa numerosi doni ai poveri della città così come ad enti di beneficenza. Uomo generoso fa dono al comune anche di diversi edifici, tra i quali l’imponente casa all’inizio del vicolo a lui intestato. Il palazzetto, distrutto nel 1954 e un tempo a disposizione degli assistiti, ha lasciato il posto ad un luogo che ha preso il nome dell’artista e scrittrice Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
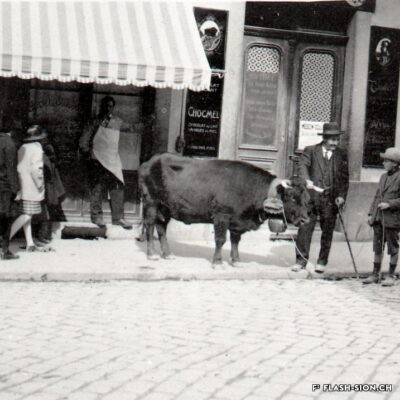
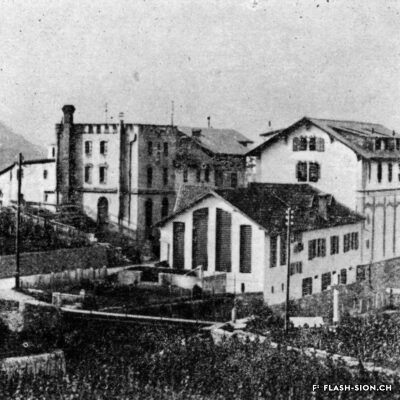
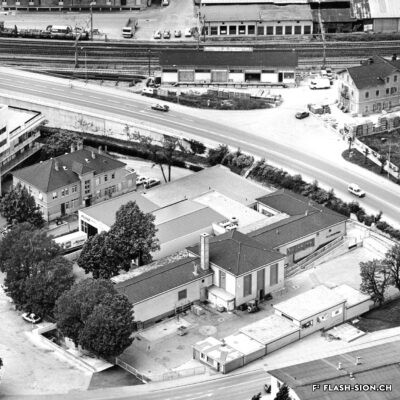
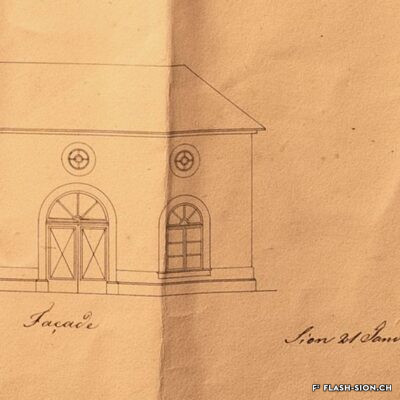
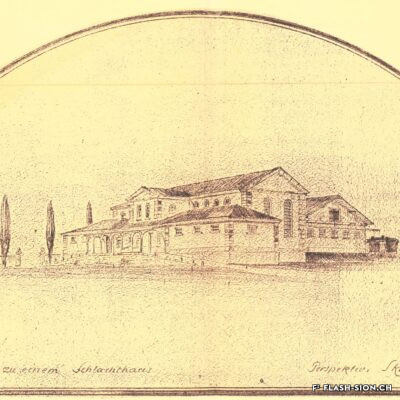
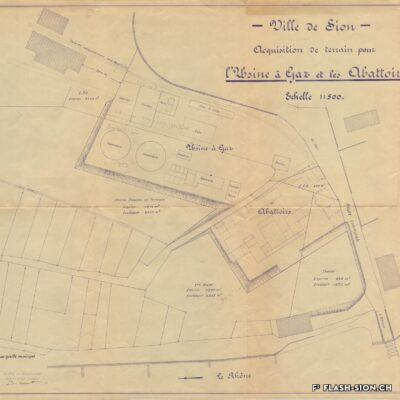
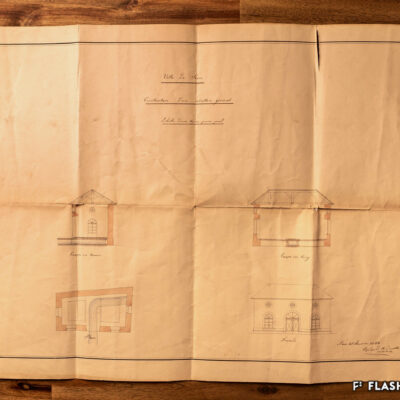
D’un abattoir à l’autre
En 1850, des abattoirs municipaux sont construits sous le rocher de la Majorie, dans un quartier encore peu habité à l’époque. Avec l’augmentation de la population, ces locaux ne répondent plus aux normes d’hygiène dès le début du 20e siècle. Les discussions pour un nouveau bâtiment commencent. Durant les années 1930, les abattoirs déménagent à la rue de l’Industrie, lieu plus approprié. Ils y resteront près de 70 ans avant de devoir fermer, n’étant plus assez rentables. L’édifice est ensuite investi par l’Œuvre suisse d’entraide ouvrière (OSEO), le Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs ainsi que certaines sociétés locales. Le départ de l’OSEO, début 2021, offre à la Ville la possibilité d’en faire un lieu dédié à la créativité et à l’innovation au cœur du quartier Ronquoz 21.
Von einem Schlachthof zum andern
1850 wird am Fusse des Majoria-Felsens in einem damals noch kaum bebauten Quartier ein erster städtischer Schlachthof errichtet. Dieser entspricht aufgrund des grossen Bevölkerungszuwachses bereits ab anfangs des 20. Jahrhunderts nicht mehr den Hygienenormen. Es folgen längere Verhandlungen, um einen neuen und geeigneteren Standort zu finden. In den 1930er Jahren siedelt der Schlachthof an die Rue de l’Industrie über, wird während 70 Jahren betrieben und dann aufgrund ungenügender Rentabilität geschlossen. Das Gebäude wird darauf von dem Schweizerischen Arbeitshilfswerk (SAH), dem städtischen Amt für Sport, Jugend und Freizeit wie auch lokalen Vereinen genutzt. Der Auszug des SAH eröffnet der Stadt schliesslich die Chance, mitten im Quartier von Ronquoz 21 einen Ort für Kreativität und Innovation anzusiedeln.
From one slaughterhouse to another
In 1850, municipal slaughterhouses were built under the Majorie rock, in a neighbourhood that was not very populated at the time. With the increase in population at the beginning of the 20th century, these premises no longer met hygiene standards. Discussions about a new building began. During the 1930s, the slaughterhouses moved to the ‘Rue de l’Industrie’, a more suitable location. They remained there for almost 70 years before being forced to close as they were no longer profitable. The building was then taken over by the Swiss Labour Assistance (OSEO, Œuvre suisse d’entraide ouvrière), the Sports, Youth and Leisure Service (Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs) and some local societies. The departure of the OSEO, at the beginning of 2021, offered the city the possibility of turning it into a venue dedicated to creativity and innovation in the heart of the Ronquoz 21 district.
Da un macello all’altro
Nel 1850 furono costruiti dei macelli comunali sotto la roccia di Majorie, in un quartiere che all’epoca era poco popolato. Con l’aumento della popolazione, all’inizio del XX secolo questi locali non soddisfacevano più gli standard igienici. Sono così iniziate le discussioni per la costruzione di un nuovo edificio. Negli anni ’30 i macelli si trasferirono nella Rue de l’Industrie, in una posizione più adatta. L’azienda rimase lì per quasi 70 anni prima di essere costretta a chiudere non essendo più abbastanza redditizia. L’edificio è stato poi preso in gestione dall’OSEO (Soccorso Operaio Svizzero,SOS), il Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs (Servizio dello sport, della gioventù e del tempo libero) e da alcune società locali. La partenza del OSEO, all’inizio del 2021, offre alla Città la possibilità di trasformarlo in un luogo dedicato alla creatività e all’innovazione nel cuore del distretto Ronquoz 21.
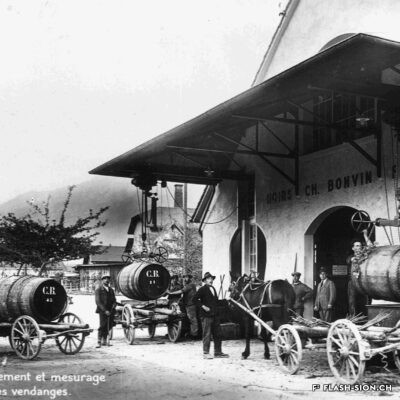
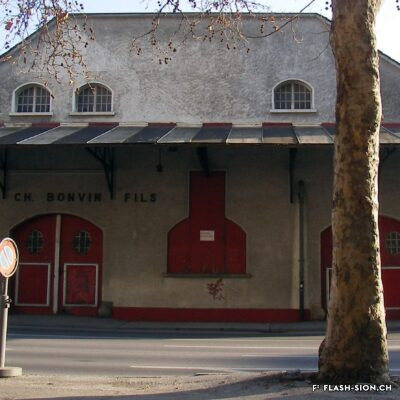
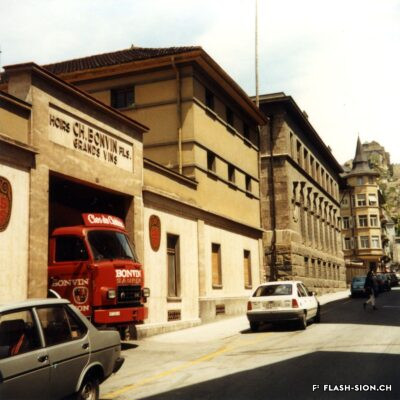
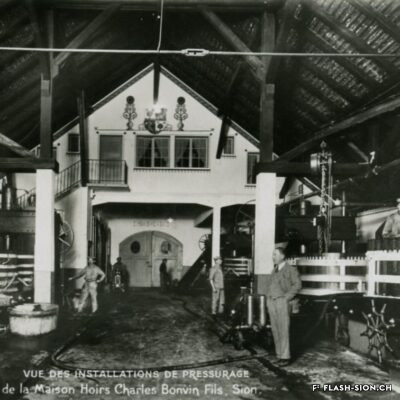
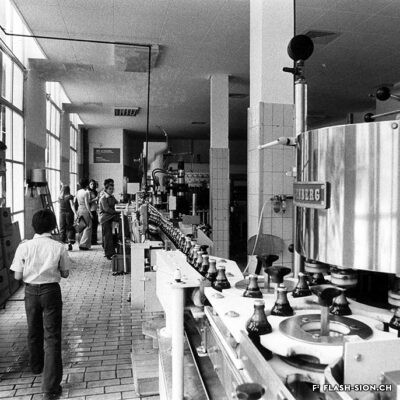
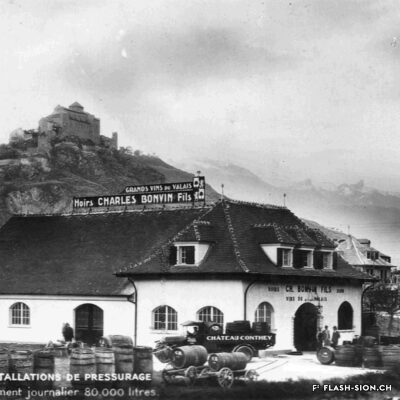
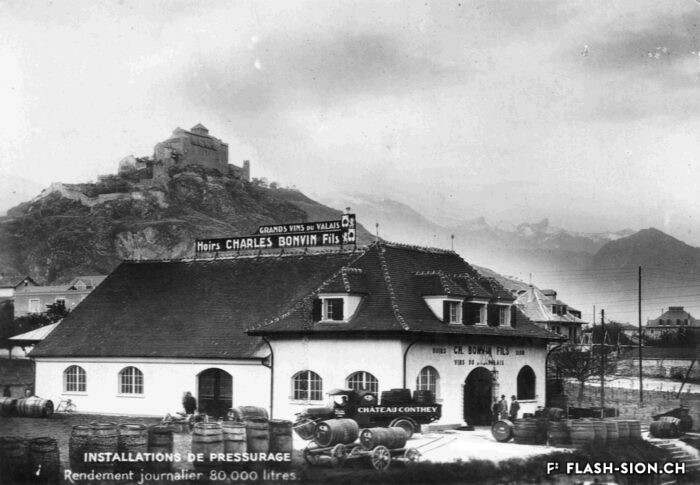
Charles et les caves festives
Fondée en 1858, la maison sédunoise des Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils fait figure de pionnière en matière de commerce vinicole en Valais. Charles-Marie Bonvin, son fondateur, donne l’impulsion au domaine et fait connaître les vins valaisans hors du canton et de la Suisse. Son fils Charles (1858-1922) prend la relève et à sa suite, ses deux fils, Charles (1888-1937) puis Félix. Aux caves et bureaux de la rue des Vergers et de la rue des Remparts s’ajoutent en 1932, les pressoirs de l’avenue de Tourbillon, face à la gare. Ces derniers deviennent alors un centre moderne de pressurage et d’encavage, jusqu’au début des années 1990. Désaffectés pendant de nombreuses années, ces pressoirs à l’abandon attirent l’attention d’un collectif qui y voit un potentiel culturel et souhaite leur redonner vie de façon éphémère. En 2008 et durant une année, l’association « Les Caves à Charles » fait vibrer ce lieu industriel chargé d’histoire, pour lui rendre un dernier hommage avant sa démolition.
Charles und die festliche Kellerei
Die 1858 in Sitten gegründete Weinkellerei der Erben von Charles Bonvin und Söhne gilt als Pionierin des Weinhandels im Wallis. Charles-Marie Bonvin, Begründer des Hauses, verstand es, den Walliser Wein ausserhalb des Kantons und der Schweiz bekannt zu machen. Der Betrieb wird in der Folge von seinem Sohn Charles (1858-1922) übernommen bevor dessen Söhne Charles (1888-1937) und später Félix die Nachfolge antreten. Zum Weinkeller und den Büroräumlichkeiten in der Rue des Vergers und der Rue des Remparts gesellt sich 1932 das Gebäude mit Weinpresse an der Avenue de Tourbillon, direkt gegenüber dem Bahnhof. Dieses entwickelt sich bis anfangs der 1990er Jahre zu einer modernen Kelterei mit Weinkeller. Danach bleibt das Gebäude während einiger Jahre ungenutzt. 2008 interessiert sich ein Kollektiv für die Kelterei und sieht deren Potenzial für eine kurzfristige kulturelle Nutzung. Während einem Jahr bringt der Verein «Les Caves à Charles» den geschichtsträchtigen Ort nochmals zum Schwingen und erweist ihm, bevor er abgebrochen wird, die letzte Ehre.
Charles and the festive wine cellars
Founded in 1858, the Sion-based company of Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils is a pioneer in the wine trade in Valais. Charles-Marie Bonvin, its founder, provided the impetus to the estate and made Valais wines known outside the canton and Switzerland. His son Charles (1858-1922) took over and was followed by his two sons, Charles (1888-1937) and Félix. In 1932, the cellars and offices in the ‘Rue des Vergers’ and the ‘Rue des Remparts’ were completed by the addition of wine presses in the ‘Avenue de Tourbillon’, opposite the railway station. They became a modern pressing and cellaring centre until the early 1990s. Disused for many years, these abandoned wine presses attracted the attention of a group who saw a cultural potential in them and wanted to bring them back to life in a temporary way. In 2008 and for one year, the Charles Cellars Association (Les Caves à Charles) filled this industrial site, full of history, with life and paid it a last tribute before its demolition.
Charles e le cantine in festa
Fondata nel 1858, l’azienda sedunese Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils, è una pioniera del commercio di vino nel Vallese. Charles-Marie Bonvin, il suo fondatore, diede impulso alla tenuta e fece conoscere i vini del Vallese al di fuori del cantone e della Svizzera. Il figlio Charles (1858-1922) prese il testimone e fu seguito dai suoi due figli, Charles (1888-1937) e Félix. Nel 1932, alle cantine e agli uffici nella Rue des Vergers e nella Rue des Remparts si aggiunsero i torchi di Avenue de Tourbillon, di fronte alla stazione. In seguito, fino all’inizio degli anni Novanta, si sono trasformati in un moderno centro di pressatura e cantina. In disuso da molti anni, questi torchi abbandonati hanno attirato l’attenzione di un gruppo che ha visto in essi un potenziale culturale e ha voluto riportarli in vita in modo temporaneo. Nel 2008 e per un anno, l’associazione “Les Caves à Charles” (Le cantine di Charles) ha riportato in vita questo luogo industriale ricco di storia, per rendergli un ultimo omaggio prima della sua demolizione.
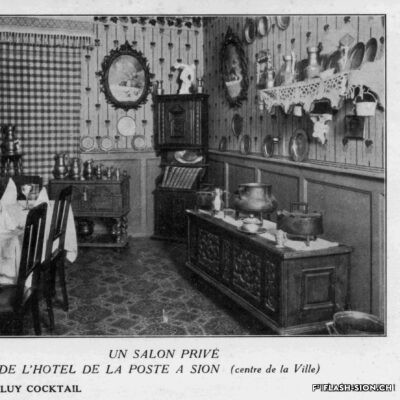
Un cuisinier avant-gardiste
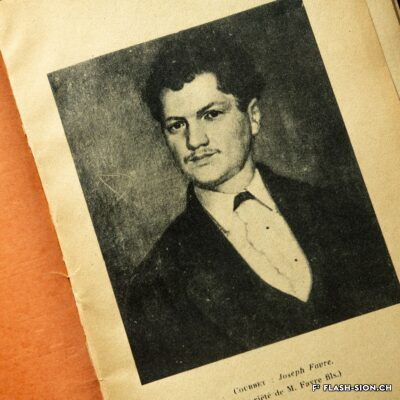
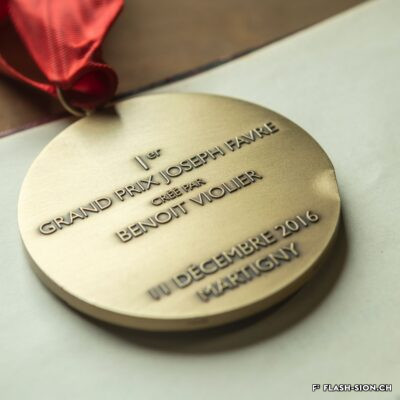
En matière de gastronomie, l’histoire a longtemps oublié un enfant du pays. Originaire de Vex, un certain Joseph Favre (1844-1903) s’illustre en tant que pionnier de la « science et de l’hygiène culinaire ». Après un apprentissage de trois ans, vraisemblablement à l’Hôtel de la Poste, à l’époque l’un des plus prestigieux hôtels de Sion, il sillonne la Suisse et l’Europe pour parfaire son art. Anarchiste à ses heures, Joseph Favre se fait surtout connaître par son acharnement à rendre à la cuisine ses lettres de noblesse. Il publie notamment dès 1877 le premier journal de cuisine écrit par des cuisiniers et participe aux premiers concours et expositions culinaires. Dès 1883, ce théoricien progressiste consacre sa vie à la rédaction de son monumental « Dictionnaire universel de cuisine pratique et d’hygiène alimentaire ». Il est également à l’origine de la fondation de l’Académie culinaire de France en 1883.
Ein fortschrittlicher Koch
Im Bereich der Gastronomie blieb der Walliser Joseph Favre (1844-1903) der breiten Öffentlichkeit lange unbekannt. Der aus Vex stammende Koch hat sich als Pionier der Kulinarik und wissenschaftlichen Küchenhygiene bekannt gemacht. Nach einer dreijährigen Lehre, vermutlich im damals renommierten Hotel Post in Sitten, bereist er die Schweiz und Europa und erweitert seine Kochkunst. Kurze Zeit einer anarchistischen Bewegung verschrieben, zeichnet sich Favre insbesondere durch sein hartnäckiges Engagement für eine moderne Ess- und Kochkultur aus. Ab 1877 veröffentlicht er die erste, von einem Koch verfasste Kochzeitschrift und nimmt an ersten Kochwettbewerben und kulinarischen Ausstellungen teil. Ab 1883 widmet sich der fortschrittliche Theoretiker ganz dem Verfassen seines bedeutendsten Werkes, dem «Universallexikon des Kochens und der Lebensmittelhygiene». Er ist ebenfalls Begründer der 1883 entstandenen «Académie culinaire de France».
An avant-garde cook
When it comes to gastronomy, history has long forgotten a local youngster. Originally from Vex, a certain Joseph Favre (1844-1903) distinguished himself as a pioneer of “culinary science and hygiene”. After a three-year apprenticeship, probably at the Hôtel de la Poste, which was one of the most prestigious hotels in Sion at the time, he travelled throughout Switzerland and Europe to perfect his art. An anarchist at times, Joseph Favre is best known for his determination to give nobility back to cuisine. In 1877, he published the first cooking journal written by cooks and he took part in the first culinary competitions and exhibitions. From 1883, this progressive theorist devoted his life to writing his monumental “Universal Dictionary of Practical Cooking and Food Hygiene”. He was also a founder of the French Culinary Academy in 1883.
Un cuoco d’avanguardia
Quando si parla di gastronomia, la storia ha dimenticato da tempo un ragazzo del posto. Originario di Vex, un certo Joseph Favre (1844-1903) si distinse come pioniere della “scienza e dell’igiene culinaria”. Dopo un apprendistato di tre anni, probabilmente presso l’Hôtel de la Poste, all’epoca uno degli alberghi più prestigiosi di Sion, viaggiò in tutta la Svizzera e in Europa per perfezionare la sua arte. A volte anarchico, Joseph Favre è noto soprattutto per la sua determinazione a dare alla cucina le sue lettere di nobiltà. Nel 1877 pubblicò il primo giornale di cucina scritto da cuochi e partecipò ai primi concorsi e mostre culinarie. A partire dal 1883, questo teorico progressista si dedicò alla stesura del suo monumentale “Dictionnaire universel de cuisine pratique et d’hygiène alimentaire”. A lui si deve anche la fondazione dell’Accademia culinaria francese nel 1883.
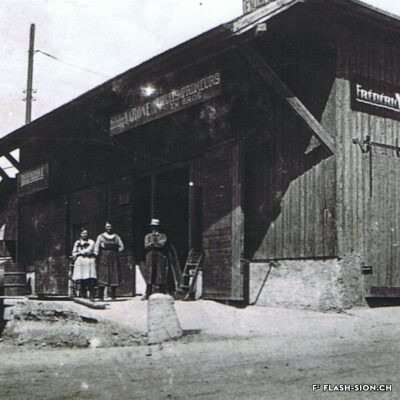
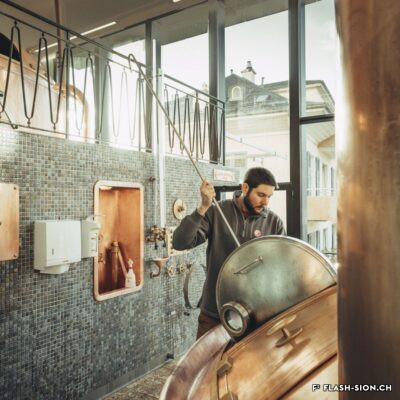
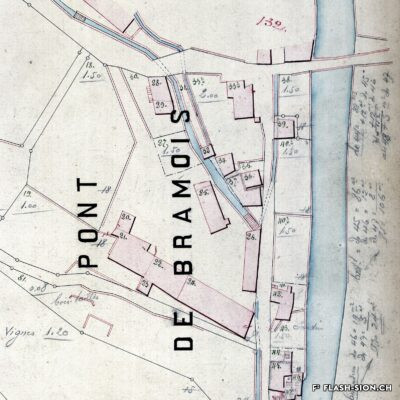
De la bière au pays du vin
Il aura fallu du temps pour que la bière s’impose en Valais, pays du vin par excellence. Malgré l’interdiction de ce « breuvage inhabituel » en 1802 par les autorités valaisannes, plusieurs brasseries s’installent dans la région sédunoise au cours du 19e siècle. En 1865, Maurice de Quay, pharmacien hollandais, en ouvre une au nord de la ville de Sion. A la même période environ, la brasserie Koebel, Aymon et Cie est également active à Bramois. Pour produire une bière de qualité, les deux entreprises recrutent leurs employés en Suisse allemande, voire en Allemagne. Vers la fin du 19e siècle, la brasserie de Quay est reprise par Johan Hofer et celle de Bramois passe aux mains des frères Fertig. En 1926, elles fusionnent pour devenir la Brasserie Valaisanne telle qu’on la connait aujourd’hui. Dès 1950, l’entreprise s’industrialise avec, notamment, des installations frigorifiques qui remplacent la glacière.
Vom Bier zum Weinland
Es ging eine ganze Weile, bis sich das Bier in dem vom Weinbau geprägten Wallis durchsetzt. Obwohl die Walliser Behörden das «ungewohnte Gebräu» verbieten, siedeln sich im Laufe des 19. Jahrhunderts mehrere Bierbrauereien in der Region Sitten an. 1865 eröffnet der holländische Apotheker Maurice de Quay im Norden der Stadt Sitten eine Brauerei. Etwa zur gleichen Zeit wird bei Koebel, Aymon et Cie in Bramois ebenfalls Bier gebraut. Zur Herstellung eines hochwertigen Bieres, heuern beide Unternehmen ihre Mitarbeiter in der Deutschschweiz oder gar in Deutschland an. Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts wird die Brauerei de Quay von Johan Hofer übernommen und die Brauerei in Bramois geht in den Besitz der Gebrüder Fertig über. 1926 fusionieren die beiden Unternehmen unter dem Namen Walliser Brauerei, welche bis heute noch besteht. Ab den 1950er Jahren wird die Produktion unter anderem durch die Installation von Kühlanlagen industrialisiert, die den Eiskeller ersetzen.
Beer in wine country
It took a long time for brewing beer to become established in Valais, a wine country par excellence. Despite the ban on this “unusual beverage” in 1802 by the Valais authorities, several breweries were set up in the Sion region during the 19th century. In 1865, Maurice de Quay, a Dutch pharmacist, opened one in the northern part of the city of Sion. Around the same time, the brewery Koebel, Aymon & Cie was also active in Bramois. In order to produce quality beer, both companies recruited their employees in German-speaking Switzerland, and even in Germany. Towards the end of the 19th century, the Quay brewery was taken over by Johan Hofer and the Bramois brewery was taken over by the Fertig brothers. In 1926, they merged to become the Brasserie Valaisanne as we know it today. From 1950 onwards, the company became more industrial, with refrigeration facilities replacing the icebox.
La birra nel paese del vino
Ci è voluto molto tempo affinché la birra si affermasse in Vallese, la terra del vino per eccellenza. Nonostante il divieto di questa “bevanda insolita” nel 1802 da parte delle autorità vallesane, nel corso del XIX secolo nella regione sedunese sono state aperte diverse birrerie. Nel 1865, Maurice de Quay, un farmacista olandese, aprì una fabbrica di birra a nord della città di Sion.
All’incirca nello stesso periodo, anche la birreria Koebel, Aymon et Cie era attiva a Bramois. Per produrre birra di qualità, entrambe le aziende reclutarono i propri dipendenti dalla Svizzera tedesca e persino dalla Germania. Verso la fine del XIX secolo, il birrificio Quay fu rilevato da Johan Hofer e il birrificio di Bramois dai fratelli Fertig. Nel 1926 si fusero per diventare la Brasserie Valaisanne come la conosciamo oggi. Dal 1950 in poi, l’azienda divenne più industriale, con impianti di refrigerazione che sostituirono la ghiacciaia.
Pomme de Reinette et pomme d’Api
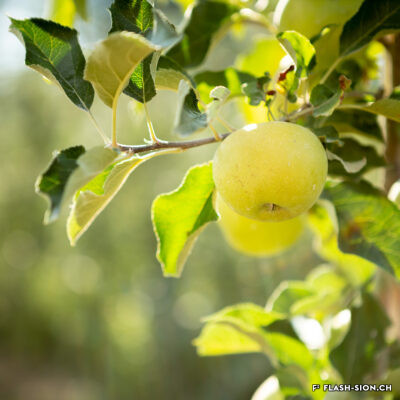
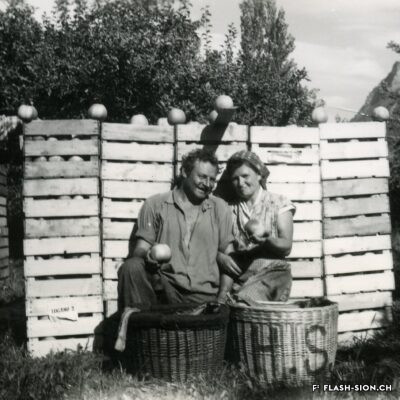
Contrairement à ce que pourrait suggérer son nom, la Reinette (monstrueuse) du Canada a ses origines en France. Elle est décrite pour la première fois en 1771 par le botaniste du Roi, Pierre Andrieux. Son introduction dans les vergers valaisans coïncide avec la première correction du Rhône (1863-1894). Les terres gagnées par l’assèchement de la plaine offrent en effet un terroir particulièrement propice à sa culture. Dès la fin du 19e siècle, la pomme Canada devient la variété emblématique des vergers et pré-vergers à hautes tiges de Bramois, d’où elle était exportée jusque dans la capitale française. Aujourd’hui, les vergers de Sion et de Vex sont dans les derniers en Suisse où cette variété ancienne est encore présente et replantée, notamment sur les terrains de la Bourgeoisie de Sion. Celle-ci offre chaque automne une cagette de ces pommes aux bourgeois. Pomme de garde par excellence, la Canada est tout particulièrement appréciée pour sa chair fondante et la saveur douce et acidulée de son jus.
In meinem kleinen Apfel…
Anders als es der Name vermuten lässt, hat die Kanada-Reinette ihren Ursprung in Frankreich. Sie wird erstmals 1771 von dem königlichen Botaniker Pierre Andrieux beschrieben. Die Einführung der Apfelsorte im Wallis fällt mit der ersten Rhonekorrektur (1863-1894) zusammen. Die Trockenlegung der Rhoneebene bietet einen besonders geeigneten Boden für den Anbau der Apfelsorte. Ab Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts entwickelt sich die Kanada-Reinette zur emblematischen Apfelsorte der Hochstamm und Wiesenobstgärten von Bramois und wird bis nach Paris exportiert. Heute ist diese alte Apfelsorte in der Schweiz insbesondere noch in den Obstgärten von Sitten und Vex anzutreffen und wird nicht zuletzt auf den Grundstücken der Burgergemeinde von Sitten neu angepflanzt. Jeden Herbst verteilt diese ihren Burgern eine Kiste Kanada-Reinetten. Als Lagerapfel beliebt, wird das Tafelobst ganz besonders für sein zart-schmelzendes Fruchtfleisch und den süss-säuerlichen Geschmack seines Saftes geschätzt.
Reinette apple and an Api apple (a children’s song)
Contrary to what its name might suggest, the Reinette (Monstrueuse) of Canada has its origins in France. It was first described in 1771 by the King’s botanist, Pierre Andrieux. Its introduction into Valais orchards coincided with the first correction of the Rhône River (1863-1894). The land obtained by the draining of the plain offered a particularly favourable soil for the cultivation of this variety. From the end of the 19th century, the Canada apple became the emblematic variety of orchards and orchard meadows of Bramois, from where it was exported all the way to the French capital. Today, the orchards of Sion and Vex are some of the only ones in Switzerland where this old variety is still present and replanted, notably on the grounds belonging to the Bourgeoisie of Sion. Every autumn, the Bourgeoisie offers a crate of these apples to its members. The Canada apple is particularly appreciated for its melt-in-the-mouth flesh and the sweet, tangy taste of its juice.
« Pomme de Reinette e pomme d’Api »
Contrariamente a quanto potrebbe far pensare il nome, la Reinette (mostruosa) del Canada ha origini francesi. Fu descritta per la prima volta nel 1771 dal botanico del re, Pierre Andrieux. La sua introduzione nei frutteti vallesani coincise con la prima correzione del Rodano (1863-1894).
I terreni bonificati dal drenaggio della pianura offrivano un terreno particolarmente favorevole alla sua coltivazione. Dalla fine del XIX secolo, la mela Canada divenne la varietà emblematica dei frutteti e dei pre-frutteti ad alto fusto di Bramois, da dove veniva esportata nella capitale francese.
Oggi i frutteti di Sion e Vex sono gli unici in Svizzera in cui questa vecchia varietà è ancora presente e viene ripiantata, in particolare nei terreni del patriziato di Sion. Ogni autunno, quest’ultimo offre una cassa di queste mele ai suoi patrizi. La Canada è la mela per eccellenza, particolarmente apprezzata per la sua polpa fondente e per il sapore dolce e acidulo del suo succo.
Une affaire de famille
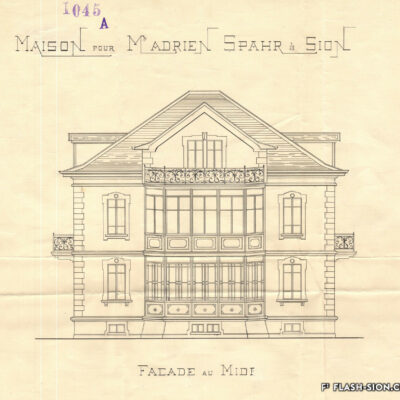
Entrepreneur piémontais né en 1845, Michel Fasanino œuvre à Sion dès son établissement en 1883. A cette époque, la ville ressemble davantage à un bourg agricole qu’à une cité urbaine. Jusqu’à son décès en 1923, Fasanino contribue notablement à son expansion. Il collabore également avec les deux architectes incontournables de l’époque, Joseph de Kalbermatten et Joseph Dufour. Ce patron bienveillant dirige son affaire prospère en bon père de famille et laisse de nombreuses réalisations, en partie disparues aujourd’hui.
Ein Familienunternehmen
Der 1845 geborene piemontesische Baumeister Michel Fasanino liess sich im Jahre 1883 in Sitten nieder. In der noch stark bäuerlich geprägten Stadt trug Fasanino bis zu seinem Tod im Jahre 1923 massgeblich zur Stadtentwicklung bei. Er arbeitete ebenfalls mit Joseph de Kalbermatten und Joseph Dufour zusammen. Diese gehörten zu den führenden Architekten jener Zeit. Der wohlwollende Arbeitgeber führte ein florierendes Geschäft und hinterliess ein umfassendes Lebenswerk, von dem heute zahlreiche Bauten abgebrochen worden sind.
A family business
Michel Fasanino, a Piedmont entrepreneur born in 1845, worked at Sion after setting up business there in 1883. In those days, Sion resembled an agricultural township rather than an urban centre. Fasanino played an outstanding part in the city’s expansion until his death in 1923. He also collaborated with the two most prominent architects of the period: Joseph de Kalbermatten and Joseph Dufour. This benevolent employer ran his prosperous business like a good family man. His legacy included many buildings, although some of them have since disappeared.
Un affare di famiglia
Imprenditore piemontese nato nel 1845, Michel Fasanino lavora a Sion sin dal suo insediamento nel 1883. A quell’epoca, la città assomiglia maggiormente ad un borgo agricolo che ad una città urbana. Fino alla sua morte nel 1923, Fasanino contribuisce in modo notevole all’espansione della città. Collabora con due architetti di spicco dell’epoca, Joseph de Kalbermatten e Joseph Dufour. Capo benevolo dirige la sua attività prospera come un buon padre di famiglia e lascia innumerevoli opere, ad oggi in parte distrutte.
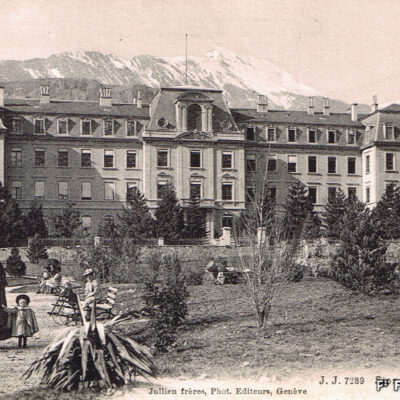
De la source au robinet
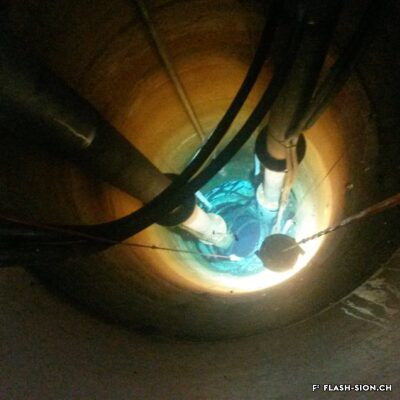
A la fin du 19e siècle, les multiples réclamations quant à la qualité et à la quantité de l’eau potable des fontaines forcent la Municipalité à réagir. En 1895, elle confie l’exécution d’un réseau d’eau potable relié à un grand réservoir à Platta à l’entreprise Dumont&fils. Cependant, les installations mises en service dès 1897, se révèlent non-conformes à plusieurs titres. Ainsi, les autorités reconsidèrent le captage des sources de la Fille et des Fontannées inauguré en 1901. Depuis, l’augmentation constante de la consommation d’eau contraint les services industriels de la Ville à trouver sans relâche de nouvelles sources d’approvisionnement. Dès 1931, le puits de Sainte-Marguerite pare aux cas d’urgence et, en 1951 et 1964, le deuxième et troisième réservoir de Tourbillon sont mis en service. Aujourd’hui, la mise en valeur de cette ressource fragile et la sensibilisation de la population à une consommation responsable représentent plus que jamais les défis de demain.
Von der Quelle zum Wasserhahn
Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts zwingen zahlreiche Beschwerden, welche Qualität und Menge des Trinkwassers in den Brunnen bemängeln, die Stadtverwaltung zum Handeln. Letztere beauftragt 1895 das Unternehmen Dumont&Söhne mit der Planung einer zentralen Wasserversorgung, zu welcher ebenfalls das Reservoir in Platta zählt. Die 1897 in Betrieb genommene Anlage erweist sich jedoch von Anfang an und in verschiedenen Punkten als nicht konform. Die Fassung der Quellen «de la Fille» und «des Fontanées» wird daher durch die Stadtbehörden wiedererwägt und 1901 eingeweiht. Seither verpflichtet der stetig steigende Trinkwasserverbrauch die Stadtwerke, immer neue Wasserquellen zu erschliessen. Ab 1931 beugt das Grundwasserpumpwerk von Sainte-Marguerite Notsituationen vor, 1951 und 1964 werden das zweite und das dritte Reservoir in Tourbillon in Betrieb genommen. Heute stellen die Erschliessung dieser lebenswichtigen Ressource und die Sensibilisierung der Bevölkerung für einen verantwortungsvollen Verbrauch mehr denn je eine Herausforderung für die Zukunft dar.
From source to tap
At the end of the 19th century, the numerous complaints about the quality and quantity of the drinking water from the fountains forced the Municipality to react. In 1895, it appointed the Dumont&fils company to execute the construction of a drinking water network connected to a large reservoir in Platta. However, the installations put into service in 1897 proved to be non-compliant in several respects. Thus, the authorities reconsidered the catchment of the Fille and Fontannées springs, which were inaugurated in 1901. The constant increase in water consumption forced the city’s industrial services to find new sources of supply. From 1931, the Sainte-Marguerite well was used for emergencies and, in 1951 and 1964, the second and third Tourbillon reservoirs were put into service respectively. Today, the development of this fragile resource and the raising of public awareness about responsible consumption are more than ever the challenges of tomorrow.
Dalla sorgente al rubinetto
Alla fine del XIX secolo, le numerose lamentele per la qualità e la quantità dell’acqua potabile delle fontane costrinsero il comune a reagire. Nel 1895, affidò la costruzione di una rete di acqua potabile collegata a un grande serbatoio a Platta alla società Dumont&fils. Tuttavia, gli impianti messi in servizio nel 1897 si rivelarono non conformi sotto diversi aspetti. Le autorità quindi riconsiderarono il bacino di raccolta delle sorgenti Fille e Fontannées, inaugurate nel 1901. Da allora, il costante aumento del consumo di acqua ha costretto i servizi industriali della città a trovare nuove fonti di approvvigionamento. Dal 1931, il pozzo di Sainte-Marguerite fu utilizzato per le emergenze e, nel 1951 e nel 1964, furono messi in funzione il secondo e il terzo serbatoio di Tourbillon. Oggi, lo sviluppo di questa fragile risorsa e la sensibilizzazione della popolazione a un consumo responsabile sono più che mai le sfide del domani.
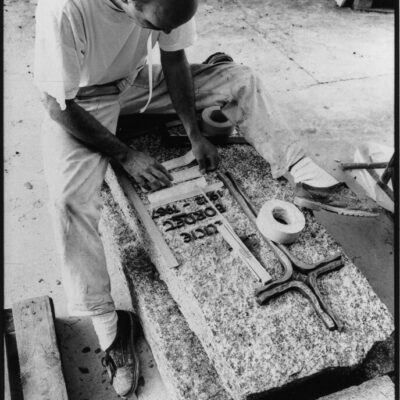
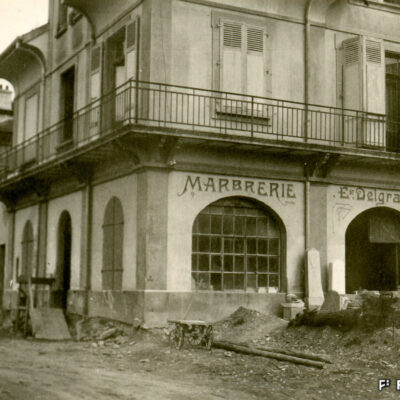
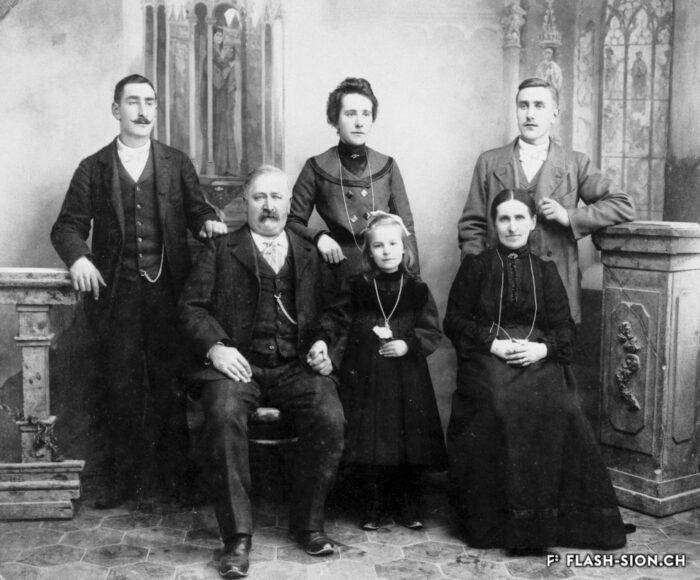
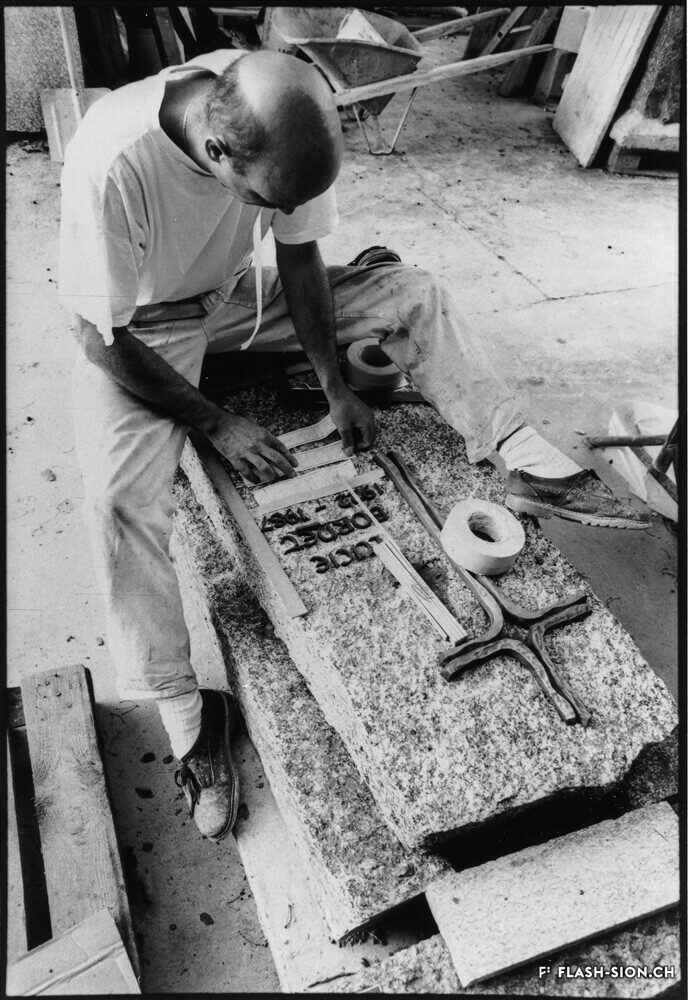
Sion gravée dans la pierre
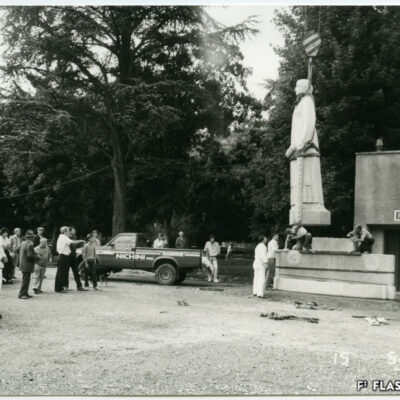
Important les compétences nécessaires au travail de la pierre, des marbriers et sculpteurs originaires du Val d’Ossola dominent le secteur dès la fin du 19e siècle et contribuent largement à l’essor de la ville du 20e siècle. En 1906, les frères Nichini déploient leur activité à Sion et marquent durant trois générations la construction en pierre de la cité. Exploitant d’une carrière à Bramois, Albert Nichini, devient par la suite propriétaire de la carrière d’Evolène, dont les pierres ornent de nombreux bâtiments et monuments de la ville.
Sion, in Stein gemeisselt
Ab Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts dominieren die für ihre Fachkenntnis bekannten Steinhauer und Steinmetze aus dem Val d’Ossola den Berufszweig der Steinbearbeitung und tragen massgeblich zur Stadtentwicklung im 20. Jahrhundert bei. Die Gebrüder Nichini nehmen im Jahr 1906 ihre Tätigkeit in Sitten auf und prägen über drei Generationen den Steinbau der Stadt. Vorerst Betreiber eines Steinbruchs in Bramois, erwirbt Albert Nichini später den Steinbruch von Evolène, dessen Steinplatten zahlreiche Gebäude und Denkmäler der Stadt schmücken.
Sion – carved in stone
Marble masons and sculptors from Val d’Ossola brought with them the skills needed to work with stone; they dominated the industry from the late 19th century onwards and played a key part in the city’s dynamic growth in the 20th century. The Nichini brothers set up their business at Sion in 1906 and for three generations, they left their mark on the city’s stone architecture. Albert Nichini operated a quarry at Bramois and then became the owner of the Evolène quarry, which supplied stone to decorate many of the city’s buildings and monuments.
Sion incisa nella pietra
Ritenute importanti le competenze necessarie al lavoro della pietra, marmisti e scultori originari della Val d’Ossola dominano il settore dalla fine del 19° secolo e contribuiscono notevolmente all’espansione della città del 20° secolo. Nel 1906, i fratelli Nichini sviluppano la loro attività a Sion e segnano per tre generazioni il settore della costruzione in pietra della città. Esercente di una cava a Bramois, Albert Nichini diventa in seguito il proprietario della cava di Evolène, le cui pietre abbelliscono numerosi edifici e monumenti della città.
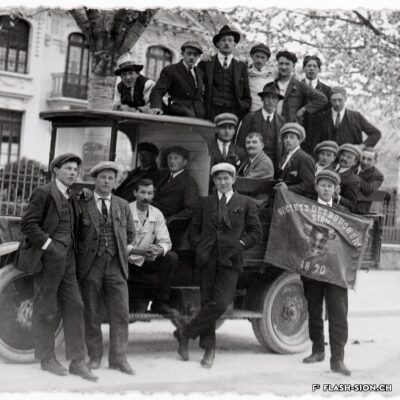
La construction dans les gènes
Depuis l’Antiquité, bâtisseurs, maître-maçons et entrepreneurs italiens marquent la construction en pierre de la cité sédunoise et du Valais. Reconnus pour leur savoir-faire artisanal et leur force de travail exemplaires, des entrepreneurs italiens feront également partie, en 1919, des membres fondateurs de l’Association Valaisanne des Entrepreneurs. Si ces « étrangers » seront perçus comme une menace lors des grandes crises économiques du 20e siècle, le secteur de la construction compte aujourd’hui encore de nombreux entrepreneurs d’origine transalpine.
Das Bauwesen im Blut
Seit der Antike prägen italienische Baumeister, Maurermeister und Unternehmer die Steinbauweise der Stadt Sitten und des Wallis. Bekannt für ihr handwerkliches Können und ihre unermüdliche Arbeitskraft, gehören 1919 ebenfalls italienische Baumeister zu den Gründungsmitgliedern des Walliser Baumeisterverbandes. Zwar werden diese “Fremdarbeiter” während den grossen Wirtschaftskrisen des 20. Jahrhunderts als Bedrohung wahrgenommen, doch prägen noch heute zahlreiche italienischstämmige Unternehmer den Bausektor.
Building is in their genes
Since ancient times, Italian builders, master masons and contractors have left their mark on the stone architecture that typifies the city of Sion and Valais canton. Italian contractors were renowned for their craftsmanship and their outstanding labour force; in 1919, they were also among the founding members of the Valais Association of Building Contractors. These “foreigners” were viewed as a threat during the major economic crises of the 20th century, but today’s construction sector still includes many contractors who trace their origins to the southern side of the Alps.
L’edilizia nei geni
Dall’antichità, costruttori, capimastri e imprenditori italiani segnano il settore della costruzione in pietra della città di Sion e del Vallese. Riconosciuti per il loro know-how, le loro competenze nell’artigianato e la loro forza lavoro esemplari, gli imprenditori italiani faranno parte nel 1919 dei membri fondatori dell’Associazione vallesana degli Imprenditori. Se questi “stranieri” sono considerati come una minaccia durante le grandi crisi economiche del 20° secolo, il settore dell’edilizia conta ancora oggi numerosi imprenditori di origine transalpina.
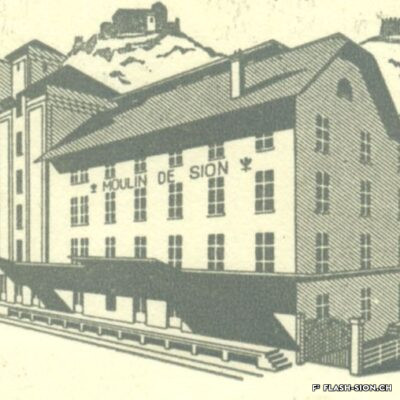
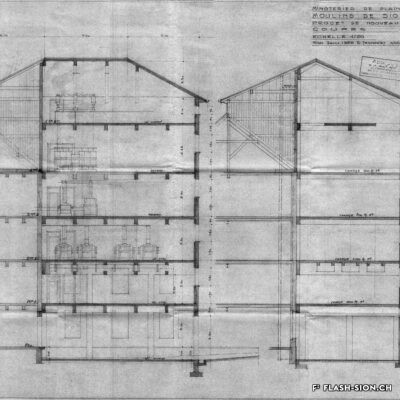
Un moulin à la pointe
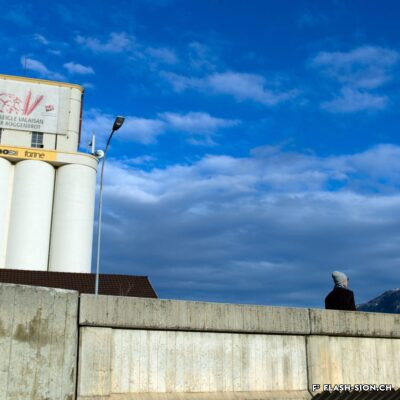
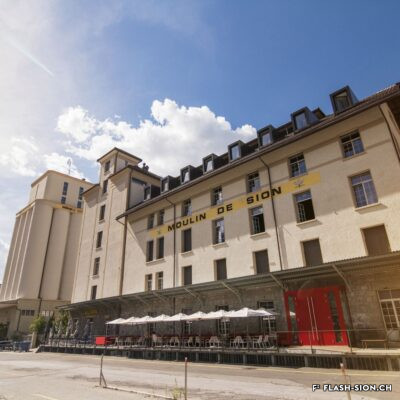
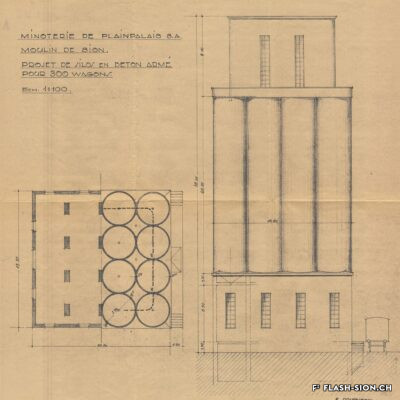
Après une tentative infructueuse à l’aube du 20e siècle, les Minoteries de Plainpalais (Genève) ouvrent une succursale à Sion en 1919. Le Moulin de Sion, entreprise d’importance pour le développement économique du Valais, s’agrandit rapidement. Les premiers silos en béton armé sont construits en 1925. Un peu moins de 15 ans plus tard, il faut en édifier d’autres. Le complexe continue de s’étendre jusqu’en 1980. Au fil du temps, les techniques évoluent et, dès 1984, les opérations sont entièrement automatisées. Le Moulin de Sion est alors un des plus modernes d’Europe ! Suite à l’obtention du label AOC pour le pain de seigle – premier pain d’Europe à le recevoir –, le Moulin de Sion se consacre entièrement à la fabrication de la farine de seigle. En 2015, la production est déplacée à Naters et le bâtiment peut alors être totalement réaffecté. Tout en conservant son apparence extérieure, les lieux accueillent désormais restaurants, fitness, bureaux et appartements notamment.
Modernste Mühlentechnik
Nach einem erfolglosen Niederlassungsversuch zu Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts eröffnen die Minoteries de Plainpalais (Genf) schliesslich 1919 eine Zweigstelle in Sitten. Die Mühle von Sitten nimmt in der wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung des Wallis eine wichtige Stellung ein und wird schon nach kurzer Zeit ausgebaut. 1925 entstehen die ersten Silos aus Stahlbeton. Nur knapp 15 Jahre später, werden weitere Silos erstellt. Bis 1980 wird der Mühlenkomplex kontinuierlich erweitert und die Mühlentechnik modernisiert. Ab 1984 wird der Betrieb schliesslich vollständig automatisiert. Die Mühle Sitten zählt zu dieser Zeit zu einem der modernsten Betriebe Europas! Nach dem Eintrag des Walliser Roggenbrotes ins Register der Ursprungsbezeichnung (GUB) – das erste Brot in Europa mit dieser Bezeichnung – widmet sich die Mühle Sitten ganz der Herstellung von Roggenmehl. 2015 wird die Produktion nach Naters verlegt und die Industriebrache wird vollständig umgenutzt. Das äussere Erscheinungsbild der Mühle bleibt erhalten, der Gebäudekomplex beherbergt jedoch neu verschiedene Restaurants, ein Fitnesscenter, Büroräumlichkeiten und moderne Wohnungen.
A mill at the forefront
After an unsuccessful attempt at the beginning of the 20th century, the Minoteries de Plainpalais (Geneva) opened a branch in Sion in 1919. The Moulin de Sion (Mill of Sion), an important company for the economic development of Valais, expanded rapidly. The first reinforced concrete silos were built in 1925. A little less than 15 years later, others had to be built. The complex continued to expand until 1980. Over time, technologies evolved and, in 1984, operations were fully automated. The Moulin de Sion became one of the most modern in Europe! After obtaining the AOC (PDO) label for rye bread – the first bread in Europe to receive it – the Moulin de Sion devoted itself entirely to the production of rye flour. In 2015, production was moved to Naters and the building’s function was completely reassigned. While retaining its external appearance, the premises now house restaurants, fitness centres, offices and flats, among other things.
Un mulino all’avanguardia
Dopo un tentativo fallito all’inizio del XX secolo, i mulini di Plainpalais (Ginevra) aprirono una filiale a Sion nel 1919. Il Moulin de Sion, un’azienda importante per lo sviluppo economico del Vallese, si espanse rapidamente. I primi silos in cemento armato furono costruiti nel 1925. Poco meno di 15 anni dopo, è stato necessario costruirne altri. Il complesso continuò ad espandersi fino al 1980. Nel corso del tempo, le tecniche si sono evolute e, a partire dal 1984, le operazioni sono state completamente automatizzate. Il Moulin de Sion è diventato così uno dei più moderni d’Europa! Dopo aver ottenuto il marchio AOC per il pane di segale – il primo pane in Europa a riceverlo – il Moulin de Sion si è dedicato interamente alla produzione di farina di segale. Nel 2015 la produzione si è spostata a Naters e l’edificio ha potuto essere completamente riutilizzato. Pur mantenendo il suo aspetto esterno, i locali ospitano oggi, tra l’altro, ristoranti, centri fitness, uffici e appartamenti.
Sion, la gourmande
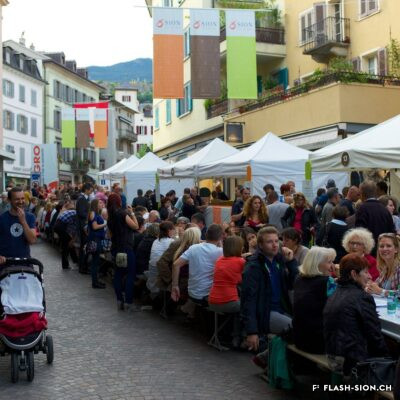
Le 17 novembre 1935, les salons de l’Hôtel de la Planta accueillent la première exposition et concours d’art culinaire du Valais. Si la mise en valeur des produits du pays et l’art culinaire sont représentés lors de fêtes des vignerons, il faudra cependant attendre 1973 pour voir s’organiser, à Sierre, un autre concours culinaire. A cette occasion, un membre du jury souligne déjà à quel point l’art du bien manger est en train de se perdre. L’avènement du fast-food et l’industrialisation de la filière alimentaire renforcent encore ce constat qui conduit à l’organisation de la première semaine romande du goût en 2001. Sion participe à la manifestation annuelle dès 2003 et est d’emblée élue ville du goût. Forte de cette expérience et pouvant compter sur des acteurs locaux enthousiastes, la nouvelle politique touristique adoptée dès 2007 positionne Sion comme ville du goût. Depuis, la ville étoffe son offre touristique autour du label « Sion terroir urbain ».
Sitten, die Genüssliche
Am 17. November 1935 findet in den Sälen des Hotels de la Planta die erste kulinarische Ausstellung des Wallis mit Kochwettbewerb statt. Obwohl Winzerfeste darauf die regionalen Produkte und die Kochkunst des Wallis würdigen, kommt es erst 1973 in Sierre zu einem weiteren Kochwettbewerb. Bei dieser Gelegenheit spricht ein Jurymitglied bereits seine Besorgnis über den zunehmenden Verlust des guten Essens aus. In der Folge verstärken das Aufkommen von Fastfood und die Industrialisierung der Lebensmittelkette zusätzlich die Junkfood-Welle, die 2001 massgeblich zur Organisation der ersten Westschweizer Genusswoche führt. Sitten nimmt ab 2003 an dieser jährlichen Veranstaltung teil und wird auf Anhieb zur Genussstadt des Jahres gewählt. Diese positive Erfahrung und die Begeisterung der lokalen Akteure ermutigen die Behörden, über ihre neue Tourismuspolitik Sitten als Genussstadt zu positionieren. Seither baut die Stadt ihr touristisches Angebot rund um die Marke «Sion, terroir urbain» kontinuierlich aus.
Sion, city of food lovers
On November 17, 1935, the lounges of the Hôtel de la Planta hosted the first exhibition and competition of culinary art in the canton of Valais. Even though the promotion of the country’s products and the culinary art were present at the time of wine festivals, it was necessary to wait until 1973 to see another culinary contest being organised in Sierre. Already on that occasion, a jury member emphasized the degree to which the art of eating well was being lost. This observation was further reinforced by the arrival of fast food and the industrialisation of the food sector, resulting in the organisation of the first Week of Taste in French-Speaking Switzerland in 2001. Sion first took part in the annual event in 2003 and was immediately elected City of Taste. Benefiting from this experience and being able to count on enthusiastic local players, the new tourism policy, adopted in 2007, positioned Sion as a City of Taste. Since then, the city has been developing its tourism offer around the label “Sion urban terroir”.
Sion, la buongustaia
Il 17 novembre 1935, i saloni dell’Hôtel della Planta ospitarono la prima mostra e concorso di arte culinaria del Vallese. Sebbene la promozione dei prodotti locali e l’arte culinaria fossero presenti nelle feste del vino, solo nel 1973 è stato organizzato un altro concorso culinario a Sierre. In questa occasione, uno dei membri della giuria ha sottolineato quanto si stia perdendo l’arte di mangiar bene. L’avvento dei fast food e l’industrializzazione dell’industria alimentare hanno rafforzato ulteriormente questa osservazione, che ha portato all’organizzazione della prima Settimana del Gusto francofona nel 2001. Sion ha partecipato all’evento annuale dal 2003 ed è stata subito eletta città del gusto. Forte di questa esperienza e potendo contare su attori locali entusiasti, la nuova politica turistica adottata nel 2007 ha posizionato Sion come città del gusto. Da allora, la città ha sviluppato la sua offerta turistica attorno al marchio “Sion terroir urbain”.
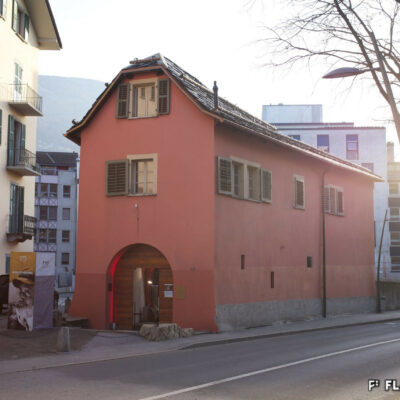
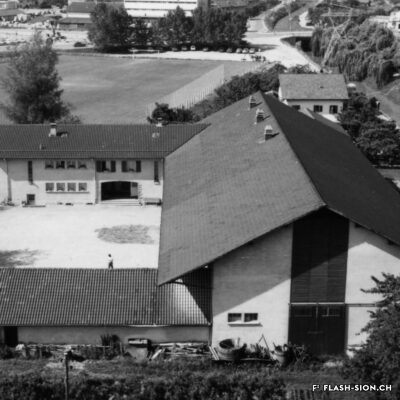
De la ferme au centre culturel
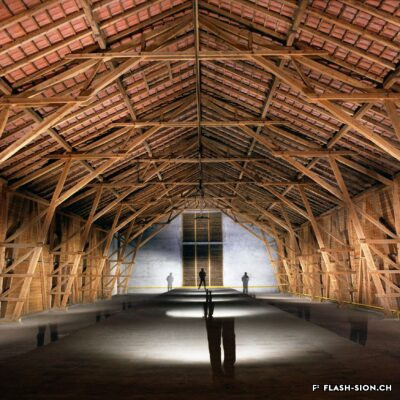
La Ferme-Asile n’a pas toujours été le centre polyvalent dédié à l’art contemporain qu’il est aujourd’hui. Autrefois ferme de l’Hôpital-Asile, l’exploitation approvisionnait l’hôpital de Sion de 1955 à 1984. Laissé à l’abandon en pleine zone urbaine durant une dizaine d’années, ce témoin unique de l’activité agricole sédunoise des années 1950 suscite l’intérêt d’un groupe d’artistes, qui y voit l’opportunité de créer un lieu pluridisciplinaire vecteur de synergies culturelles. Ce centre artistique, nommé tout d’abord « Centre Culturel LézArt » voit le jour et se développe grâce à l’investissement d’artistes et de bénévoles. Depuis 1996, la bâtisse transformée abrite des ateliers d’artistes et un restaurant. Des expositions temporaires y sont régulièrement organisées. Au gré des financements et des agrandissements, l’établissement ouvre salle de concert, nouveaux espaces et ateliers supplémentaires. La rénovation de 2009 permet enfin l’utilisation sur toute l’année de la grange à la charpente impressionnante.
Vom Bauernhof zum Kulturzentrum
Heute widmet sich das vielseitige Zentrum der «Ferme-Asile» der zeitgenössischen Kunst – das war nicht immer so. Der ehemalige Bauernhof des Burgerspitals versorgte von 1955 bis 1984 das Krankenhaus von Sitten. Dieser einzigartige landwirtschaftliche Zeitzeuge der 1950er Jahre weckte das Interesse einer Gruppe von Kunstschaffenden, die hier einen multidisziplinären Ort einrichten wollten, um kulturelle Synergien zu nutzen. Das “Centre Culturel LézArt”, wie anfangs das Kulturzentrum genannt wurde, konnte nur dank grossem Engagement der beteiligten Kunstschaffenden und ehrenamtlicher Arbeit eröffnet werden. Seit 1996 beherbergen die umgebauten landwirtschaftlichen Gebäude Künstlerateliers und ein Restaurant. Es werden regelmässig Wechselausstellungen gezeigt. Durch weitere Finanzierungsmittel konnten im Laufe der Jahre ein Konzertsaal, neue Räumlichkeiten und zusätzliche Ateliers eröffnet werden. Die Renovation von 2009 ermöglicht nun die ganzjährige Nutzung der Scheune mit ihrem imposanten Dachstuhl.
From being a farm to becoming a cultural centre
The Ferme-Asile was not always the multi-purpose centre dedicated to contemporary art that it is today. Formerly the farm of the Hôpital-Asile, it supplied the hospital of Sion from 1955 to 1984. Left abandoned in the middle of an urban area for about ten years, this unique witness to the agricultural activity of Sion in the 1950s aroused the interest of a group of artists, who saw in it the opportunity to create a multi-disciplinary venue, a vector of cultural synergies. The artistic centre, initially named “Centre Culturel LézArt”, was born and developed thanks to the investment of artists and volunteers. Since 1996, the transformed building has housed artists’ studios and a restaurant. Temporary exhibitions are regularly held there. As funding was received and extensions were built, the establishment opened a concert hall, new rooms and additional workshops. The renovation in 2009 finally made it possible to use the barn with its impressive roof structure all year round.
Da fattoria a centro culturale
La Ferme-Asile non è sempre stata il centro polifunzionale dedicato all’arte contemporanea che è oggi. Un tempo fattoria dell’ospedale psichiatrico, ha rifornito l’ospedale di Sion dal 1955 al 1984. Abbandonata per dieci anni nel bel mezzo di un’area urbana, questa testimonianza unica dell’attività agricola sedunese negli anni Cinquanta ha suscitato l’interesse di un gruppo di artisti che hanno visto in essa l’opportunità di creare un luogo multidisciplinare, vettore di sinergie culturali. Questo centro artistico, inizialmente denominato “Centre Culturel LézArt”, è nato e si è sviluppato grazie all’investimento di artisti e volontari. Dal 1996, l’edificio trasformato ospita ateliers di artisti e un ristorante. Inoltre, vi si tengono regolarmente mostre temporanee. Grazie ai finanziamenti e agli ampliamenti, lo stabilimento ha aperto una sala concerti, nuovi spazi e ateliers. La ristrutturazione del 2009 ha finalmente consentito di utilizzare tutto l’anno il fienile con la sua imponente struttura del tetto.
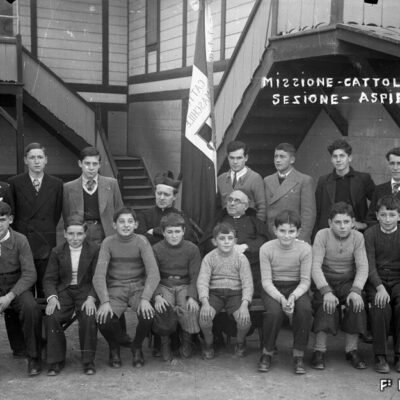
Un point de rencontre italo-sédunois
Institution historique et lieu de rassemblement, la Colonia Italiana réunit la communauté des Italiens de Sion dans son bâtiment de la rue de la Majorie depuis plus de soixante ans. Le foyer italien est fondé en 1958 sous l’impulsion de groupes actifs sur les plans sportif et artistique. Leur souhait est de disposer d’un lieu pour se réunir et partager leurs traditions. Rencontres culinaires, expositions, animations culturelles et autres activités rythment depuis lors la vie de ce lieu italo-sédunois.
Begegnungsort der Italienischen und Sittener Gemeinde
Seit mehr als 60 Jahren versammelt sich die italienische Gemeinde in der Colonia Italiana an der Rue de la Majorie. Die geschichtsträchtige Institution und der Treffpunkt von Italienern und Italienerinnen aus Sitten wurde 1958 auf Anregung verschiedener in Sport und Kultur tätigen Gruppen gegründet. Sie hatten das Bedürfnis einen Begegnungsort zu schaffen, wo sie sich treffen und austauschen konnten. Kulinarische Anlässe, Ausstellungen, kulturelle Veranstaltungen sowie weitere Aktivitäten prägen seither das Leben des “Italo-Sittener” Vereinslokals.
Where Italy meets Sion
The Colonia Italiana building in Rue de la Majorie is a historic institution where Sion’s Italian community has gathered together for over 60 years. This Italian centre was founded in 1958 at the initiative of various groups involved in sports and the arts. They wanted a place to meet and share their traditions. This venue where Italy meets Sion stages a regular programme of culinary events, exhibitions, cultural entertainment and other activities.
Un punto di ritrovo italo-sedunese
Istituzione storica e luogo di ritrovo, la Colonia italiana raduna la comunità degli Italiani di Sion nell’edificio in “rue de la Majorie” da oltre sessant’anni. Il focolare italiano è stato fondato nel 1958 sotto l’impulso di gruppi attivi nel campo sportivo e artistico. Il loro intento è quello di disporre di un luogo per riunirsi e condividere le proprie tradizioni. Incontri culinari, mostre, animazioni culturali e altre attività scandiscono da quel momento la vita di questo luogo italo-sedunese.
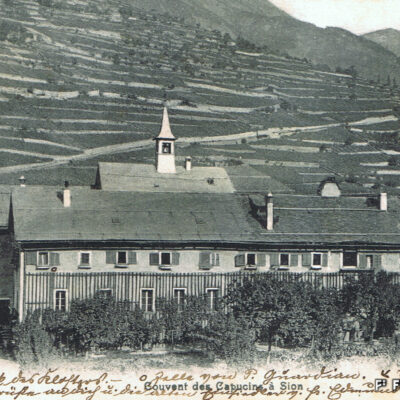
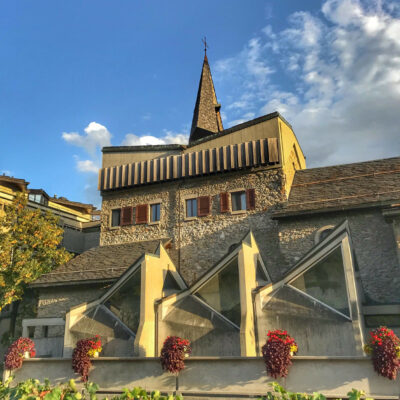
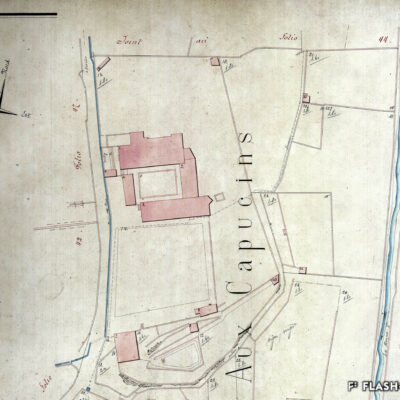
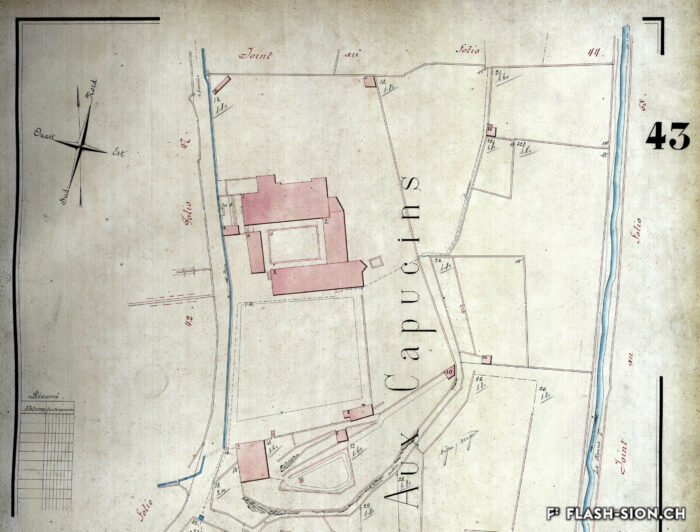
Un monument d’importance (inter-)nationale
Le travail du Vénitien Mirco Ravanne ne passe pas inaperçu au couvent des Capucins. L’architecte est appelé au début des années 1960 par le père Damien qui le charge de transformer et d’agrandir l’édifice religieux. A l’avant-garde à l’époque, son intervention résolument moderne vient contraster avec les structures de la bâtisse du 17e siècle tout en les respectant. Ravanne ne néglige aucun détail que ce soit dans l’architecture ou dans le mobilier « made in Italy ». Aujourd’hui, le couvent, propriété de la Bourgeoisie, est considéré comme son œuvre architecturale majeure.
Ein Denkmal von (inter-)nationaler Bedeutung
Die Arbeit des Venezianers Mirco Ravanne sorgte für Aufruhr im Kapuzinerkloster von Sitten. Der Architekt wurde Anfang der 1960er Jahre vom Guardian Pater Damien mit der Umgestaltung und Erweiterung der Klosteranlage beauftragt. Sein avantgardistischer Eingriff steht auf den ersten Blick in starkem Kontrast mit der historischen Struktur der Anlage aus dem 17. Jahrhundert, vermag aber bei genauerem Hinschauen eindrücklich zwischen Alt und Neu zu vermitteln. Ravannes Liebe zum Detail offenbart sich sowohl in seiner Architektur als auch in der von ihm entworfenen Ausstattung “Made in Italy”. Heute gilt das im Besitz der Burgergemeinde befindliche Kapuzinerkloster als das bedeutendste Werk des Architekten.
A monument of national and international importance
Visitors to the Capuchin Monastery are bound to admire the work of the Venetian architect Mirco Ravanne. In the early 1960s, Father Damien commissioned him to transform and extend this religious building. The architect took a decidedly modern, avant-garde approach to his work, which contrasts with the 17th-century structures of the building but also shows respect for them. Ravanne paid full attention to every detail, both in the architecture and the “made in Italy” furnishings. The monastery, which now belongs to the Bourgeoisie (municipality), is regarded as his architectural masterpiece.
Un monumento d’importanza (inter-)nazionale
L’operato del Veneziano Mirco Ravanne non passa di certo inosservato al convento dei Cappuccini. L’architetto è chiamato all’inizio degli anni 60 dal padre Damien che gli affida il compito di trasformare e ampliare l’edificio religioso. All’epoca all’avanguardia, il suo intervento decisamente moderno contrasta con le strutture dell’edificio del 17° secolo pur rispettandole. Ravanne non trascura alcun dettaglio sia nell’architettura che nel mobilio “made in Italy”. Ad oggi, il convento, proprietà della Borghesia, è considerato come la sua operata architettonica maggiore.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Le « Boccalino » ouvre ses portes en 1968 à la rue de Conthey. Il est le premier établissement sédunois à mettre à l’honneur la pizza, plat symbole de toute une nation. Des épiceries aux noms italiens existaient par ailleurs en vieille ville dès le début du 20e siècle, tels que Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli ou encore Guido Nichini. Ce dernier, spécialisé dans la charcuterie et salaisons « exclusivement italiennes » avait à l’origine pignon sur la « via regia », une des appellations de l’actuelle rue de Conthey.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Das Restaurant “Boccalino” wurde 1968 in der Rue de Conthey eröffnet. Es war das erste Restaurant der Stadt, das sich ganz dem italienischen Nationalgericht, der Pizza, verschrieb. Seit Anfang des 20. Jahrhunderts sind in der Altstadt von Sitten auch Lebensmittelgeschäfte mit italienischen Namen wie Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli und Guido Nichini bekannt. Letzterer hatte sich insbesondere auf italienische Wurst- und Pökelwaren spezialisiert und führte seinen Feinkostladen ursprünglich an der “Via Regia”, wie die heutige Rue de Conthey ebenfalls genannt wurde.
Mangia che ti fa bene
The Boccalino opened on Rue de Conthey in 1968. It was the first restaurant in Sion to feature pizza – the iconic dish of an entire nation. Elsewhere in the old town, there had been grocery stores with Italian names such as Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli and Guido Nichini since the early 20th century. Nichini, which specialised in “exclusively Italian” cooked and cured meats, originally fronted onto the “via regia”, one of the names for the street now known as Rue de Conthey.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Il “Bocccalino” apre le sue porte nel 1968 nella “rue de Conthey”. È il primo stabilimento di Sion ad omaggiare la pizza, piatto simbolo di tutta una nazione. Botteghe con nomi italiani esistevano d’altronde nella città vecchia già all’inizio del 20° secolo, come Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli oppure Guido Nichini. Quest’ultimo, specializzato in prodotti di salumeria e carni affumicate “esclusivamente italiane” possedeva un negozio nella “via regia”, uno dei nomi dell’attuale “rue de Conthey”.
Studio, studi, studia…
Initiés par le gouvernement italien en 1971, les cours de langue et de culture italienne deviennent une institution incontournable, à Sion notamment. Ils garantissent une identité culturelle aux jeunes de la seconde génération et favorisent leur insertion dans les structures socio-culturelles locales. De plus, cette école reflète à merveille la volonté de maintenir vivant le lien qui unit le pays d’émigration et la cité d’accueil.
Studio, studi, studia…
1971 von der Italienischen Regierung initiiert, wurden die Schulen für Italienische Sprache und Kultur schweizweit zu einer eigentlichen Institution – so auch in Sitten. Sie vermitteln den jungen Menschen der zweiten Generation eine kulturelle Identität und fördern die Integration in die lokalen Strukturen. Darüber hinaus zeigt die Italienische Schule von Sitten den Wunsch, die Beziehung zwischen Herkunftsland und Gaststadt aufrechtzuerhalten.
Studio, studi, studia…
In 1971, the Italian government launched a series of Italian language and culture courses that have become an invaluable institution at Sion in particular. The courses ensure that second-generation youngsters benefit from a cultural identity, encouraging them to integrate into local socio-cultural structures. This school is also a superb expression of the desire to maintain a living link between immigrants’ country of origin and their host city.
Studio, studi, studia…
Avviati dal governo italiano nel 1971, i corsi di lingua e cultura italiana diventano un’istituzione imprescindibile, in particolare a Sion. Questi tutelano un’identità culturale ai giovani della seconda generazione e favoriscono il loro inserimento nelle strutture socioculturali locali. Inoltre, i corsi rispecchiano alla perfezione la volontà di mantenere vivo il legame che unisce il paese d’immigrazione e la città di accoglienza.
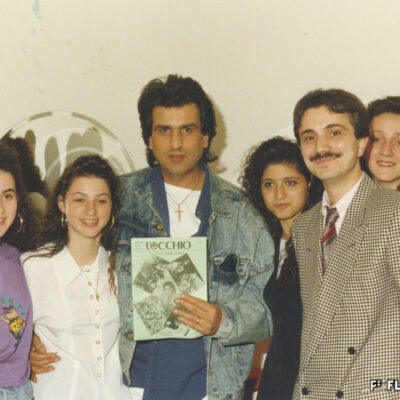
L’Occhio, le journal des Italiens
En 1986, un groupe de jeunes Italiens de Sion se lancent le défi de publier un journal pour informer leurs compatriotes. Cette chronique bilingue est éditée en français et en italien jusqu’en 1993. Pour les auteurs, il s’agit de montrer leur respect envers leur cité d’accueil et de mieux faire connaître leur culture d’origine aux Sédunois. Ces journalistes en herbe abordent entre autres les activités de la colonie italienne et les sorties culturelles, réalisent des portraits de personnalités italiennes et nous mettent l’eau à la bouche avec leurs recettes en fin de journal.
L’Occhio, die Zeitschrift der Italiener und Italienerinnen
Eine Gruppe italienischer Jugendlicher stellt sich 1986 der Herausforderung, eine Zeitung zur Information ihrer Landsleute herauszugeben. Die bis 1993 veröffentlichte Zeitschrift erscheint zweisprachig – auf italienisch und französisch. Damit bekundet das Redaktionsteam ihrer Gaststadt nicht nur seine Wertschätzung, sondern bringt den Einheimischen ebenfalls ihren kulturellen Hintergrund näher. Die Jung-Journalisten thematisieren unter anderem die Aktivitäten der Colonia Italiana sowie weitere kulturelle Anlässe. Sie präsentieren Porträts italienischer Persönlichkeiten und lassen der Leserschaft auf der letzten Seite mit ihren Rezepten buchstäblich das Wasser im Munde zusammenlaufen.
L’Occhio – the Italians’ magazine
In 1986, a group of young Italians at Sion took on the challenge of publishing a magazine to provide information for their compatriots. This bilingual periodical was published in French and Italian until 1993. The contributors aimed to show their respect for their host city, and to make their home culture better known to the people of Sion. Topics addressed by these budding journalists included the activities of the Italian community as well as cultural events; they painted portraits of prominent Italian figures and whetted our appetites with their recipes at the end of the magazine.
L’Occhio, il giornale degli italiani
Nel 1986, un gruppo di giovani italiani di Sion decidono di pubblicare un giornale informativo destinati ai connazionali. La cronaca bilingue viene redatta in francese e in italiano fino al 1993. L’intento degli autori era quello di mostrare il proprio rispetto nei confronti della città di accoglienza e di far conoscere agli abitanti di Sion la loro cultura di origine. Questi giornalisti in erba si occupano tra l’altro delle attività della colonia italiana e delle gite culturali, dipingono i ritratti delle personalità italiane e ci mettono l’acquolina in bocca con le ricette nelle ultime pagine del giornale.
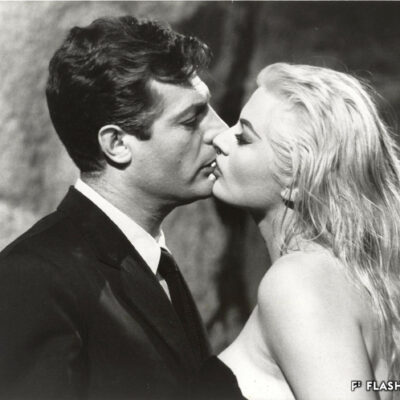
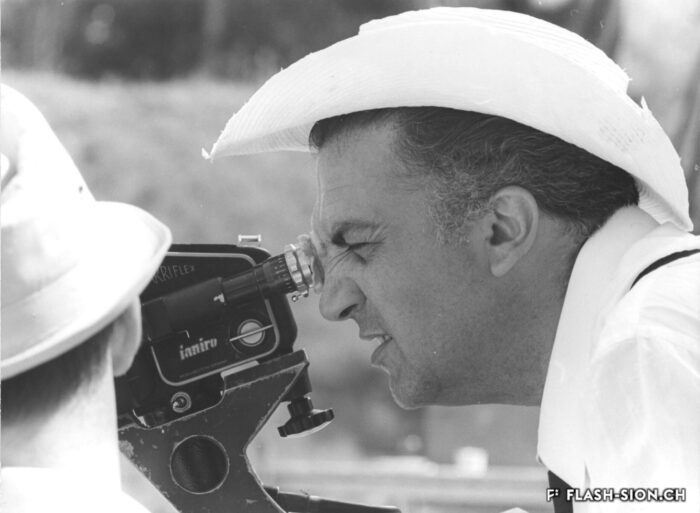
Evviva il Maestro
L’œuvre du réalisateur italien Federico Fellini est au cœur des activités de la Fondation Fellini pour le cinéma. Cette dernière possède un fonds de plus de 15’000 documents dont les 2/3 environ concernent l’œuvre du maestro. Depuis sa création en 2001, cette fondation organise des expositions en Suisse et à travers le monde. Elle permet ainsi au public de découvrir la richesse du travail du réalisateur en mettant en évidence les liens entre cinéma, littérature, photographie, architecture et musique. L’espace culturel ouvert en 2011 à la Maison du Diable apporte une touche méridionale supplémentaire à Sion.
Evviva il Maestro
Das Werk des italienischen Regisseurs Federico Fellini steht im Mittelpunkt der Aktivitäten der Stiftung Fellini. Diese verfügt über eine Sammlung von über 15’000 Dokumenten, von denen etwa zwei Drittel die Arbeit des Maestros betreffen. Seit ihrer Gründung im Jahr 2001 organisiert die Stiftung Ausstellungen in der Schweiz und auf der ganzen Welt. Ziel ist es, den Reichtum des Werkes des Regisseurs in Zusammenhang mit Kino, Literatur, Fotografie, Architektur und Musik aufzuzeigen. Mit der Eröffnung des Kulturraums in der “Maison du Diable” im Jahr 2011 erhielt Sittens südlicher Einschlag eine weitere Bereicherung.
Evviva il Maestro
The Fellini Foundation for Cinema focuses on the work of Federico Fellini, the Italian film director. It owns a collection of over 15,000 documents, about two thirds of which relate to the maestro’s work. The Foundation has staged exhibitions in Switzerland and across the globe since it was set up in 2001. It enables the public to explore the wealth of the director’s work by highlighting links between the cinema, literature, photography, architecture and music. The cultural centre, opened in 2011 at the Maison du Diable, brings yet another hint of the South to Sion.
Evviva il Maestro
L’opera del regista italiano, Federico Fellino, è il fulcro delle attività della Fondazione Fellini per il cinema. Quest’ultima possiede una collezione di più di 15’000 documenti, i cui 2/3 circa riguardano l’opera del maestro. Dalla sua nascita, nel 2001, la fondazione organizza delle mostre in Svizzera e attraverso il mondo. Permette in tal modo al pubblico di scoprire la ricchezza del lavoro del regista mettendo in risalto i legami tra cinema, letteratura, fotografia, architettura e musica. Lo spazio culturale aperto nel 2011 alla Casa del Diavolo offre un tocco meridionale rilevante a Sion.
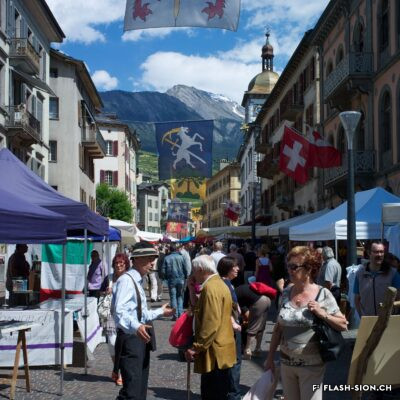
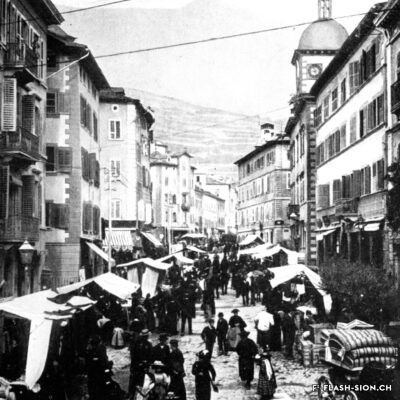
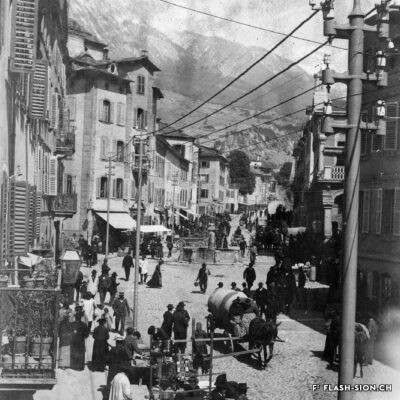
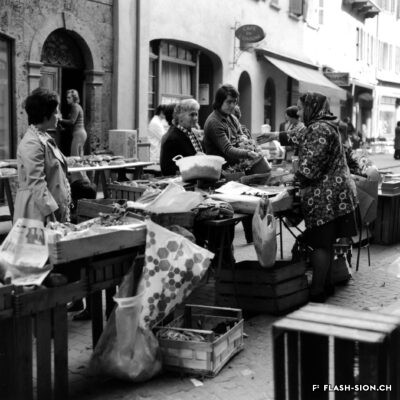
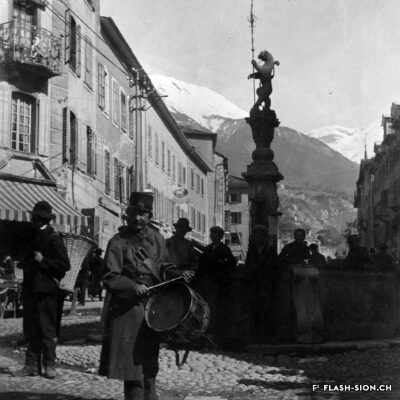
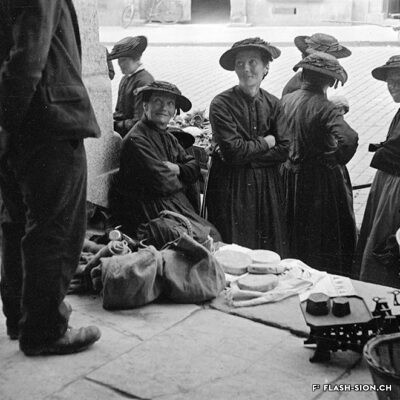
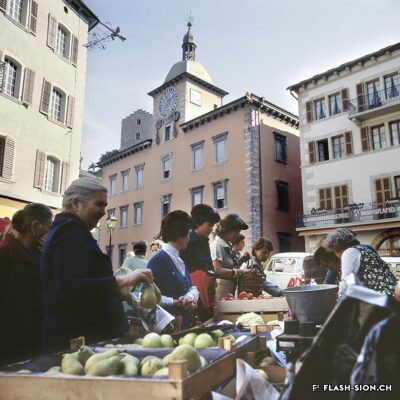
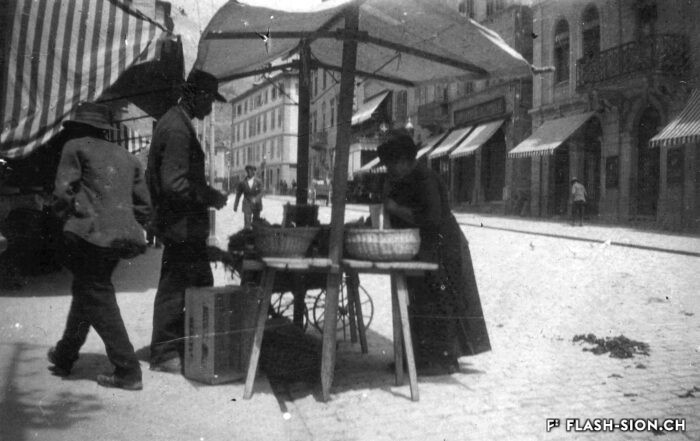
La convivialité dans le panier
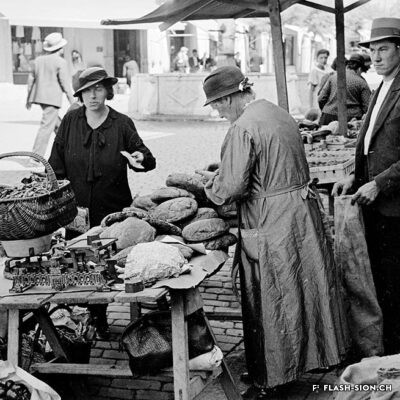
Dès le Moyen Age, les foires annuelles et concours de bétail animent la cité. Rythmant les saisons au gré des marchandises, les marchés des 19e et 20e siècles drainent un public varié et reconnectent la plaine à la montagne, ainsi que les clients aux producteurs et aux marchands. Qualité, prix et poids des marchandises sont contrôlés et les stands réglementés. Situé au cœur de la ville, le marché est alors un acteur principal de l’économie locale. Après un désintérêt progressif dès la seconde moitié du 20e siècle, le marché renaît en 2003, à l’initiative de l’Association des habitants de la vieille ville. Renouant avec la tradition, l’événement hebdomadaire très fréquenté atteste de sa grande attractivité. Devenu incontournable, le marché de la vieille ville s’affirme aujourd’hui comme lieu de rencontre et de convivialité.
Ein Marktkorb voller Geselligkeit
Seit dem Mittelalter beleben Jahrmärkte und Viehschauen die Stadt. Das rein saisonale Angebot auf den Wochenmärkten des 19. und 20. Jahrhunderts veranschaulicht den Lauf der Jahreszeiten, zieht ein vielfältiges Publikum an, verbindet die Seitentäler mit der Rhoneebene, sowie die Käufer mit den Produzenten und Händlern. Qualität, Preis und Gewicht der Waren werden kontrolliert und die Stände sind reglementiert. Mitten in der Stadt angesiedelt, entwickelt sich der Wochenmarkt zu einem der wichtigsten Zweige der lokalen Wirtschaft. In der zweiten Hälfte des 20. Jahrhunderts verliert der Markt zusehends an Bedeutung, bis er 2003 auf Initiative des Altstadt-Quartiervereins schliesslich wieder auflebt. Heute knüpft der Wochenmarkt gebührend an seine Tradition an und die vielen Besucherinnen und Besucher zeugen von seiner Attraktivität. Die Veranstaltung ist zu einem wöchentlichen Treffpunkt geworden, wo das gesellige Beisammensein im Vordergrund steht.
Conviviality in the basket
Since the Middle Ages, annual fairs and livestock competitions have brought life to the city. Throughout the seasons and their related produce, the markets of the 19th and 20th centuries attracted a varied public and connected the plain to the mountains, as well as customers to producers and merchants. The quality, price and weight of the goods were controlled, and the stalls were regulated. Situated in the heart of the city, the market became a major player in the local economy. After a gradual loss of interest in the second half of the 20th century, the market was revived in 2003 thanks to the initiative of the Association of the inhabitants in the old town. The weekly event, which is very well attended, is a revival of tradition and has become a major attraction. The market in the old town has become a must and is now a place where people meet and socialise.
Convivialità nel carrello
Fin dal Medioevo, le fiere annuali e i concorsi di bestiame hanno animato la città. Le stagioni erano scandite dalle merci proposte, i mercati del XIX e XX secolo hanno portato un pubblico variegato e hanno ricollegato la pianura alla montagna, nonché i clienti ai produttori e ai commercianti. La qualità, il prezzo e il peso delle merci erano controllati e gli stand regolamentati. Situato nel cuore della città, il mercato divenne un attore importante dell’economia locale. Dopo una graduale perdita di interesse nella seconda metà del XX secolo, il mercato è stato rilanciato nel 2003 su iniziativa dell’Association des habitants de la vieille ville (Associazione degli abitanti del centro storico). L’evento settimanale, molto frequentato, è un ritorno alla tradizione e testimonia la sua grande