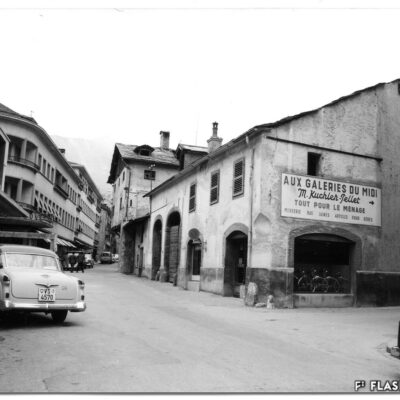
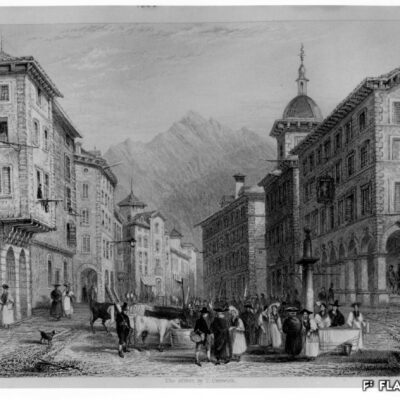
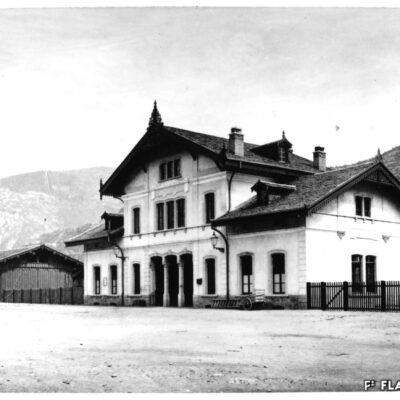
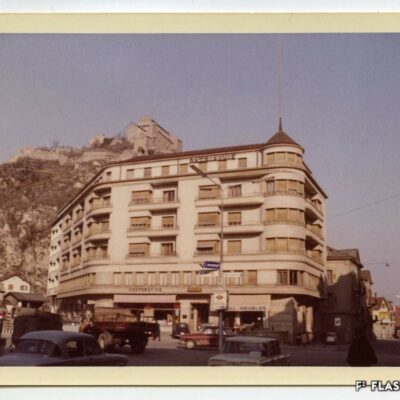
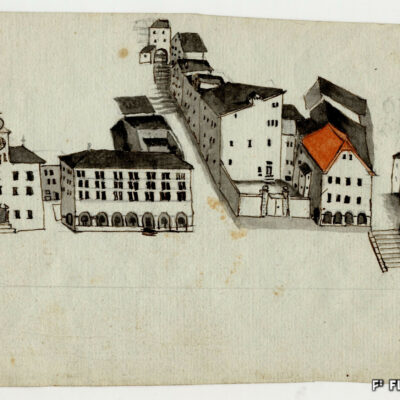
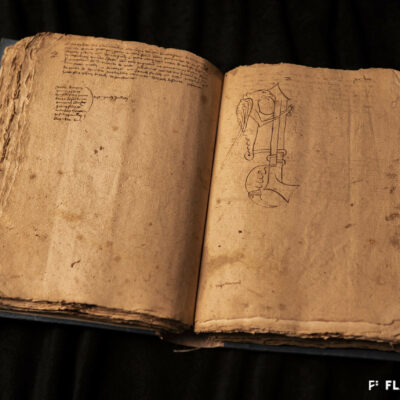
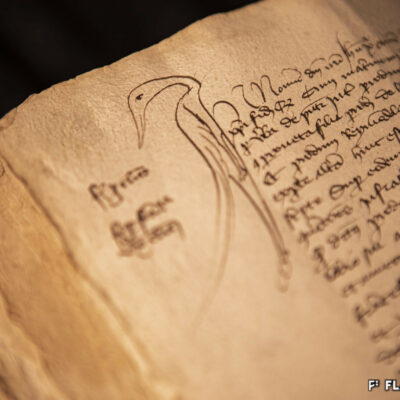
Des Lombards à Sion
A Sion, la présence de Lombards est attestée dès le 13e siècle. Actifs dans la banque et le commerce, ils prennent part au développement de la vie économique et politique sédunoise. Pourtant, la mention du quartier « en Lombardie » n’apparaît dans les écrits qu’à partir du 17e siècle, soit plusieurs siècles après leur installation. La rue qui porte leur nom est un hommage tardif. Une plaque commémorative posée au début de la rue de la Lombardie renforce encore ce souvenir des liens qui unissent le Valais et la Lombardie.
Lombarden in Sitten
In Sitten ist die Präsenz von Lombarden ab dem 13. Jahrhundert belegt. Sie betätigten sich als Kaufleute und Bankiers und waren massgeblich an der politischen und wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung der Stadt beteiligt. Der Name des Stadtteils “en Lombardie” tritt jedoch erst im 17. Jahrhundert in den Schriften auf. Die Strasse, die heute ihren Namen trägt, ist eine späte Hommage. Am Anfang der Rue de la Lombardie erinnert eine Gedenktafel an die Beziehungen zwischen der Lombardei und dem Wallis.
Lombards in Sion
There is evidence that Lombards were present in Sion from the 13th century onwards. They played an active part in banking and commerce, and they contributed to the development of Sion’s economic and political life. However, the city district known as “en Lombardie” is not mentioned in documentation until the 17th century – several centuries after the Lombards settled here. The street that bears their name is a belated tribute. A commemorative plaque installed at the start of Rue de la Lombardie is another reminder of the bonds that link Valais and Lombardy.
I lombardi a Sion
A Sion, la presenza dei lombardi è confermata dal 13° secolo. Attivi nel settore bancario e commerciale, prendono parte allo sviluppo della vita economica e politica di Sion.
Ciò nonostante, la menzione del quartiere “in Lombardia” appare negli scritti solo dal 17° secolo, ossia molti secoli dopo il loro insediamento. La via, che porta il loro nome, è un omaggio tardivo. Una targa commemorativa installata all’inizio della via “rue de la Lombardie” rafforza maggiormente il ricordo dei legami tra il Vallese e la Lombardia.
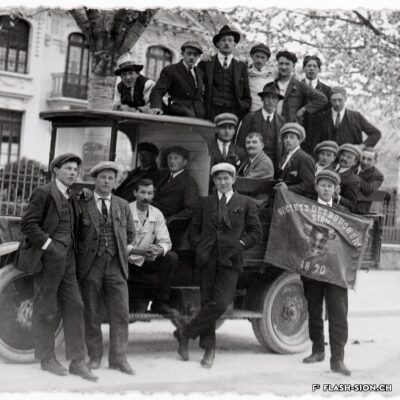
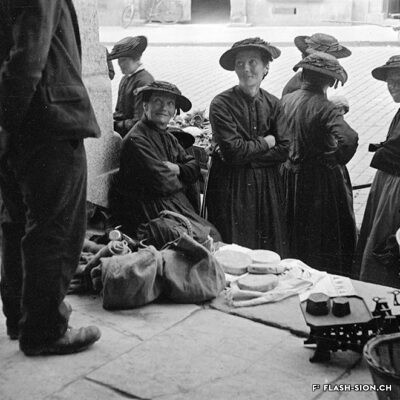
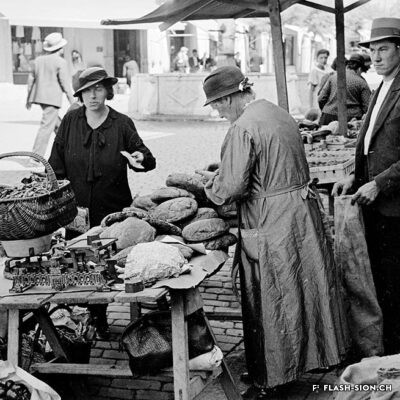
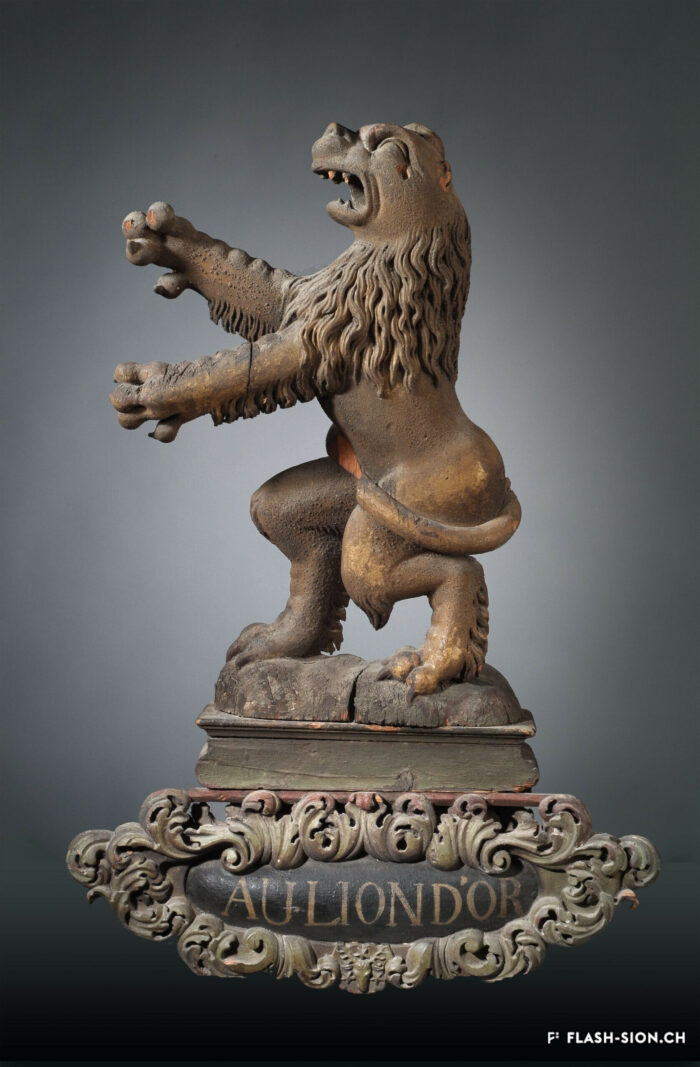
Une chambre, aubergiste !
En quête de romantisme alpin, les premiers touristes apparaissent en Valais dans la seconde moitié du 18e siècle. Les voyageurs de passage pour la nuit font halte chez l’aubergiste. Le plus souvent familiale, l’auberge accueille tant les nobles que les voyageurs ou commerçants. L’auberge du Lion d’Or était l’un des plus anciens établissements de la capitale. Des célébrités telles que Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1744), Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1779) ou encore l’impératrice Joséphine (1812) y prirent une chambre lors de leur séjour à Sion. Dès le milieu du 19e siècle, les auberges cèdent progressivement la place aux hôtels qui se professionnalisent. Peu à peu, les guides de voyage aident les touristes dans leurs déplacements, proposent des itinéraires et fournissent les informations pratiques.
Ein Zimmer bitte!
Auf der Suche nach der viel besungenen Alpenromantik kommen in der zweiten Hälfte des 18. Jahrhunderts die ersten Touristen ins Wallis. Die Reisenden finden über Nacht in Gasthöfen Unterkunft. In diesen meist von Familien geführten Gasthäusern steigen Adlige genauso ab wie einfache Reisende oder Händler. Das Gasthaus Lion d’Or gehört zu den ältesten Unterkünften der Hauptstadt. Berühmte Persönlichkeiten wie Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1744), Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1779) oder auch die Kaiserin Joséphine (1812) haben hier übernachtet. Ab Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts werden die Gasthöfe allmählich von Hotels abgelöst, die sich über eine professionelle Führung auszeichnen. Nach und nach helfen Reiseführer den Touristen, ihre Reisen zu organisieren, schlagen Routen vor und geben weitere praktische Informationen.
Innkeeper, a room please!
The first tourists looking for mountain romance appeared in Valais in the second half of the 18th century. Passing travellers looking for an overnight stay made a stop at one of the inns. Those mostly family-run inns welcomed noblemen as well as travellers or merchants. The Lion d’Or Inn was one of the oldest establishments in the capital city. Celebrities such as Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1744), Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1779) or the Empress Joséphine (1812) took up a room there during their stay in Sion. From the mid-19th century, inns gradually gave way to hotels, which became more professional. Little by little tourist guides started helping tourists with their travels, offering excursions and providing practical information.
Una camera, locandiere !
Alla ricerca di romanticismo alpino, i primi turisti appaiono in Vallese nella seconda metà del 18esimo secolo. Nella locanda si fermano i viaggiatori di passaggio per la notte. Spesso a conduzione famigliare accoglie sia nobili che viaggiatori o commercianti. L’auberge du Lion d’or era una dei più vecchi stabili della capitale. Celebrità come Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1744), Goethe (1779) o ancora l’imperatrice Joséphine (1812) presero una camera qui durante il loro soggiorno a Sion. Dalla metà del 19esimo secolo, le locande cedono progressivamente il posto agli Hotel che diventano più professionali. Poco a poco le guide di viaggio aiutano i turisti nei loro spostamenti, proponendo itinerari e fornendo loro informazioni pratiche.
De Jean-Baptiste à Marguerite
Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia ou Garbazzia (1790-1865) s’établit à Sion en tant que maître-maçon au début du 19e siècle. Piémontais originaire de Varallo, il fait de nombreux dons aux pauvres de la cité ainsi qu’aux établissements de charité. Cet homme généreux lègue également à la Municipalité divers bâtiments, dont l’imposante maison en bas de la ruelle qui porte aujourd’hui son nom. Démolie en 1954, cette bâtisse, un temps mise à la disposition des assistés, a laissé place à un espace baptisé en hommage à l’artiste et écrivaine Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
Von Jean-Baptiste zu Marguerite
Der Maurermeister Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia oder Garbazzia (1790-1865) siedelte sich Anfang des 19. Jahrhunderts in Sitten an. Der gebürtige Piemonteser aus Varallo zeichnete sich durch zahlreiche Spenden zu Gunsten von Mittellosen und Wohltätigkeitseinrichtungen der Stadt aus. Der grosszügige Bürger hinterliess der Gemeinde verschiedene Immobilien, darunter das imposante Haus in der Gasse, die heute seinen Namen trägt. Dieses diente einige Zeit als Unterkunft für Unterstützungsbedürftige der Stadt. Es wurde 1954 abgerissen und wich so einem Platz zu Ehren der Schriftstellerin Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
From Jean-Baptiste to Marguerite
Jean-Baptiste Garbaccia or Garbazzia (1790-1865) set up his business as a master mason in Sion at the start of the 19th century. This native of Varallo in Piedmont bestowed many gifts on the city’s poor and its charitable institutions. He also showed his generosity by bequeathing various buildings to the Municipality, including the impressive house at the bottom of the street that now bears his name. This building was placed at the disposal of people in need of social assistance before it was demolished in 1954; it made way for a space named in honour of Marguerite Burnat-Provins, the artist and writer.
Da Giovanni Battista a Marguerite
Giovanni Battista Garbaccia o Garbazzia (1790-1865) si stabilisce a Sion come capomastro all’inizio del 19° secolo. Piemontese, originario di Varallo, fa numerosi doni ai poveri della città così come ad enti di beneficenza. Uomo generoso fa dono al comune anche di diversi edifici, tra i quali l’imponente casa all’inizio del vicolo a lui intestato. Il palazzetto, distrutto nel 1954 e un tempo a disposizione degli assistiti, ha lasciato il posto ad un luogo che ha preso il nome dell’artista e scrittrice Marguerite Burnat-Provins.
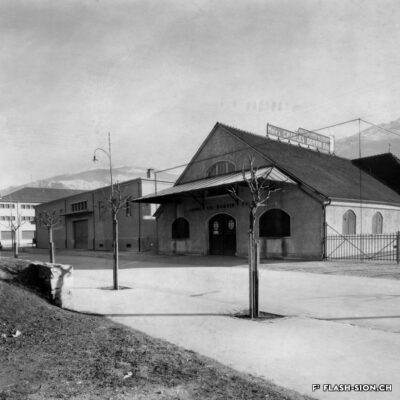
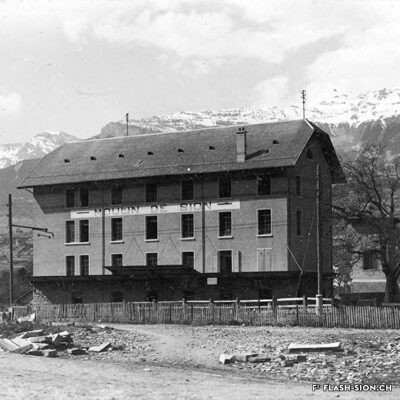
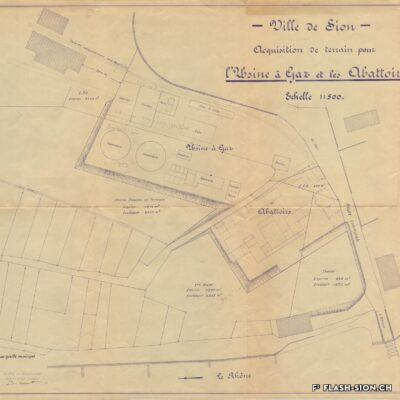
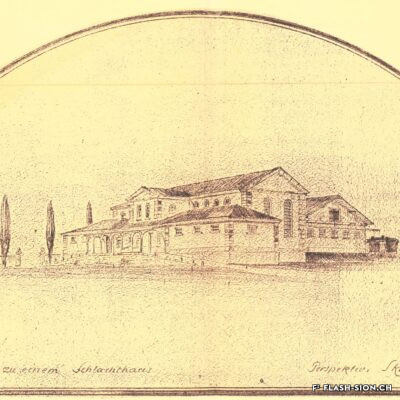
D’un abattoir à l’autre
En 1850, des abattoirs municipaux sont construits sous le rocher de la Majorie, dans un quartier encore peu habité à l’époque. Avec l’augmentation de la population, ces locaux ne répondent plus aux normes d’hygiène dès le début du 20e siècle. Les discussions pour un nouveau bâtiment commencent. Durant les années 1930, les abattoirs déménagent à la rue de l’Industrie, lieu plus approprié. Ils y resteront près de 70 ans avant de devoir fermer, n’étant plus assez rentables. L’édifice est ensuite investi par l’Œuvre suisse d’entraide ouvrière (OSEO), le Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs ainsi que certaines sociétés locales. Le départ de l’OSEO, début 2021, offre à la Ville la possibilité d’en faire un lieu dédié à la créativité et à l’innovation au cœur du quartier Ronquoz 21.
Von einem Schlachthof zum andern
1850 wird am Fusse des Majoria-Felsens in einem damals noch kaum bebauten Quartier ein erster städtischer Schlachthof errichtet. Dieser entspricht aufgrund des grossen Bevölkerungszuwachses bereits ab anfangs des 20. Jahrhunderts nicht mehr den Hygienenormen. Es folgen längere Verhandlungen, um einen neuen und geeigneteren Standort zu finden. In den 1930er Jahren siedelt der Schlachthof an die Rue de l’Industrie über, wird während 70 Jahren betrieben und dann aufgrund ungenügender Rentabilität geschlossen. Das Gebäude wird darauf von dem Schweizerischen Arbeitshilfswerk (SAH), dem städtischen Amt für Sport, Jugend und Freizeit wie auch lokalen Vereinen genutzt. Der Auszug des SAH eröffnet der Stadt schliesslich die Chance, mitten im Quartier von Ronquoz 21 einen Ort für Kreativität und Innovation anzusiedeln.
From one slaughterhouse to another
In 1850, municipal slaughterhouses were built under the Majorie rock, in a neighbourhood that was not very populated at the time. With the increase in population at the beginning of the 20th century, these premises no longer met hygiene standards. Discussions about a new building began. During the 1930s, the slaughterhouses moved to the ‘Rue de l’Industrie’, a more suitable location. They remained there for almost 70 years before being forced to close as they were no longer profitable. The building was then taken over by the Swiss Labour Assistance (OSEO, Œuvre suisse d’entraide ouvrière), the Sports, Youth and Leisure Service (Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs) and some local societies. The departure of the OSEO, at the beginning of 2021, offered the city the possibility of turning it into a venue dedicated to creativity and innovation in the heart of the Ronquoz 21 district.
Da un macello all’altro
Nel 1850 furono costruiti dei macelli comunali sotto la roccia di Majorie, in un quartiere che all’epoca era poco popolato. Con l’aumento della popolazione, all’inizio del XX secolo questi locali non soddisfacevano più gli standard igienici. Sono così iniziate le discussioni per la costruzione di un nuovo edificio. Negli anni ’30 i macelli si trasferirono nella Rue de l’Industrie, in una posizione più adatta. L’azienda rimase lì per quasi 70 anni prima di essere costretta a chiudere non essendo più abbastanza redditizia. L’edificio è stato poi preso in gestione dall’OSEO (Soccorso Operaio Svizzero,SOS), il Service des sports, de la jeunesse et des loisirs (Servizio dello sport, della gioventù e del tempo libero) e da alcune società locali. La partenza del OSEO, all’inizio del 2021, offre alla Città la possibilità di trasformarlo in un luogo dedicato alla creatività e all’innovazione nel cuore del distretto Ronquoz 21.
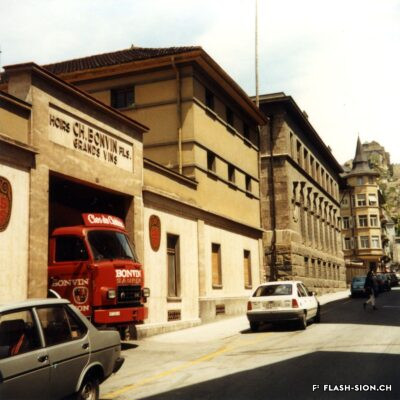
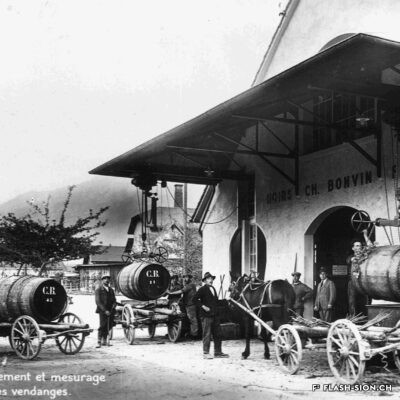
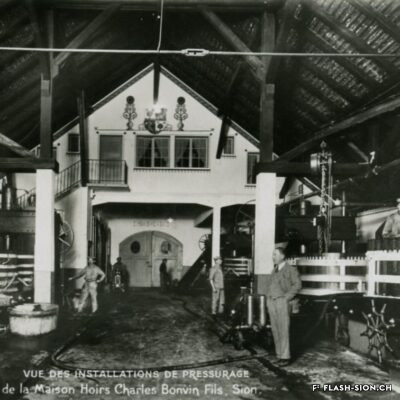
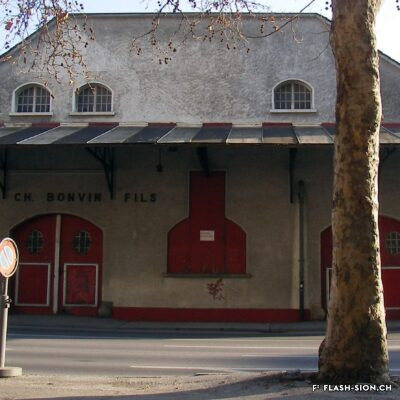
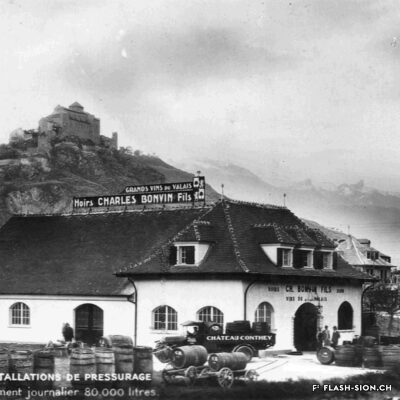
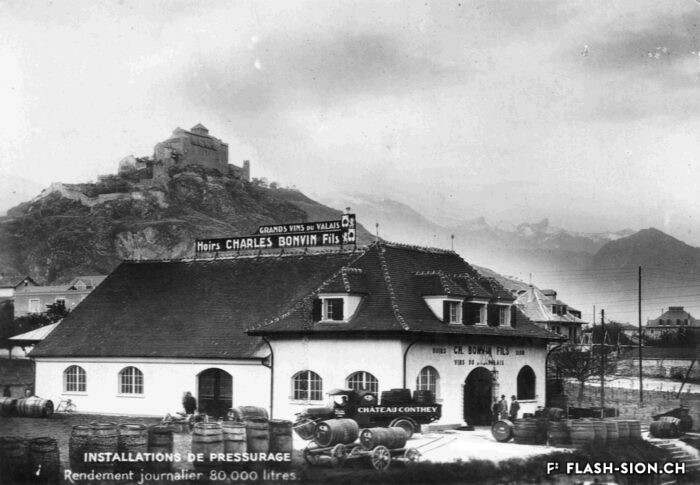
Charles et les caves festives
Fondée en 1858, la maison sédunoise des Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils fait figure de pionnière en matière de commerce vinicole en Valais. Charles-Marie Bonvin, son fondateur, donne l’impulsion au domaine et fait connaître les vins valaisans hors du canton et de la Suisse. Son fils Charles (1858-1922) prend la relève et à sa suite, ses deux fils, Charles (1888-1937) puis Félix. Aux caves et bureaux de la rue des Vergers et de la rue des Remparts s’ajoutent en 1932, les pressoirs de l’avenue de Tourbillon, face à la gare. Ces derniers deviennent alors un centre moderne de pressurage et d’encavage, jusqu’au début des années 1990. Désaffectés pendant de nombreuses années, ces pressoirs à l’abandon attirent l’attention d’un collectif qui y voit un potentiel culturel et souhaite leur redonner vie de façon éphémère. En 2008 et durant une année, l’association « Les Caves à Charles » fait vibrer ce lieu industriel chargé d’histoire, pour lui rendre un dernier hommage avant sa démolition.
Charles und die festliche Kellerei
Die 1858 in Sitten gegründete Weinkellerei der Erben von Charles Bonvin und Söhne gilt als Pionierin des Weinhandels im Wallis. Charles-Marie Bonvin, Begründer des Hauses, verstand es, den Walliser Wein ausserhalb des Kantons und der Schweiz bekannt zu machen. Der Betrieb wird in der Folge von seinem Sohn Charles (1858-1922) übernommen bevor dessen Söhne Charles (1888-1937) und später Félix die Nachfolge antreten. Zum Weinkeller und den Büroräumlichkeiten in der Rue des Vergers und der Rue des Remparts gesellt sich 1932 das Gebäude mit Weinpresse an der Avenue de Tourbillon, direkt gegenüber dem Bahnhof. Dieses entwickelt sich bis anfangs der 1990er Jahre zu einer modernen Kelterei mit Weinkeller. Danach bleibt das Gebäude während einiger Jahre ungenutzt. 2008 interessiert sich ein Kollektiv für die Kelterei und sieht deren Potenzial für eine kurzfristige kulturelle Nutzung. Während einem Jahr bringt der Verein «Les Caves à Charles» den geschichtsträchtigen Ort nochmals zum Schwingen und erweist ihm, bevor er abgebrochen wird, die letzte Ehre.
Charles and the festive wine cellars
Founded in 1858, the Sion-based company of Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils is a pioneer in the wine trade in Valais. Charles-Marie Bonvin, its founder, provided the impetus to the estate and made Valais wines known outside the canton and Switzerland. His son Charles (1858-1922) took over and was followed by his two sons, Charles (1888-1937) and Félix. In 1932, the cellars and offices in the ‘Rue des Vergers’ and the ‘Rue des Remparts’ were completed by the addition of wine presses in the ‘Avenue de Tourbillon’, opposite the railway station. They became a modern pressing and cellaring centre until the early 1990s. Disused for many years, these abandoned wine presses attracted the attention of a group who saw a cultural potential in them and wanted to bring them back to life in a temporary way. In 2008 and for one year, the Charles Cellars Association (Les Caves à Charles) filled this industrial site, full of history, with life and paid it a last tribute before its demolition.
Charles e le cantine in festa
Fondata nel 1858, l’azienda sedunese Hoirs Charles Bonvin Fils, è una pioniera del commercio di vino nel Vallese. Charles-Marie Bonvin, il suo fondatore, diede impulso alla tenuta e fece conoscere i vini del Vallese al di fuori del cantone e della Svizzera. Il figlio Charles (1858-1922) prese il testimone e fu seguito dai suoi due figli, Charles (1888-1937) e Félix. Nel 1932, alle cantine e agli uffici nella Rue des Vergers e nella Rue des Remparts si aggiunsero i torchi di Avenue de Tourbillon, di fronte alla stazione. In seguito, fino all’inizio degli anni Novanta, si sono trasformati in un moderno centro di pressatura e cantina. In disuso da molti anni, questi torchi abbandonati hanno attirato l’attenzione di un gruppo che ha visto in essi un potenziale culturale e ha voluto riportarli in vita in modo temporaneo. Nel 2008 e per un anno, l’associazione “Les Caves à Charles” (Le cantine di Charles) ha riportato in vita questo luogo industriale ricco di storia, per rendergli un ultimo omaggio prima della sua demolizione.
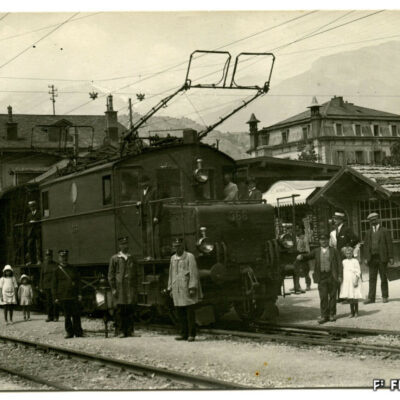
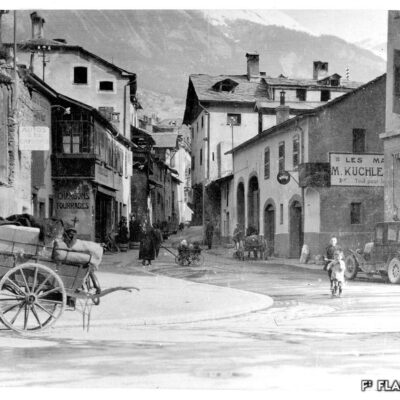
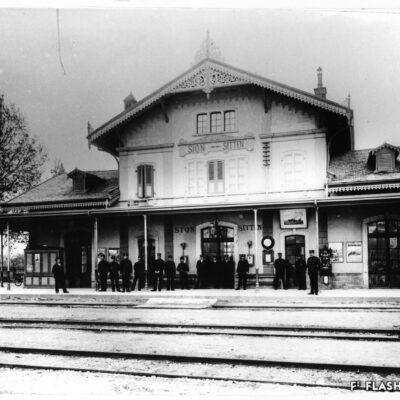
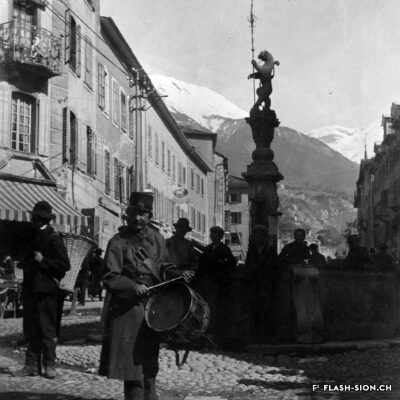
Train en vue
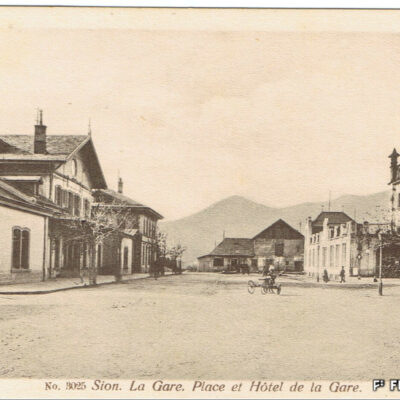
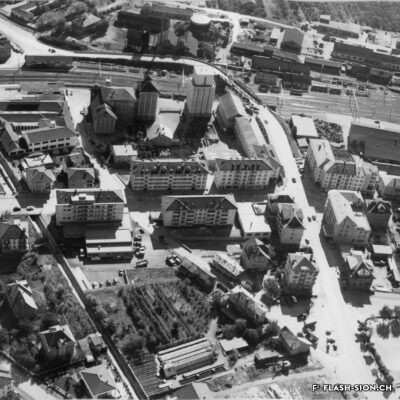
La première locomotive arrive à Sion le 5 mai 1860, accueillie par une foule émerveillée par ce spectacle d’un genre nouveau. Les travaux de la ligne du Simplon, reliant alors le port du Bouveret à la capitale, continuent ainsi leur lente progression entamée par la Compagnie de la Ligne d’Italie. La gare n’est encore qu’un simple baraquement en bois. Il faut attendre 1873 pour la construction d’une « gare convenable » par la compagnie Jura-Simplon. L’arrivée du chemin de fer accroît le transport des marchandises et des voyageurs, modifiant peu à peu la composition de la population sédunoise. Il favorisera aussi l’implantation d’un quartier industriel tout autour de la gare.
Zug in Sicht
Eine staunende und vom ungewohnten Spektakel begeisterte Menschenmenge erwartet am 5. Mai 1860 das Eintreffen der ersten Lokomotive in Sitten. Die Arbeiten an der Simplonlinie, die von der Eisenbahngesellschaft «Ligne d’Italie» begonnen wurde und den Hafen von Le Bouveret mit der Hauptstadt verbindet, kommen langsam voran. Das erste Bahnhofgebäude besteht aus einem einfachen Holzschuppen. Erst 1873 erstellt die Jura-Simplon Bahngesellschaft ein Bahnhofgebäude. Mit dem Bau der Eisenbahn nimmt der Güter- und Personenverkehr zu und verändert nach und nach die Bevölkerungsstruktur. Er begünstigt ebenfalls die Ansiedelung eines Industriequartiers rund um den Bahnhof.
Train within reach
The first locomotive arrived in Sion on 5 May 1860 and was welcomed by the crowd amazed by the show of a new kind. The works on the Simplon line connecting the Bouveret port to the capital city, initiated by Italian Railway Company, continued their slow but steady progress. The railway station of that time was a simple wooden shelter. It was only in 1873 that an « acceptable railway station » was built by Jura-Simplon Company. The arrival of the railway increased the transport of goods and the number of passengers, gradually changing the composition of Sion’s population. It would also facilitate the establishment of a new industrial district around the railway station.
Treno in vista
La prima locomotiva arriva a Sion il 5 maggio 1860, accolta da una folla meravigliata da questo nuovo tipo di spettacolo. I lavori della linea del Sempione che collegano il porto di Bouveret con la capitale, continuano il lento avanzamento iniziato dalla “Compagnie de la Ligne d’Italie”. La stazione è ancora una semplice baracca in legno. Bisognerà aspettare il 1873 per la costruzione di una “stazione adeguata” da parte della “Compagnie Jura-Simplon”. L’arrivo della rete ferroviaria permette di aumentare il trasporto di merci e di viaggiatori, modificando così gradualmente la composizione della popolazione di Sion. Inoltre incoraggia anche lo sviluppo di una zona industriale lungo la stazione.
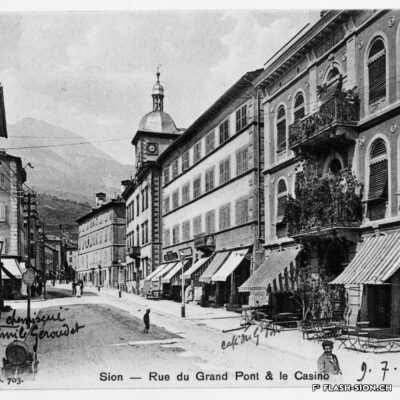
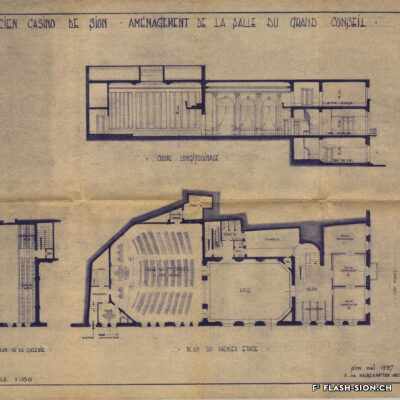
Des jeux de société aux jeux politiques
Contrairement à ce que son nom pourrait suggérer, le Casino de Sion n’a jamais hébergé de jeux de hasard sous son toit. Destiné à resserrer les liens de la société sédunoise, l’établissement, représentatif de l’architecte Emile Vuilloud, est construit en 1861 sur décision de la Bourgeoisie de Sion. L’édifice, avec sa grande salle de fête et les différents salons de lecture et de jeux de société, est inauguré en 1865. Parallèlement, la Société du Casino est constituée et un règlement de police strict est adopté. Après presque 40 ans d’existence, la société rencontre de plus en plus de difficultés à rassembler des membres. Elle est dissoute en 1904 et le bâtiment est racheté en 1912 par la Municipalité. En 1924, pour éviter de devoir mettre à disposition, à ses frais, des locaux plus spacieux pour les séances du Parlement valaisan, le conseil communal autorise le Grand Conseil à siéger, à bien plaire, dans la salle du Casino. Rénové et agrandi de 1938 à 1939, le Casino devient le siège permanent du Grand Conseil, excluant définitivement son utilisation parallèle comme salle de fête.
Von Gesellschaftsspielen zu politischen Spielchen
Entgegen seinem Namen sind im Casino von Sitten nie Glücksspiele angeboten worden. Der repräsentative Bau des Architekten Emile Vuilloud ist vielmehr dazu bestimmt, den gesellschaftlichen Zusammenhalt unter den Sittener Bürgern zu festigen und zu pflegen. 1861 beschliesst die Burgergemeinde von Sitten die Errichtung des Gebäudes. Die Einweihung des Casinos mit seinem großen Festsaal und den verschiedenen Salons zum Lesen und für Gesellschaftsspiele findet 1865 statt. Gleichzeitig erfolgt die Gründung der Société du Casino, welche ein strenges Polizeireglement für das Casino verabschiedet. Knapp 40 Jahre nach der Gründung verzeichnet die Gesellschaft jedoch zunehmend Schwierigkeiten, Mitglieder zu werben. Sie wird 1904 aufgelöst und das Gebäude 1912 von der Gemeinde aufgekauft. Um nicht auf eigene Kosten größere Räumlichkeiten für das Walliser Parlament zur Verfügung stellen zu müssen, kommt der Gemeinderat 1924 schliesslich dem Großen Rat entgegen und gestattet ihm, vorübergehend im Saal des Casinos zu tagen. Nach den Renovierungs- und Ausbauarbeiten zwischen 1938 und 1939 wird das Casino schliesslich zum ständigen Sitz des Großen Rates – eine parallele Nutzung als Festsaal wird damit endgültig ausgeschlossen.
From society games to political games
Contrary to what one might think of when considering its name, the Casino of Sion never hosted any gambling activities. The building was erected in 1861 upon approval of the Bourgeoisie of Sion. Well represeting the works of Emile Vuilloud, it aimed at reinforcing the bounds within the community members of Sion. The building was inaugurated in 1865 and consists of a huge hall for celebrations and several salons for reading and playing board games.
The ‘‘Société du Casino’’ was established concurrently and strict police regulations were enforced. Nearly 40 years later it was becoming harder and harder for the society to attract members, so it was dissolved in 1904 and the Municipality bought the building in 1912. In 1924, the town council -to avoid the costs that would have been encured by renting rooms more spacious for the meetings of the Parlement of Valais- gave the Grand Conseil the permission to sit ‘‘à bien plaire’’ (temporarily, so long as the Conseil approves of it) in the hall oft he Casino. It was renovated and extended between 1938 and 1939 and became the permanent seat of the Great Conseil, thus definitely excluding the possibilities to concurrently use it as a banquet hall.
Dai giochi di società ai giochi politici
Contrariamente a quanto potrebbe suggerire il nome, il Casinò di Sion non ha mai ospitato i giochi d’azzardo sotto il suo tetto. Destinato a rafforzare i legami della società di Sion, l’edificio rappresentativo dell’epoca, fu progettato dall’architetto Emile Vuilloud nel 1861 per decisione della borghesia di Sion. L’edificio con il grande salone delle feste e le varie sale di lettura e di giochi da tavolo, venne inaugurato nel 1865. Allo stesso tempo venne costituita la “Società del Casinò” e furono adottati severi regolamenti di polizia. Dopo quasi 40 anni di esistenza, la società trova sempre più difficoltà a riunire i membri. Fu sciolta nel 1904 e l’edificio fu acquistato nel 1912 dal Comune. Nel 1924, per evitare di dover fornire, a proprie spese, locali più spaziosi per le sedute del Parlamento vallesano, il Consiglio comunale autorizzò il Gran Consiglio a riunirsi, a suo piacimento, nella sala del Casinò. Ristrutturato e ampliato dal 1938 al 1939, il Casinò divenne la sede permanente del Gran Consiglio, escludendo definitivamente il suo utilizzo parallelo come salone delle feste.
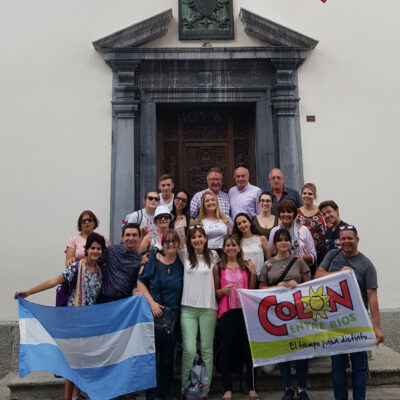
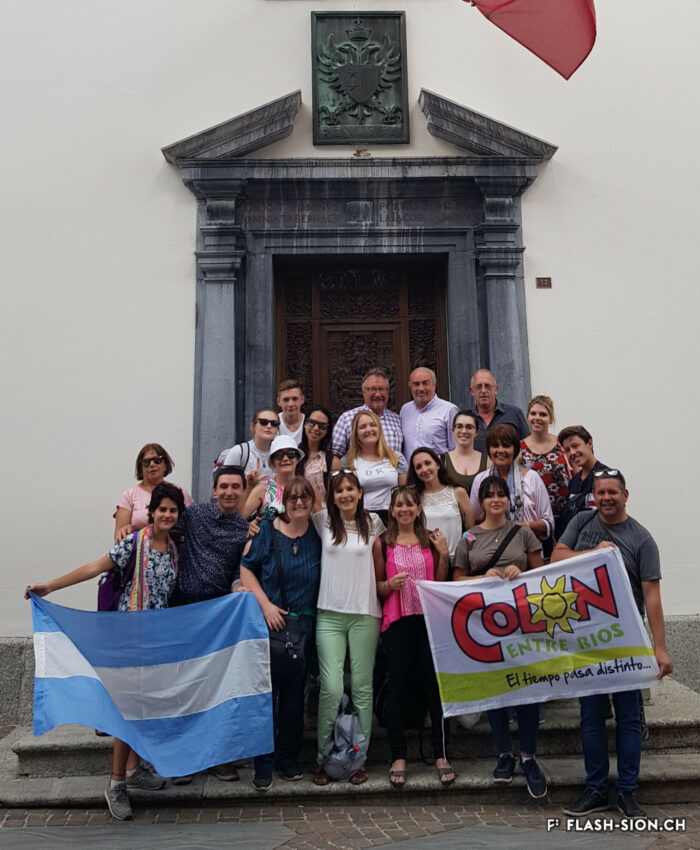
Départ pour le Nouveau Monde
Hospitalité, bonheur et fortune, voilà ce que les Valaisans qui émigrent en Argentine au milieu du 19e siècle espèrent trouver. De nombreux Valaisans, pour la plupart des paysans, partent pour l’Amérique du Sud car ils arrivent à peine à survivre chez eux. Cette importante émigration entraîne la création de plusieurs colonies dont la ville de Colón, fondée en 1862. Le départ pour le Nouveau Monde est une réussite pour certains Valaisans qui invitent leurs proches à les rejoindre. Les liens entre les Valaisans d’Argentine et ceux restés au pays perdurent, entre autres, grâce à l’association Valais-Argentine et au jumelage entre Sion et Colón.
Aufbruch in die neue Welt
Gastfreundschaft, Glück und Reichtum erhofften sich die Walliser, welche Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts nach Argentinien auswanderten. Unzählige Walliser, insbesondere Bauern, reisten nach Südamerika aus. Sie hatten in ihrer Heimat zu wenig zum Überleben. Diese massiven Auswanderungsströme führten zur Gründung verschiedener Kolonien, unter anderem der Stadt Colón im Jahre 1862. Der Aufbruch in die Neue Welt bescherte einigen Wallisern Erfolg. Diese regten wiederum Verwandte an, sich ihnen anzuschliessen. Die Beziehung zwischen den Wallisern in Argentinien und den Zurückgebliebenen werden dank der Vereinigung «Valais-Argentine» und der Städtepartnerschaft von Sion und Colón weiter gepflegt.
Departure for the New World
Hospitality, happiness, and wealth – this is what people emigrating from Valais to Argentina in the middle of the 19th century were hoping to find. Many people of Valais, mostly farmers, left for South America because they could barely survive in their homeland. As a result of this important wave of emigration, several colonies were founded, for instance the town of Colón, which was established in 1862. Some people of Valais, having made a successful start in the New World, invited their relatives to join them. The relationship between people of Valais established in Argentina and those who stayed in the country has been maintained, among other things, thanks to the Valais-Argentina Association and twinning projects between Sion and Colón.
Partenza per il nuovo mondo
Ospitalità, felicità e fortuna erano ciò che sperano di trovare i vallesani emigrando in Argentina a metà del 19esimo secolo. Numerosi vallesani, la maggioranza contadini, partirono per l’America del Sud poiché a casa loro sopravvivevano a malapena. Questa importante emigrazione, portò alla creazione di diverse colonie, tra cui la città di Colón, fondata nel 1862. La partenza per il Nuovo Mondo fu un successo per alcuni vallesani che invitarono i loro famigliari a raggiungerli. I legami tra i vallesani in Argentina e quelli che rimasti in patria continuano ad esistere, e questo grazie anche all’associazione Vallese-Argentina e al gemellaggio tra Sion e Colón.
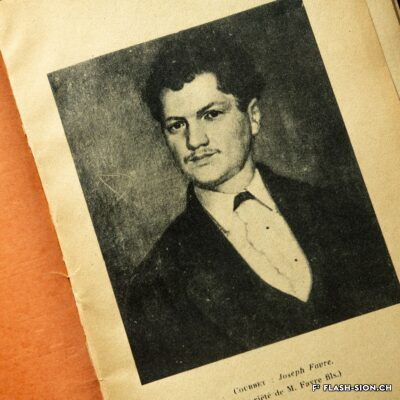
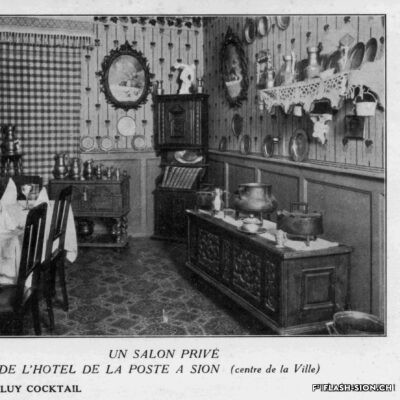
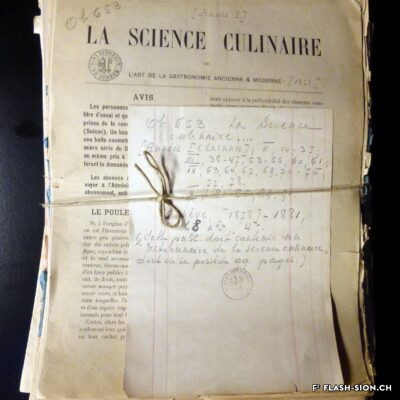
Un cuisinier avant-gardiste
En matière de gastronomie, l’histoire a longtemps oublié un enfant du pays. Originaire de Vex, un certain Joseph Favre (1844-1903) s’illustre en tant que pionnier de la « science et de l’hygiène culinaire ». Après un apprentissage de trois ans, vraisemblablement à l’Hôtel de la Poste, à l’époque l’un des plus prestigieux hôtels de Sion, il sillonne la Suisse et l’Europe pour parfaire son art. Anarchiste à ses heures, Joseph Favre se fait surtout connaître par son acharnement à rendre à la cuisine ses lettres de noblesse. Il publie notamment dès 1877 le premier journal de cuisine écrit par des cuisiniers et participe aux premiers concours et expositions culinaires. Dès 1883, ce théoricien progressiste consacre sa vie à la rédaction de son monumental « Dictionnaire universel de cuisine pratique et d’hygiène alimentaire ». Il est également à l’origine de la fondation de l’Académie culinaire de France en 1883.
Ein fortschrittlicher Koch
Im Bereich der Gastronomie blieb der Walliser Joseph Favre (1844-1903) der breiten Öffentlichkeit lange unbekannt. Der aus Vex stammende Koch hat sich als Pionier der Kulinarik und wissenschaftlichen Küchenhygiene bekannt gemacht. Nach einer dreijährigen Lehre, vermutlich im damals renommierten Hotel Post in Sitten, bereist er die Schweiz und Europa und erweitert seine Kochkunst. Kurze Zeit einer anarchistischen Bewegung verschrieben, zeichnet sich Favre insbesondere durch sein hartnäckiges Engagement für eine moderne Ess- und Kochkultur aus. Ab 1877 veröffentlicht er die erste, von einem Koch verfasste Kochzeitschrift und nimmt an ersten Kochwettbewerben und kulinarischen Ausstellungen teil. Ab 1883 widmet sich der fortschrittliche Theoretiker ganz dem Verfassen seines bedeutendsten Werkes, dem «Universallexikon des Kochens und der Lebensmittelhygiene». Er ist ebenfalls Begründer der 1883 entstandenen «Académie culinaire de France».
An avant-garde cook
When it comes to gastronomy, history has long forgotten a local youngster. Originally from Vex, a certain Joseph Favre (1844-1903) distinguished himself as a pioneer of “culinary science and hygiene”. After a three-year apprenticeship, probably at the Hôtel de la Poste, which was one of the most prestigious hotels in Sion at the time, he travelled throughout Switzerland and Europe to perfect his art. An anarchist at times, Joseph Favre is best known for his determination to give nobility back to cuisine. In 1877, he published the first cooking journal written by cooks and he took part in the first culinary competitions and exhibitions. From 1883, this progressive theorist devoted his life to writing his monumental “Universal Dictionary of Practical Cooking and Food Hygiene”. He was also a founder of the French Culinary Academy in 1883.
Un cuoco d’avanguardia
Quando si parla di gastronomia, la storia ha dimenticato da tempo un ragazzo del posto. Originario di Vex, un certo Joseph Favre (1844-1903) si distinse come pioniere della “scienza e dell’igiene culinaria”. Dopo un apprendistato di tre anni, probabilmente presso l’Hôtel de la Poste, all’epoca uno degli alberghi più prestigiosi di Sion, viaggiò in tutta la Svizzera e in Europa per perfezionare la sua arte. A volte anarchico, Joseph Favre è noto soprattutto per la sua determinazione a dare alla cucina le sue lettere di nobiltà. Nel 1877 pubblicò il primo giornale di cucina scritto da cuochi e partecipò ai primi concorsi e mostre culinarie. A partire dal 1883, questo teorico progressista si dedicò alla stesura del suo monumentale “Dictionnaire universel de cuisine pratique et d’hygiène alimentaire”. A lui si deve anche la fondazione dell’Accademia culinaria francese nel 1883.
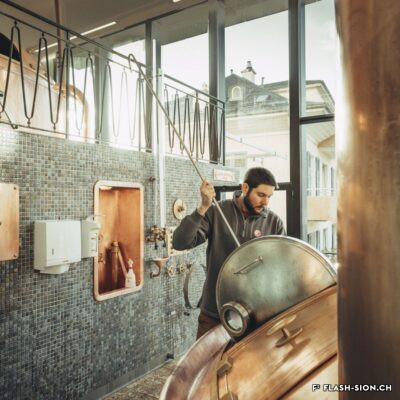
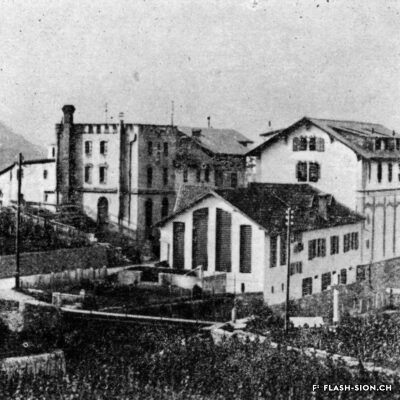
De la bière au pays du vin
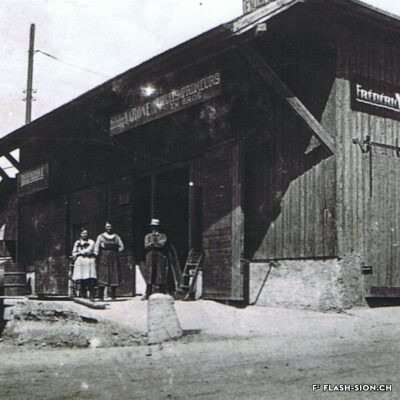
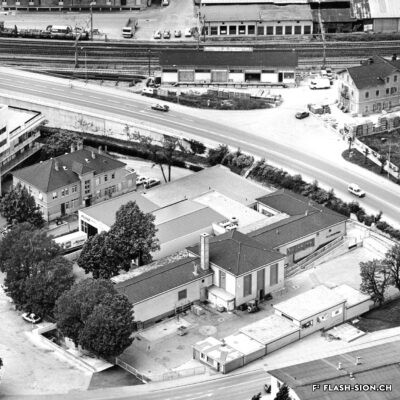
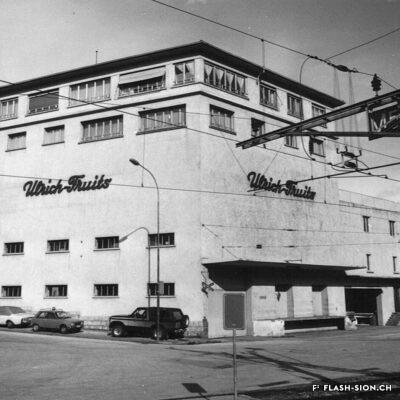
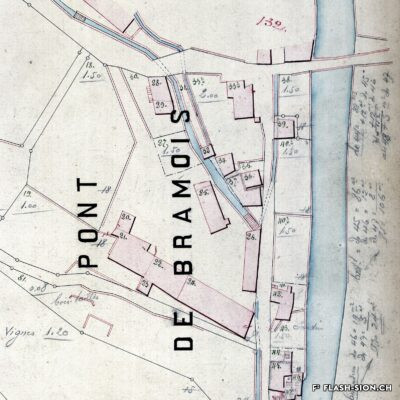
Il aura fallu du temps pour que la bière s’impose en Valais, pays du vin par excellence. Malgré l’interdiction de ce « breuvage inhabituel » en 1802 par les autorités valaisannes, plusieurs brasseries s’installent dans la région sédunoise au cours du 19e siècle. En 1865, Maurice de Quay, pharmacien hollandais, en ouvre une au nord de la ville de Sion. A la même période environ, la brasserie Koebel, Aymon et Cie est également active à Bramois. Pour produire une bière de qualité, les deux entreprises recrutent leurs employés en Suisse allemande, voire en Allemagne. Vers la fin du 19e siècle, la brasserie de Quay est reprise par Johan Hofer et celle de Bramois passe aux mains des frères Fertig. En 1926, elles fusionnent pour devenir la Brasserie Valaisanne telle qu’on la connait aujourd’hui. Dès 1950, l’entreprise s’industrialise avec, notamment, des installations frigorifiques qui remplacent la glacière.
Vom Bier zum Weinland
Es ging eine ganze Weile, bis sich das Bier in dem vom Weinbau geprägten Wallis durchsetzt. Obwohl die Walliser Behörden das «ungewohnte Gebräu» verbieten, siedeln sich im Laufe des 19. Jahrhunderts mehrere Bierbrauereien in der Region Sitten an. 1865 eröffnet der holländische Apotheker Maurice de Quay im Norden der Stadt Sitten eine Brauerei. Etwa zur gleichen Zeit wird bei Koebel, Aymon et Cie in Bramois ebenfalls Bier gebraut. Zur Herstellung eines hochwertigen Bieres, heuern beide Unternehmen ihre Mitarbeiter in der Deutschschweiz oder gar in Deutschland an. Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts wird die Brauerei de Quay von Johan Hofer übernommen und die Brauerei in Bramois geht in den Besitz der Gebrüder Fertig über. 1926 fusionieren die beiden Unternehmen unter dem Namen Walliser Brauerei, welche bis heute noch besteht. Ab den 1950er Jahren wird die Produktion unter anderem durch die Installation von Kühlanlagen industrialisiert, die den Eiskeller ersetzen.
Beer in wine country
It took a long time for brewing beer to become established in Valais, a wine country par excellence. Despite the ban on this “unusual beverage” in 1802 by the Valais authorities, several breweries were set up in the Sion region during the 19th century. In 1865, Maurice de Quay, a Dutch pharmacist, opened one in the northern part of the city of Sion. Around the same time, the brewery Koebel, Aymon & Cie was also active in Bramois. In order to produce quality beer, both companies recruited their employees in German-speaking Switzerland, and even in Germany. Towards the end of the 19th century, the Quay brewery was taken over by Johan Hofer and the Bramois brewery was taken over by the Fertig brothers. In 1926, they merged to become the Brasserie Valaisanne as we know it today. From 1950 onwards, the company became more industrial, with refrigeration facilities replacing the icebox.
La birra nel paese del vino
Ci è voluto molto tempo affinché la birra si affermasse in Vallese, la terra del vino per eccellenza. Nonostante il divieto di questa “bevanda insolita” nel 1802 da parte delle autorità vallesane, nel corso del XIX secolo nella regione sedunese sono state aperte diverse birrerie. Nel 1865, Maurice de Quay, un farmacista olandese, aprì una fabbrica di birra a nord della città di Sion.
All’incirca nello stesso periodo, anche la birreria Koebel, Aymon et Cie era attiva a Bramois. Per produrre birra di qualità, entrambe le aziende reclutarono i propri dipendenti dalla Svizzera tedesca e persino dalla Germania. Verso la fine del XIX secolo, il birrificio Quay fu rilevato da Johan Hofer e il birrificio di Bramois dai fratelli Fertig. Nel 1926 si fusero per diventare la Brasserie Valaisanne come la conosciamo oggi. Dal 1950 in poi, l’azienda divenne più industriale, con impianti di refrigerazione che sostituirono la ghiacciaia.
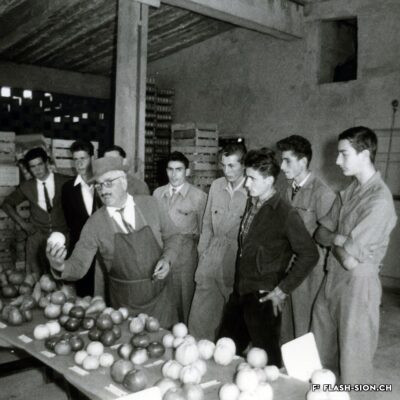
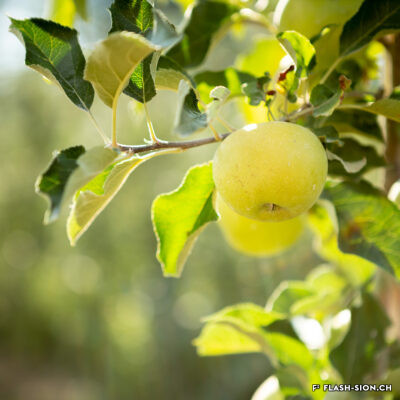
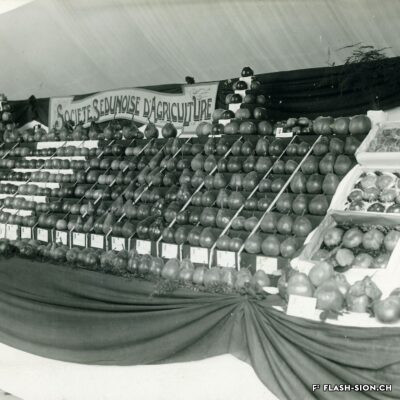
Pomme de Reinette et pomme d’Api
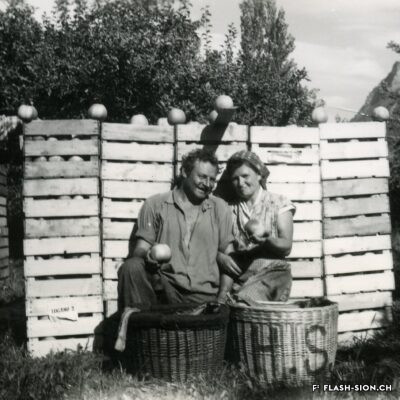
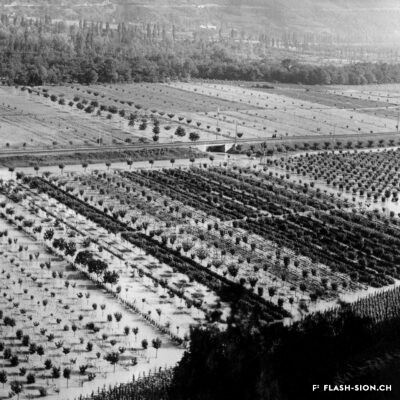
Contrairement à ce que pourrait suggérer son nom, la Reinette (monstrueuse) du Canada a ses origines en France. Elle est décrite pour la première fois en 1771 par le botaniste du Roi, Pierre Andrieux. Son introduction dans les vergers valaisans coïncide avec la première correction du Rhône (1863-1894). Les terres gagnées par l’assèchement de la plaine offrent en effet un terroir particulièrement propice à sa culture. Dès la fin du 19e siècle, la pomme Canada devient la variété emblématique des vergers et pré-vergers à hautes tiges de Bramois, d’où elle était exportée jusque dans la capitale française. Aujourd’hui, les vergers de Sion et de Vex sont dans les derniers en Suisse où cette variété ancienne est encore présente et replantée, notamment sur les terrains de la Bourgeoisie de Sion. Celle-ci offre chaque automne une cagette de ces pommes aux bourgeois. Pomme de garde par excellence, la Canada est tout particulièrement appréciée pour sa chair fondante et la saveur douce et acidulée de son jus.
In meinem kleinen Apfel…
Anders als es der Name vermuten lässt, hat die Kanada-Reinette ihren Ursprung in Frankreich. Sie wird erstmals 1771 von dem königlichen Botaniker Pierre Andrieux beschrieben. Die Einführung der Apfelsorte im Wallis fällt mit der ersten Rhonekorrektur (1863-1894) zusammen. Die Trockenlegung der Rhoneebene bietet einen besonders geeigneten Boden für den Anbau der Apfelsorte. Ab Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts entwickelt sich die Kanada-Reinette zur emblematischen Apfelsorte der Hochstamm und Wiesenobstgärten von Bramois und wird bis nach Paris exportiert. Heute ist diese alte Apfelsorte in der Schweiz insbesondere noch in den Obstgärten von Sitten und Vex anzutreffen und wird nicht zuletzt auf den Grundstücken der Burgergemeinde von Sitten neu angepflanzt. Jeden Herbst verteilt diese ihren Burgern eine Kiste Kanada-Reinetten. Als Lagerapfel beliebt, wird das Tafelobst ganz besonders für sein zart-schmelzendes Fruchtfleisch und den süss-säuerlichen Geschmack seines Saftes geschätzt.
Reinette apple and an Api apple (a children’s song)
Contrary to what its name might suggest, the Reinette (Monstrueuse) of Canada has its origins in France. It was first described in 1771 by the King’s botanist, Pierre Andrieux. Its introduction into Valais orchards coincided with the first correction of the Rhône River (1863-1894). The land obtained by the draining of the plain offered a particularly favourable soil for the cultivation of this variety. From the end of the 19th century, the Canada apple became the emblematic variety of orchards and orchard meadows of Bramois, from where it was exported all the way to the French capital. Today, the orchards of Sion and Vex are some of the only ones in Switzerland where this old variety is still present and replanted, notably on the grounds belonging to the Bourgeoisie of Sion. Every autumn, the Bourgeoisie offers a crate of these apples to its members. The Canada apple is particularly appreciated for its melt-in-the-mouth flesh and the sweet, tangy taste of its juice.
« Pomme de Reinette e pomme d’Api »
Contrariamente a quanto potrebbe far pensare il nome, la Reinette (mostruosa) del Canada ha origini francesi. Fu descritta per la prima volta nel 1771 dal botanico del re, Pierre Andrieux. La sua introduzione nei frutteti vallesani coincise con la prima correzione del Rodano (1863-1894).
I terreni bonificati dal drenaggio della pianura offrivano un terreno particolarmente favorevole alla sua coltivazione. Dalla fine del XIX secolo, la mela Canada divenne la varietà emblematica dei frutteti e dei pre-frutteti ad alto fusto di Bramois, da dove veniva esportata nella capitale francese.
Oggi i frutteti di Sion e Vex sono gli unici in Svizzera in cui questa vecchia varietà è ancora presente e viene ripiantata, in particolare nei terreni del patriziato di Sion. Ogni autunno, quest’ultimo offre una cassa di queste mele ai suoi patrizi. La Canada è la mela per eccellenza, particolarmente apprezzata per la sua polpa fondente e per il sapore dolce e acidulo del suo succo.
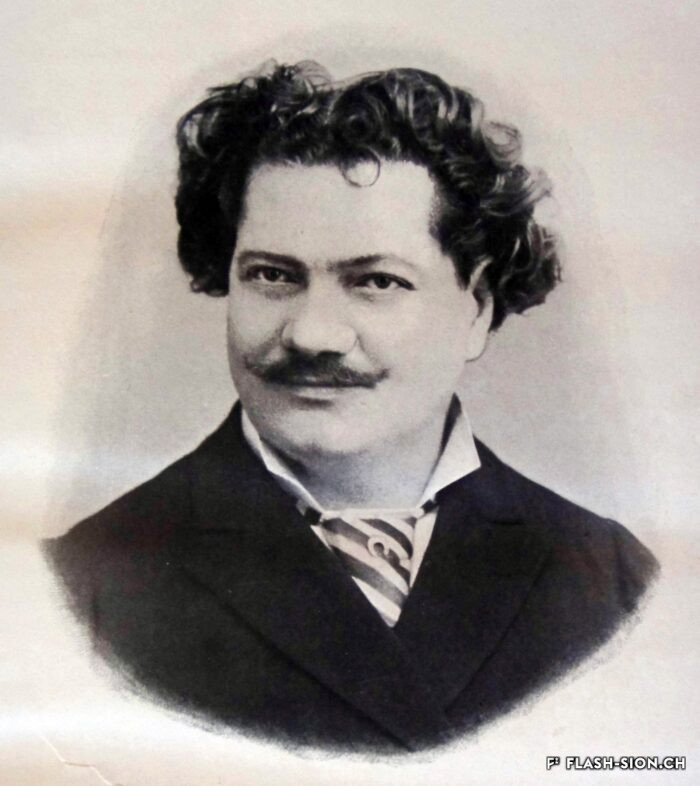
Une affaire de famille
Entrepreneur piémontais né en 1845, Michel Fasanino œuvre à Sion dès son établissement en 1883. A cette époque, la ville ressemble davantage à un bourg agricole qu’à une cité urbaine. Jusqu’à son décès en 1923, Fasanino contribue notablement à son expansion. Il collabore également avec les deux architectes incontournables de l’époque, Joseph de Kalbermatten et Joseph Dufour. Ce patron bienveillant dirige son affaire prospère en bon père de famille et laisse de nombreuses réalisations, en partie disparues aujourd’hui.
Ein Familienunternehmen
Der 1845 geborene piemontesische Baumeister Michel Fasanino liess sich im Jahre 1883 in Sitten nieder. In der noch stark bäuerlich geprägten Stadt trug Fasanino bis zu seinem Tod im Jahre 1923 massgeblich zur Stadtentwicklung bei. Er arbeitete ebenfalls mit Joseph de Kalbermatten und Joseph Dufour zusammen. Diese gehörten zu den führenden Architekten jener Zeit. Der wohlwollende Arbeitgeber führte ein florierendes Geschäft und hinterliess ein umfassendes Lebenswerk, von dem heute zahlreiche Bauten abgebrochen worden sind.
A family business
Michel Fasanino, a Piedmont entrepreneur born in 1845, worked at Sion after setting up business there in 1883. In those days, Sion resembled an agricultural township rather than an urban centre. Fasanino played an outstanding part in the city’s expansion until his death in 1923. He also collaborated with the two most prominent architects of the period: Joseph de Kalbermatten and Joseph Dufour. This benevolent employer ran his prosperous business like a good family man. His legacy included many buildings, although some of them have since disappeared.
Un affare di famiglia
Imprenditore piemontese nato nel 1845, Michel Fasanino lavora a Sion sin dal suo insediamento nel 1883. A quell’epoca, la città assomiglia maggiormente ad un borgo agricolo che ad una città urbana. Fino alla sua morte nel 1923, Fasanino contribuisce in modo notevole all’espansione della città. Collabora con due architetti di spicco dell’epoca, Joseph de Kalbermatten e Joseph Dufour. Capo benevolo dirige la sua attività prospera come un buon padre di famiglia e lascia innumerevoli opere, ad oggi in parte distrutte.
De la source au robinet
A la fin du 19e siècle, les multiples réclamations quant à la qualité et à la quantité de l’eau potable des fontaines forcent la Municipalité à réagir. En 1895, elle confie l’exécution d’un réseau d’eau potable relié à un grand réservoir à Platta à l’entreprise Dumont&fils. Cependant, les installations mises en service dès 1897, se révèlent non-conformes à plusieurs titres. Ainsi, les autorités reconsidèrent le captage des sources de la Fille et des Fontannées inauguré en 1901. Depuis, l’augmentation constante de la consommation d’eau contraint les services industriels de la Ville à trouver sans relâche de nouvelles sources d’approvisionnement. Dès 1931, le puits de Sainte-Marguerite pare aux cas d’urgence et, en 1951 et 1964, le deuxième et troisième réservoir de Tourbillon sont mis en service. Aujourd’hui, la mise en valeur de cette ressource fragile et la sensibilisation de la population à une consommation responsable représentent plus que jamais les défis de demain.
Von der Quelle zum Wasserhahn
Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts zwingen zahlreiche Beschwerden, welche Qualität und Menge des Trinkwassers in den Brunnen bemängeln, die Stadtverwaltung zum Handeln. Letztere beauftragt 1895 das Unternehmen Dumont&Söhne mit der Planung einer zentralen Wasserversorgung, zu welcher ebenfalls das Reservoir in Platta zählt. Die 1897 in Betrieb genommene Anlage erweist sich jedoch von Anfang an und in verschiedenen Punkten als nicht konform. Die Fassung der Quellen «de la Fille» und «des Fontanées» wird daher durch die Stadtbehörden wiedererwägt und 1901 eingeweiht. Seither verpflichtet der stetig steigende Trinkwasserverbrauch die Stadtwerke, immer neue Wasserquellen zu erschliessen. Ab 1931 beugt das Grundwasserpumpwerk von Sainte-Marguerite Notsituationen vor, 1951 und 1964 werden das zweite und das dritte Reservoir in Tourbillon in Betrieb genommen. Heute stellen die Erschliessung dieser lebenswichtigen Ressource und die Sensibilisierung der Bevölkerung für einen verantwortungsvollen Verbrauch mehr denn je eine Herausforderung für die Zukunft dar.
From source to tap
At the end of the 19th century, the numerous complaints about the quality and quantity of the drinking water from the fountains forced the Municipality to react. In 1895, it appointed the Dumont&fils company to execute the construction of a drinking water network connected to a large reservoir in Platta. However, the installations put into service in 1897 proved to be non-compliant in several respects. Thus, the authorities reconsidered the catchment of the Fille and Fontannées springs, which were inaugurated in 1901. The constant increase in water consumption forced the city’s industrial services to find new sources of supply. From 1931, the Sainte-Marguerite well was used for emergencies and, in 1951 and 1964, the second and third Tourbillon reservoirs were put into service respectively. Today, the development of this fragile resource and the raising of public awareness about responsible consumption are more than ever the challenges of tomorrow.
Dalla sorgente al rubinetto
Alla fine del XIX secolo, le numerose lamentele per la qualità e la quantità dell’acqua potabile delle fontane costrinsero il comune a reagire. Nel 1895, affidò la costruzione di una rete di acqua potabile collegata a un grande serbatoio a Platta alla società Dumont&fils. Tuttavia, gli impianti messi in servizio nel 1897 si rivelarono non conformi sotto diversi aspetti. Le autorità quindi riconsiderarono il bacino di raccolta delle sorgenti Fille e Fontannées, inaugurate nel 1901. Da allora, il costante aumento del consumo di acqua ha costretto i servizi industriali della città a trovare nuove fonti di approvvigionamento. Dal 1931, il pozzo di Sainte-Marguerite fu utilizzato per le emergenze e, nel 1951 e nel 1964, furono messi in funzione il secondo e il terzo serbatoio di Tourbillon. Oggi, lo sviluppo di questa fragile risorsa e la sensibilizzazione della popolazione a un consumo responsabile sono più che mai le sfide del domani.
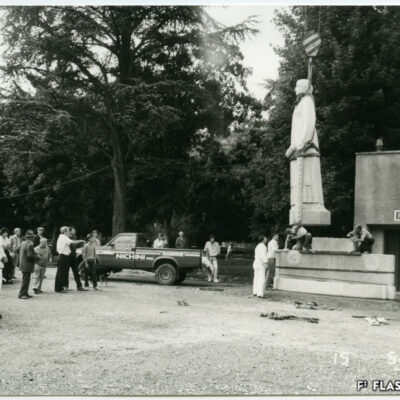
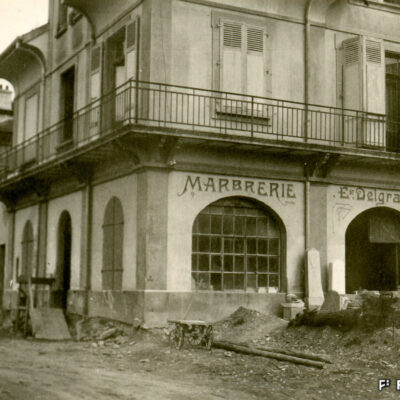
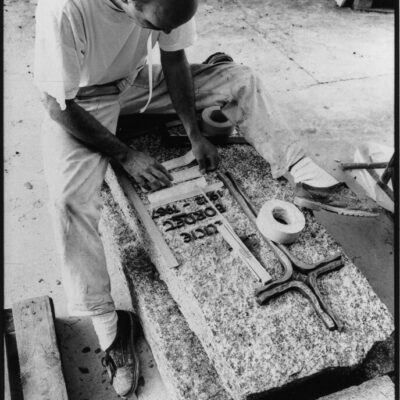
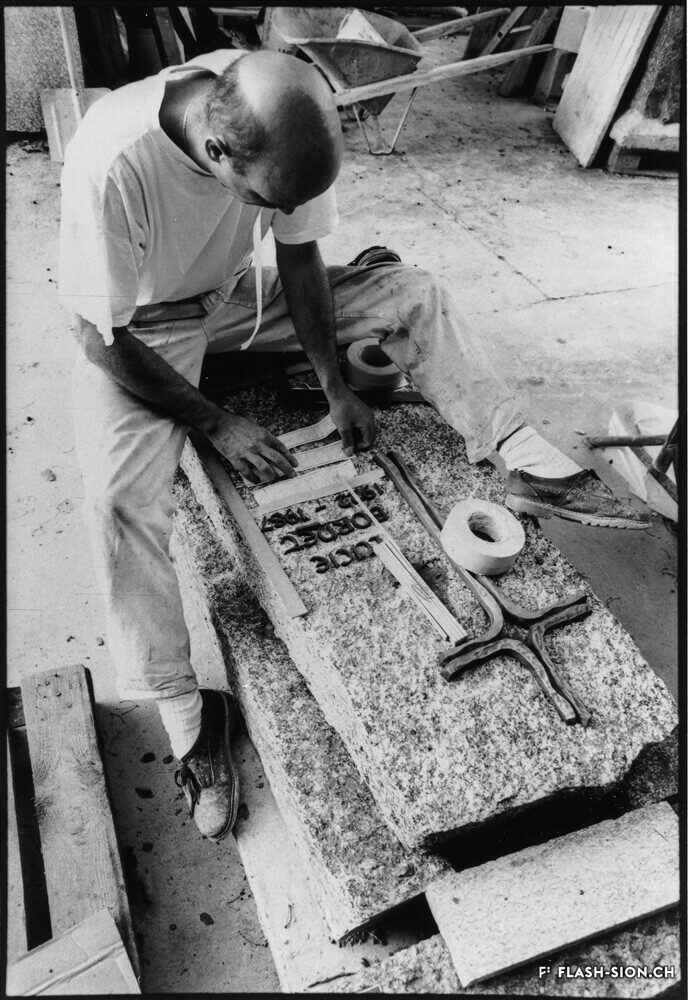
Sion gravée dans la pierre
Important les compétences nécessaires au travail de la pierre, des marbriers et sculpteurs originaires du Val d’Ossola dominent le secteur dès la fin du 19e siècle et contribuent largement à l’essor de la ville du 20e siècle. En 1906, les frères Nichini déploient leur activité à Sion et marquent durant trois générations la construction en pierre de la cité. Exploitant d’une carrière à Bramois, Albert Nichini, devient par la suite propriétaire de la carrière d’Evolène, dont les pierres ornent de nombreux bâtiments et monuments de la ville.
Sion, in Stein gemeisselt
Ab Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts dominieren die für ihre Fachkenntnis bekannten Steinhauer und Steinmetze aus dem Val d’Ossola den Berufszweig der Steinbearbeitung und tragen massgeblich zur Stadtentwicklung im 20. Jahrhundert bei. Die Gebrüder Nichini nehmen im Jahr 1906 ihre Tätigkeit in Sitten auf und prägen über drei Generationen den Steinbau der Stadt. Vorerst Betreiber eines Steinbruchs in Bramois, erwirbt Albert Nichini später den Steinbruch von Evolène, dessen Steinplatten zahlreiche Gebäude und Denkmäler der Stadt schmücken.
Sion – carved in stone
Marble masons and sculptors from Val d’Ossola brought with them the skills needed to work with stone; they dominated the industry from the late 19th century onwards and played a key part in the city’s dynamic growth in the 20th century. The Nichini brothers set up their business at Sion in 1906 and for three generations, they left their mark on the city’s stone architecture. Albert Nichini operated a quarry at Bramois and then became the owner of the Evolène quarry, which supplied stone to decorate many of the city’s buildings and monuments.
Sion incisa nella pietra
Ritenute importanti le competenze necessarie al lavoro della pietra, marmisti e scultori originari della Val d’Ossola dominano il settore dalla fine del 19° secolo e contribuiscono notevolmente all’espansione della città del 20° secolo. Nel 1906, i fratelli Nichini sviluppano la loro attività a Sion e segnano per tre generazioni il settore della costruzione in pietra della città. Esercente di una cava a Bramois, Albert Nichini diventa in seguito il proprietario della cava di Evolène, le cui pietre abbelliscono numerosi edifici e monumenti della città.
Destinations à l’affiche
Principal vecteur de communication et de promotion à la fin du 19e et au 20e siècle, l’affiche se fait témoin du tourisme naissant. Elle contribue sensiblement à façonner une image du Valais ponctuée de symboles identitaires forts. L’arrivée du chemin de fer rend accessible de nouvelles destinations, qu’il s’agit de faire connaître. Vantant les atouts de ses villes et stations, l’affiche touristique valaisanne met en avant les beautés naturelles de la montagne, les activités sportives et récréatives. En parallèle, l’affiche commerciale contribue également à la promotion du canton, comme par exemple les producteurs de vin.
Reiseziel Plakat
Im aufblühenden Tourismus Ende des 19. Jahrhunderts und im 20. Jahrhundert spielt das Plakat als wichtigstes Kommunikationsmittel eine entscheidende Rolle. Es prägt ein verklärtes Bild des Wallis, welches sich meist identitätsstiftender Symbolbilder bedient. Mit dem Bau der Eisenbahn werden neue Destinationen erschlossen, die es zu bewerben gilt. Um die Vorzüge der Walliser Städte und Ferienorte hervorzuheben, stellt das Walliser Tourismusplakat das Naturschauspiel der Bergwelt sowie die Sport- und Freizeitaktivitäten in den Vordergrund. Gleichzeitig trägt das Werbeplakat auch zur wirtschaftlichen Förderung des Kantons bei, wie dies beispielsweise bei den Weinproduzenten zu sehen ist.
Travel Destinations Posters
At the end of the 19th and during the 20th century, travel posters were the main means of communication and promotion, bearing witness of the emerging tourism. They contributed significantly to creating the image of Valais, marked by powerful identity symbols. The arrival of the railway made new destinations accessible and ready to be discovered. Travel posters of Valais were highlighting the advantages of cities and resorts as well as emphasizing the natural beauty of the mountains, leisure and sport activities. At the same time, commercial posters were also contributing to the promotion of the canton, for instance of wine producers.
Destinazioni in risalto
Il manifesto è stato il principale mezzo di comunicazione e di promozione alla fine del XIX e XX secolo, ed è stato un testimone della nascita del turismo. Ha contribuito significativamente a dar forma a un’immagine del Vallese caratterizzata da forti simboli identitari. L’arrivo della ferrovia ha reso accessibili nuove destinazioni che si intendeva far conoscere e promuovere. Il manifesto turistico del Vallese mette in risalto i punti di forza delle sue città e località, le bellezze naturali della montagna, le attività sportive e ricreative. Allo stesso tempo, il manifesto commerciale contribuisce anche alla promozione economica del cantone, come ad esempio i produttori di vino.
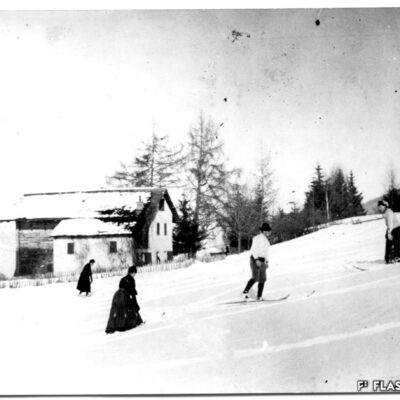
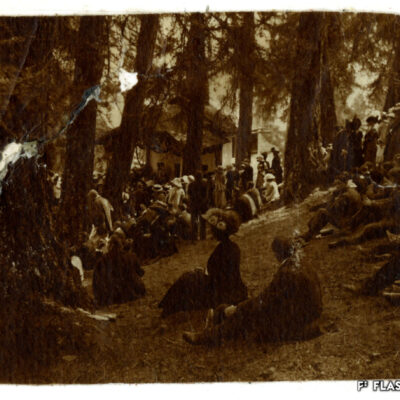
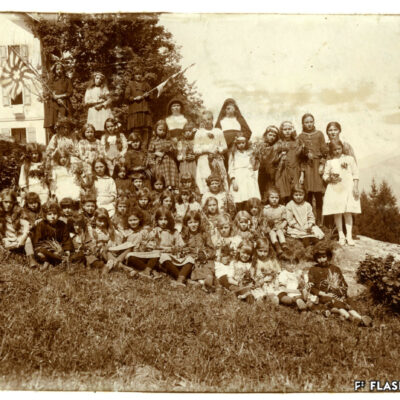
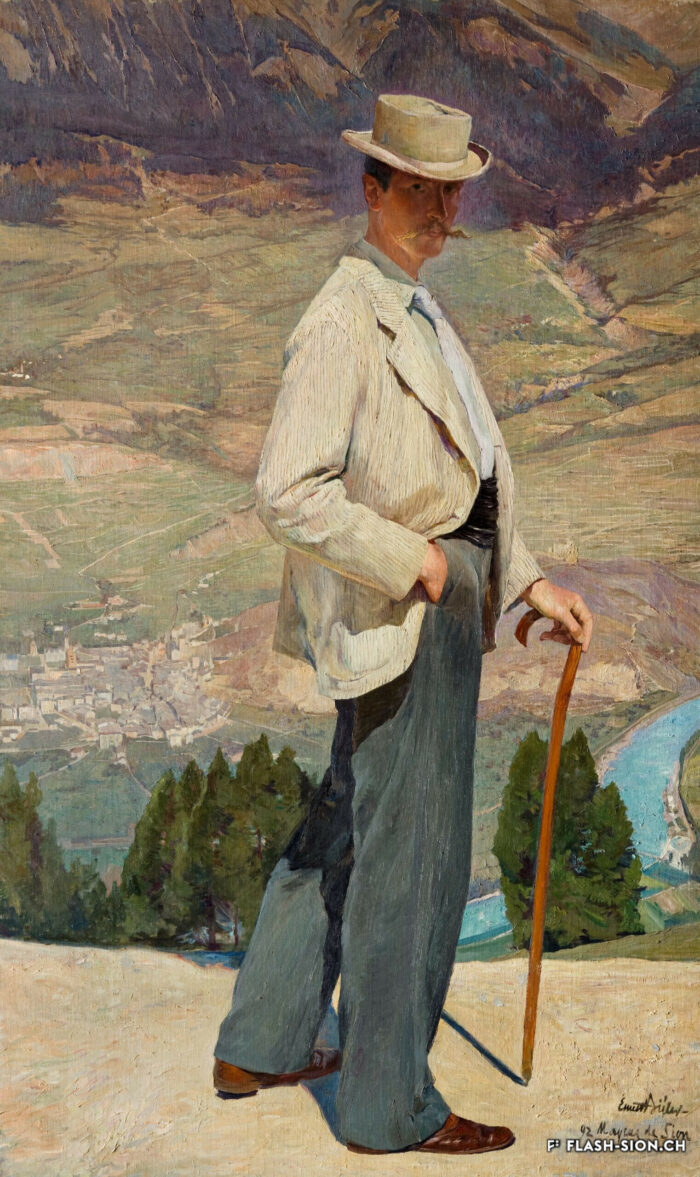
La montagne des Sédunois
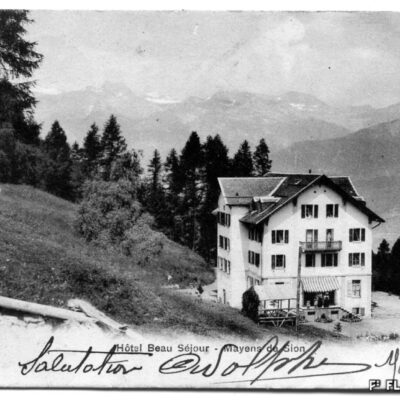
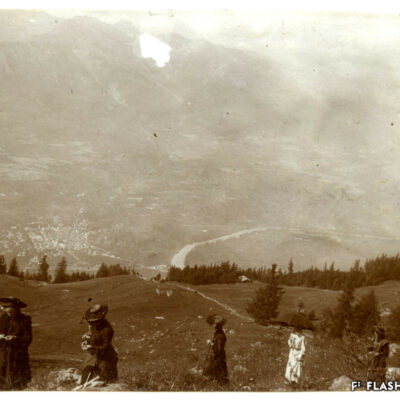
Lieu de villégiature estival par excellence, les Mayens-de-Sion ont fait et font encore la fierté des Sédunois. A la fin du 19e et au début du 20e siècle, ce territoire à cheval sur les communes de Vex, Salins, Les Agettes et même Veysonnaz, est le témoin d’un boom touristique. Les Mayens-de-Sion doivent beaucoup au succès de leurs hôtels, en particulier Le Grand-Hôtel, qui accueille alpinistes et clientèle de luxe suisse et étrangère. Epiceries, boucheries, boulangeries, cafés-restaurants, salon de coiffure et tennis viennent agrémenter la vie aux Mayens-de-Sion pour le grand bonheur des touristes comme des Sédunois habitués de longue date à y résider l’été.
Der Sittener Hausberg
Die Mayens-de-Sion sind bis heute ein wohlbekannter Sommerresidenzort und der Stolz der Sittener Bürger. Ende des 19. und Anfang des 20. Jahrhunderts erlebte das Gebiet der Maiensässe, das sich über die Gemeinden von Vex, Salins, Les Agettes und sogar Veysonnaz erstreckt, einen markanten touristischen Aufschwung. Diese Blütezeit ist auf den Erfolg der Hotellerie zurückzuführen. Das «Grand Hôtel», wo Bergsteiger und eine gehobene Klientel aus dem In- und Ausland absteigen, nimmt dabei eine ganz wichtige Rolle ein. Zudem tragen Lebensmittelgeschäfte, Metzgereien, Bäckereien, Cafés, Restaurants, Friseure und Tennisplätze zum angenehmen Sommeraufenthalt der Touristen und der Sittener Bevölkerung bei.
Sion residents’ mountain
The Mayens-de-Sion, a summer resort par excellence, has been and still is the pride of Sion residents. At the end of the 19th century and at the beginning of the 20th century, this territory straddling the municipalities of Vex, Salins, Les Agettes and even Veysonnaz witnessed a tourist boom. The Mayens-de-Sion owned much to the success of its hotels, in particular the Grand-Hôtel, which welcomed mountaineers as well as luxury Swiss and foreign clients. The enjoyment of life in the Mayens-de-Sion was ensured by grocery stores, butcher’s shops, bakeries, cafés-restaurants, hairdressers and tennis courts, much to the delight of both tourists and Sion residents, who traditionally spent their summer there.
La montagna dei Sedunesi
Luogo di villeggiatura estiva per eccellenza, i Mayens-de-Sion erano e sono ancora oggi l’orgoglio dei Sedunesi. Alla fine del 19esimo secolo e all’inizio del 20esimo secolo questo territorio a cavallo con i comuni di Vex, Salins, Les Agettes e anche Veysonnaz, è testimone di un boom turistico. I Mayens-de-Sion devono molto al successo dei loro hôtels, in particolare il Grand-Hôtel che accoglie alpinisti e clientela di lusso svizzera e straniera. Per la grande gioia dei turisti come pure dei Sedunesi abituati da tempo a passare la loro estate ai Mayens-de-Sion, si possono trovare negozi di alimentari, macellerie, panetterie, bar-ristoranti, parrucchieri e campi da tennis, contribuendo così a rendere più piacevole il soggiorno.
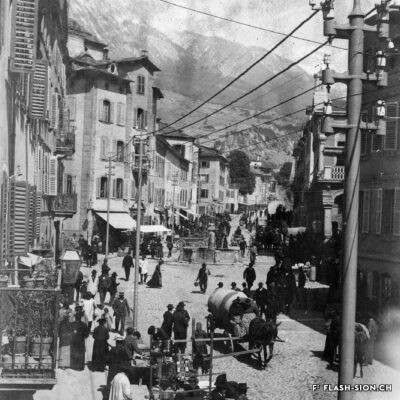
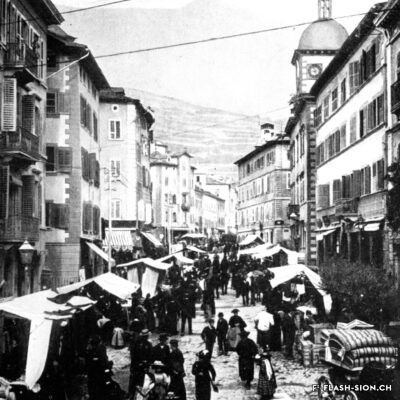
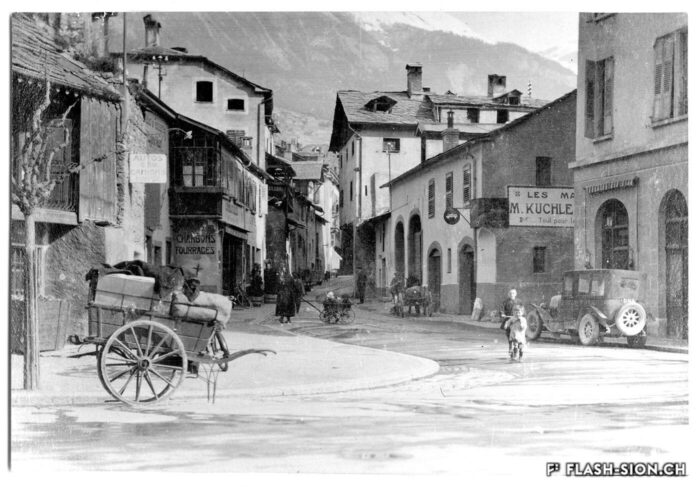
Sion, ville étape ou ville touristique ?
Au tournant du 20e siècle, les voyageurs de transit en Valais ne s’attardent guère à Sion qui semble avoir peu à leur offrir. La Société de développement de Sion (1902), l’Association touristique du Centre (1945) et l’Office du tourisme (1962) sont donc créés pour promouvoir la région de Sion. Cela passe par divers projets comme le jardin public de la Planta, par la mise en avant des monuments historiques, notamment lors de spectacles de type son et lumière, par les candidatures aux Jeux Olympiques ou encore la proximité avec les stations. Alors que les moyens de promotion évoluent au fil du temps, certains projets demeurent.
Sitten, Etappenort oder Tourismusort?
Zu Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts schien Sitten den Reisenden, die auf der Durchfahrt durchs Wallis waren, kaum etwas zu bieten zu haben. Zur touristischen Förderung der Region wurden daher über die Jahre verschiedene Institutionen gegründet: der Verkehrsverein von Sitten (1902), der Tourismusverein des Zentralwallis (1945) und das Tourismusbüro (1962). Sie lancierten Projekte wie der Bau der Parkanlage Planta, setzten sich mit Ton- und Lichtshows für die Aufwertung der Sittener Baudenkmäler ein, reichten Kandidaturen für die Olympischen Spiele ein und nutzten die Nähe zu den umliegenden Wintersportorten. Obwohl sich die Marketingmittel ständig weiterentwickeln, haben gewisse Tourismusprodukte bis heute nichts an ihrer Aktualität verloren.
Sion, a stopover or a tourist city?
At the turn of the 20th century, travellers passing through Valais hardly made a stop in Sion, which didn’t seem to have much to offer. The Sion Development Society (1902), the Centre Tourist Association (1945) and the Tourist Information Office (1962) were created to promote the region of Sion. This was achieved through various projects such as Planta Public Garden, by putting forward historical monuments, particularly during shows such as “Sound and light”, by bidding for the Olympic Games and thanks to the proximity to ski resorts. Even though the means of promotion have evolved over time, some projects remain.
Sion, città di transito o città turistica?
All’inizio del XX secolo i viaggiatori che transitavano in Vallese non si fermavano mai a Sion, città che sembrava avere poco da offrire. Il locale Ente del turismo (Société de développement de Sion, 1902), l’Associazione turistica del Centro (Association touristique du Centre, 1945) e l’Ufficio del turismo (l’Office du tourisme, 1962) furono quindi creati per promuovere la regione di Sion. Tale scopo è stato realizzato attraverso vari progetti come il giardino pubblico della Planta, la messa in risalto dei monumenti storici (in particolare durante gli spettacoli di suoni e luci), le candidature ai Giochi Olimpici e la vicinanza soprattutto alle stazioni invernali. Mentre i mezzi di promozione si evolvono nel corso del tempo, alcuni progetti rimangono.
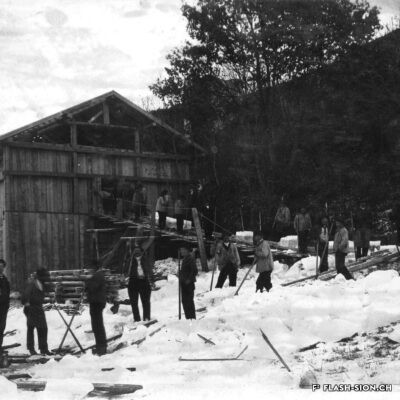
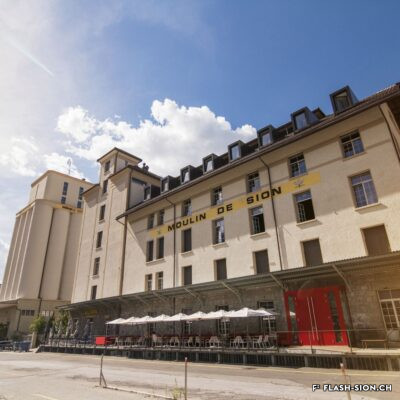
Un moulin à la pointe
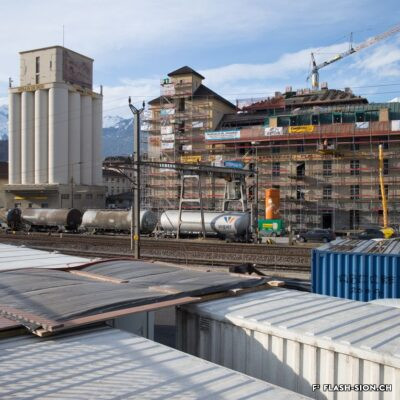
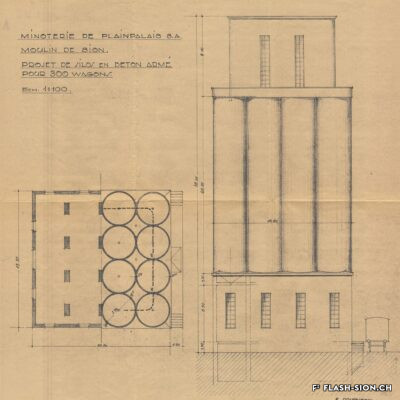
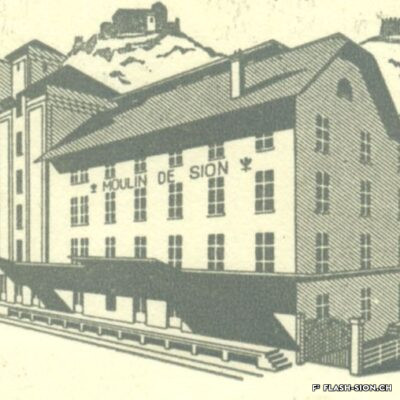
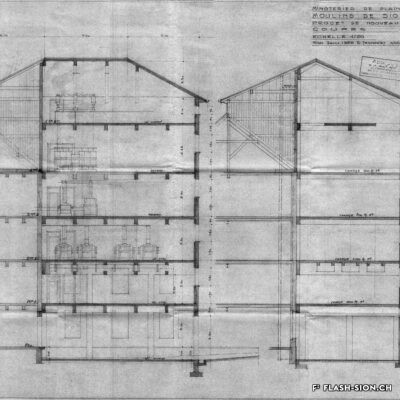
Après une tentative infructueuse à l’aube du 20e siècle, les Minoteries de Plainpalais (Genève) ouvrent une succursale à Sion en 1919. Le Moulin de Sion, entreprise d’importance pour le développement économique du Valais, s’agrandit rapidement. Les premiers silos en béton armé sont construits en 1925. Un peu moins de 15 ans plus tard, il faut en édifier d’autres. Le complexe continue de s’étendre jusqu’en 1980. Au fil du temps, les techniques évoluent et, dès 1984, les opérations sont entièrement automatisées. Le Moulin de Sion est alors un des plus modernes d’Europe ! Suite à l’obtention du label AOC pour le pain de seigle – premier pain d’Europe à le recevoir –, le Moulin de Sion se consacre entièrement à la fabrication de la farine de seigle. En 2015, la production est déplacée à Naters et le bâtiment peut alors être totalement réaffecté. Tout en conservant son apparence extérieure, les lieux accueillent désormais restaurants, fitness, bureaux et appartements notamment.
Modernste Mühlentechnik
Nach einem erfolglosen Niederlassungsversuch zu Beginn des 20. Jahrhunderts eröffnen die Minoteries de Plainpalais (Genf) schliesslich 1919 eine Zweigstelle in Sitten. Die Mühle von Sitten nimmt in der wirtschaftlichen Entwicklung des Wallis eine wichtige Stellung ein und wird schon nach kurzer Zeit ausgebaut. 1925 entstehen die ersten Silos aus Stahlbeton. Nur knapp 15 Jahre später, werden weitere Silos erstellt. Bis 1980 wird der Mühlenkomplex kontinuierlich erweitert und die Mühlentechnik modernisiert. Ab 1984 wird der Betrieb schliesslich vollständig automatisiert. Die Mühle Sitten zählt zu dieser Zeit zu einem der modernsten Betriebe Europas! Nach dem Eintrag des Walliser Roggenbrotes ins Register der Ursprungsbezeichnung (GUB) – das erste Brot in Europa mit dieser Bezeichnung – widmet sich die Mühle Sitten ganz der Herstellung von Roggenmehl. 2015 wird die Produktion nach Naters verlegt und die Industriebrache wird vollständig umgenutzt. Das äussere Erscheinungsbild der Mühle bleibt erhalten, der Gebäudekomplex beherbergt jedoch neu verschiedene Restaurants, ein Fitnesscenter, Büroräumlichkeiten und moderne Wohnungen.
A mill at the forefront
After an unsuccessful attempt at the beginning of the 20th century, the Minoteries de Plainpalais (Geneva) opened a branch in Sion in 1919. The Moulin de Sion (Mill of Sion), an important company for the economic development of Valais, expanded rapidly. The first reinforced concrete silos were built in 1925. A little less than 15 years later, others had to be built. The complex continued to expand until 1980. Over time, technologies evolved and, in 1984, operations were fully automated. The Moulin de Sion became one of the most modern in Europe! After obtaining the AOC (PDO) label for rye bread – the first bread in Europe to receive it – the Moulin de Sion devoted itself entirely to the production of rye flour. In 2015, production was moved to Naters and the building’s function was completely reassigned. While retaining its external appearance, the premises now house restaurants, fitness centres, offices and flats, among other things.
Un mulino all’avanguardia
Dopo un tentativo fallito all’inizio del XX secolo, i mulini di Plainpalais (Ginevra) aprirono una filiale a Sion nel 1919. Il Moulin de Sion, un’azienda importante per lo sviluppo economico del Vallese, si espanse rapidamente. I primi silos in cemento armato furono costruiti nel 1925. Poco meno di 15 anni dopo, è stato necessario costruirne altri. Il complesso continuò ad espandersi fino al 1980. Nel corso del tempo, le tecniche si sono evolute e, a partire dal 1984, le operazioni sono state completamente automatizzate. Il Moulin de Sion è diventato così uno dei più moderni d’Europa! Dopo aver ottenuto il marchio AOC per il pane di segale – il primo pane in Europa a riceverlo – il Moulin de Sion si è dedicato interamente alla produzione di farina di segale. Nel 2015 la produzione si è spostata a Naters e l’edificio ha potuto essere completamente riutilizzato. Pur mantenendo il suo aspetto esterno, i locali ospitano oggi, tra l’altro, ristoranti, centri fitness, uffici e appartamenti.
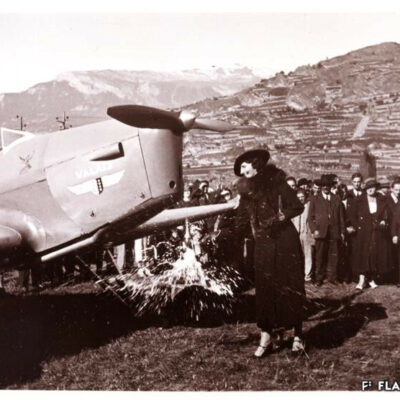
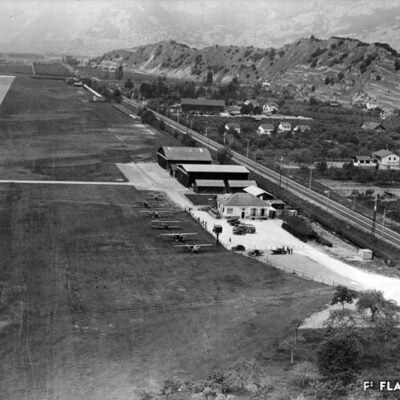
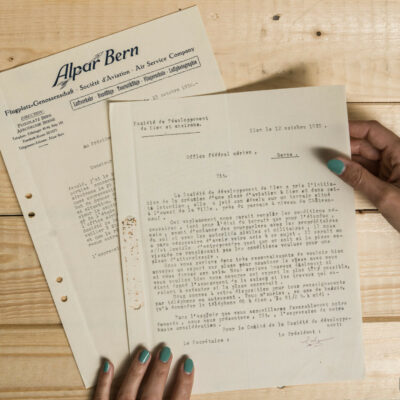
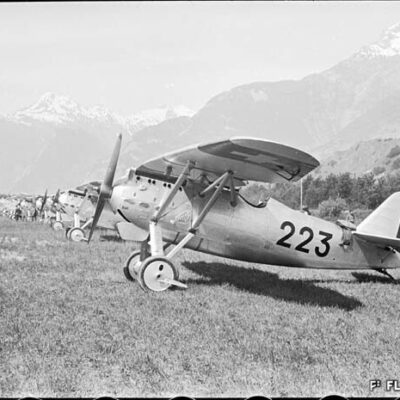
La conquête de l’air sédunoise
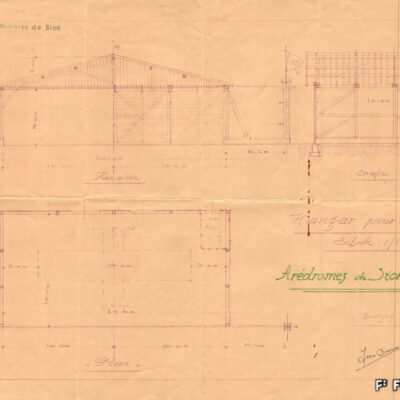
En 1925, les vols d’essai de la société « Transalpina » marqueront les esprits. L’entreprise inscrivant Sion comme aéroport douanier dans le réseau naissant des lignes aériennes internationales sera finalement jugée trop coûteuse. L’idée d’un service aérien touristique et commercial Genève-Milan par le Valais sera pourtant reprise peu après par l’aviateur visionnaire Jean Broccard. Suite au grave accident de ce dernier, la société de développement de Sion, conquise par la création d’un aéroport, se mobilise dès 1930 et mène avec succès les démarches aboutissant à l’inauguration de l’aérodrome sédunois en juin 1935. Celui-ci deviendra, dès 1943, l’unique aéroport de suisse où se côtoient vols civils et militaires.
Die Erschliessung des Luftraums von Sitten
Die Testflüge der Fluggesellschaft «Transalpina» von 1925 beeindruckten die Öffentlichkeit. Das Vorhaben, Sitten als Zollflughafen im entstehenden internationalen Flugnetz zu etablieren, scheitert schliesslich an allzu hohen Investitionskosten. Dennoch wird die Idee einer Flugverbindung Genf-Mailand mit Zwischenlandung im Wallis für Tourismus und Handel wenige Jahre später von dem visionären Piloten Jean Broccard wieder aufgegriffen. Überzeugt von dem Nutzen eines Flughafens, nimmt sich der Verkehrsverein Sitten nach dem folgenschweren Unfall Broccards dem Dossier an. Das Verhandlungsgeschick des Vereins führt im Juni 1935 zur Einweihung des Flugplatzes von Sitten. Ab 1943 wird dieser zum einzigen Schweizer Flughafen, wo sich Militär- und Zivilluftfahrt die Anlagen teilen.
Sion’s conquest of the air
In 1925, the « Transalpina » company’s test flights made a lasting impression. The enterprise to establish Sion as a customs airport within the emerging network of international airlines was eventually deemed too costly. However, the idea of tourist and commercial air service from Geneva to Milan via Valais was taken up shortly afterwards by a visionary aviator, Jean Broccard. Following Broccard’s serious accident, the Sion Development Society, convinced by the idea of the creation of an airport, took action as of 1930 and successfully carried out steps leading to the inauguration of Sion’s airfield in June 1935. Since 1943 it has been the only airport in Switzerland where civil and military flights come together.
La conquista del cielo sedunense
Nel 1925 i voli di prova della compagnia “Transalpina” lasciarono il segno. Il tentativo della società di includere Sion come aeroporto doganale nella rete emergente delle compagnie aeree internazionali venne infine ritenuto troppo oneroso. L’idea di un servizio aereo turistico e commerciale Ginevra-Milano attraverso il Vallese fu tuttavia ripresa poco dopo dall’aviatore visionario Jean Broccard. Dopo il grave incidente di quest’ultimo, l’Ente del turismo di Sion, conquistato dall’idea di creare un aeroporto, si attivò fin dal 1930 e condusse con successo il processo che portò all’inaugurazione dell’aeroporto di Sion nel giugno 1935. A partire dal 1943 divenne l’unico aeroporto della Svizzera in cui potevano essere combinati voli civili e militari.
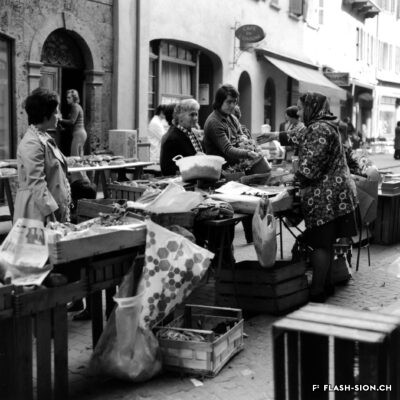
Sion, la gourmande
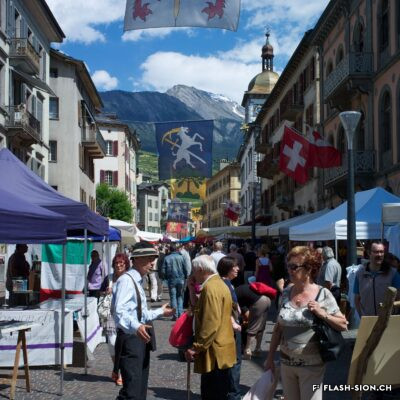
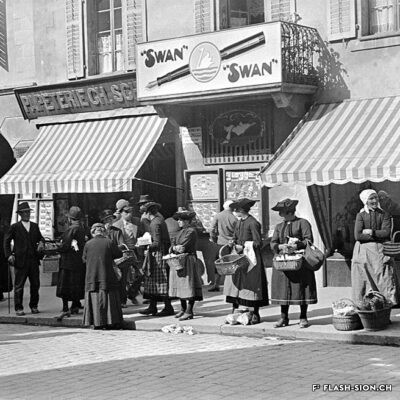
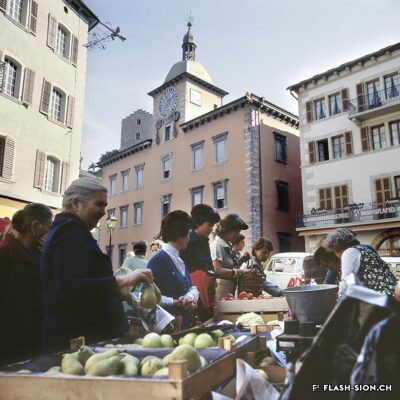
Le 17 novembre 1935, les salons de l’Hôtel de la Planta accueillent la première exposition et concours d’art culinaire du Valais. Si la mise en valeur des produits du pays et l’art culinaire sont représentés lors de fêtes des vignerons, il faudra cependant attendre 1973 pour voir s’organiser, à Sierre, un autre concours culinaire. A cette occasion, un membre du jury souligne déjà à quel point l’art du bien manger est en train de se perdre. L’avènement du fast-food et l’industrialisation de la filière alimentaire renforcent encore ce constat qui conduit à l’organisation de la première semaine romande du goût en 2001. Sion participe à la manifestation annuelle dès 2003 et est d’emblée élue ville du goût. Forte de cette expérience et pouvant compter sur des acteurs locaux enthousiastes, la nouvelle politique touristique adoptée dès 2007 positionne Sion comme ville du goût. Depuis, la ville étoffe son offre touristique autour du label « Sion terroir urbain ».
Sitten, die Genüssliche
Am 17. November 1935 findet in den Sälen des Hotels de la Planta die erste kulinarische Ausstellung des Wallis mit Kochwettbewerb statt. Obwohl Winzerfeste darauf die regionalen Produkte und die Kochkunst des Wallis würdigen, kommt es erst 1973 in Sierre zu einem weiteren Kochwettbewerb. Bei dieser Gelegenheit spricht ein Jurymitglied bereits seine Besorgnis über den zunehmenden Verlust des guten Essens aus. In der Folge verstärken das Aufkommen von Fastfood und die Industrialisierung der Lebensmittelkette zusätzlich die Junkfood-Welle, die 2001 massgeblich zur Organisation der ersten Westschweizer Genusswoche führt. Sitten nimmt ab 2003 an dieser jährlichen Veranstaltung teil und wird auf Anhieb zur Genussstadt des Jahres gewählt. Diese positive Erfahrung und die Begeisterung der lokalen Akteure ermutigen die Behörden, über ihre neue Tourismuspolitik Sitten als Genussstadt zu positionieren. Seither baut die Stadt ihr touristisches Angebot rund um die Marke «Sion, terroir urbain» kontinuierlich aus.
Sion, city of food lovers
On November 17, 1935, the lounges of the Hôtel de la Planta hosted the first exhibition and competition of culinary art in the canton of Valais. Even though the promotion of the country’s products and the culinary art were present at the time of wine festivals, it was necessary to wait until 1973 to see another culinary contest being organised in Sierre. Already on that occasion, a jury member emphasized the degree to which the art of eating well was being lost. This observation was further reinforced by the arrival of fast food and the industrialisation of the food sector, resulting in the organisation of the first Week of Taste in French-Speaking Switzerland in 2001. Sion first took part in the annual event in 2003 and was immediately elected City of Taste. Benefiting from this experience and being able to count on enthusiastic local players, the new tourism policy, adopted in 2007, positioned Sion as a City of Taste. Since then, the city has been developing its tourism offer around the label “Sion urban terroir”.
Sion, la buongustaia
Il 17 novembre 1935, i saloni dell’Hôtel della Planta ospitarono la prima mostra e concorso di arte culinaria del Vallese. Sebbene la promozione dei prodotti locali e l’arte culinaria fossero presenti nelle feste del vino, solo nel 1973 è stato organizzato un altro concorso culinario a Sierre. In questa occasione, uno dei membri della giuria ha sottolineato quanto si stia perdendo l’arte di mangiar bene. L’avvento dei fast food e l’industrializzazione dell’industria alimentare hanno rafforzato ulteriormente questa osservazione, che ha portato all’organizzazione della prima Settimana del Gusto francofona nel 2001. Sion ha partecipato all’evento annuale dal 2003 ed è stata subito eletta città del gusto. Forte di questa esperienza e potendo contare su attori locali entusiasti, la nuova politica turistica adottata nel 2007 ha posizionato Sion come città del gusto. Da allora, la città ha sviluppato la sua offerta turistica attorno al marchio “Sion terroir urbain”.
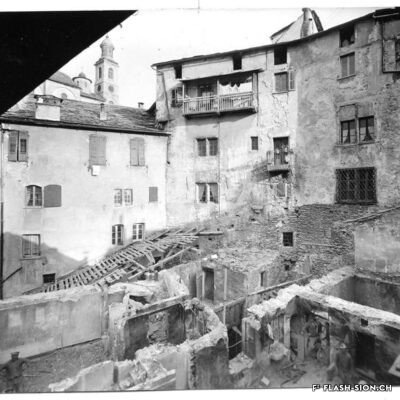
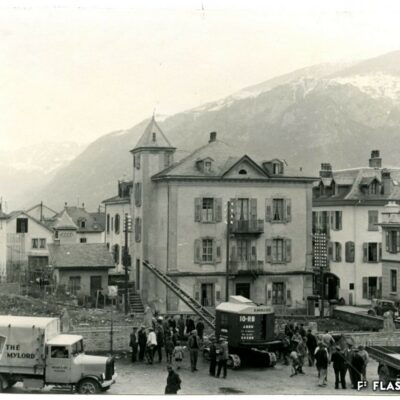
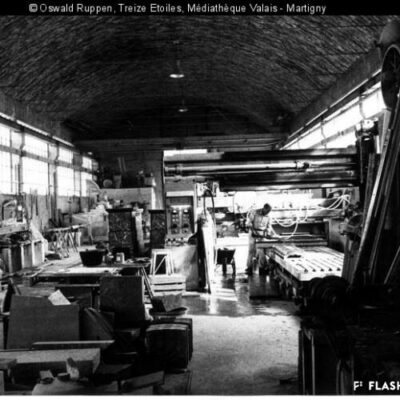
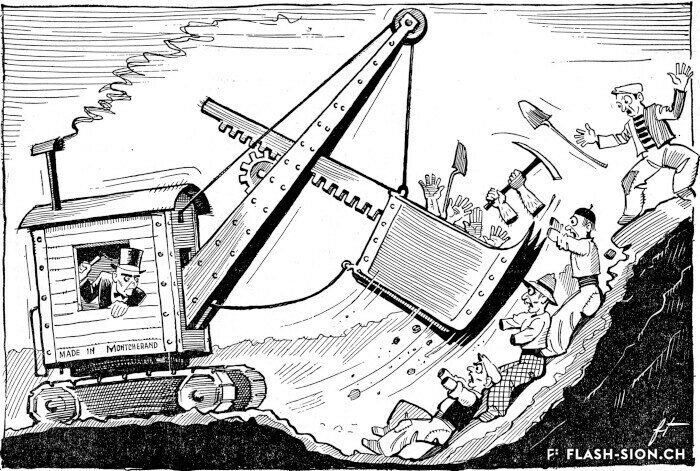
La machine infernale
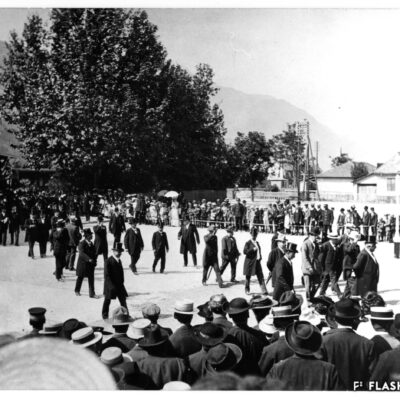
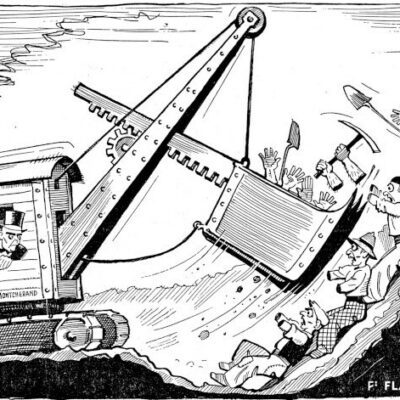
Scandale lors de la première utilisation d’une pelle mécanique à Sion ! En 1937, lors des fouilles pour la construction de l’immeuble « Les Rochers » sur la place du Midi, l’engin diabolique suscita le mécontentement des ouvriers du bâtiment, dont beaucoup étaient au chômage. Face au grondement prolétaire, le conseil communal, réuni en urgence, interdit l’emploi de cette machine « voleuse de travail ». Une interdiction générale en Valais, imposée par le Conseil d’Etat, suivit cette décision. Elle ne durera finalement que quatre mois.
Die Höllenmaschine
Es kam zu einem regelrechten Skandal, als 1937 der erste Bagger in Sitten auffuhr. Auf der Baustelle der Liegenschaft „Les Rochers“ an der Place du Midi weckte die Höllenmaschine gewaltigen Unmut unter den von Arbeitslosigkeit geplagten Bauarbeitern. Ob dem Groll der Arbeiterschaft berief der Gemeinderat umgehend eine Dringlichkeitssitzung ein und verbot kurzum den Einsatz der „arbeitsklauenden“ Baumaschine. Diesem Entscheid folgte der Staatsrat mit einem generellen Verbot für das ganze Wallis. Nach 4 Monaten wurde dieses bereits wieder aufgehoben.
The infernal machine
The first use of a power shovel in Sion resulted in a scandal ! In 1937, while digging ground for the construction of the building “Les Rochers » on the Place du Midi, the evil machine caused workmen discontent, as many of them were unemployed at the time. As a reaction to rising proletarian discontent, the City Council gathered urgently and forbid the use of a „job-stealing“ machine. Following this decision, a general prohibition was declared in Valais by the Conseil d‘Etat. In the end, it only last for four months.
La machine infernale
Scandale lors de la première utilisation d’une pelle mécanique à Sion ! En 1937, lors des fouilles pour la construction de l’immeuble « Les Rochers » sur la place du Midi, l’engin diabolique suscita le mécontentement des ouvriers du bâtiment, dont beaucoup étaient au chômage. Face au grondement prolétaire, le conseil communal, réuni en urgence, interdit l’emploi de cette machine « voleuse de travail ». Une interdiction générale en Valais, imposée par le Conseil d’Etat, suivit cette décision. Elle ne durera finalement que quatre mois.
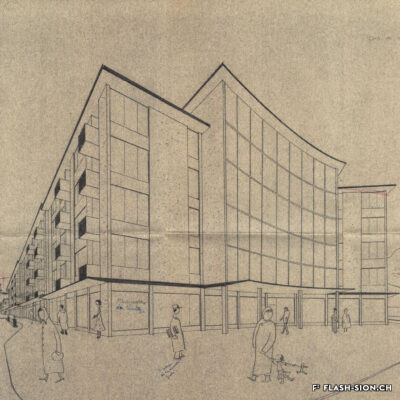
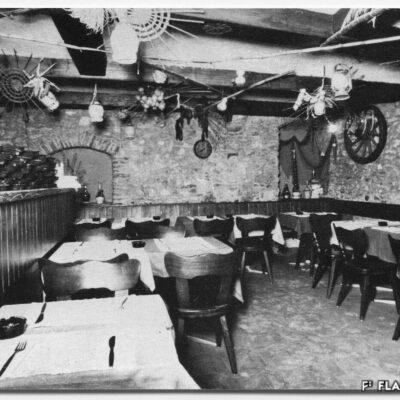
Danses interdites à la Matze
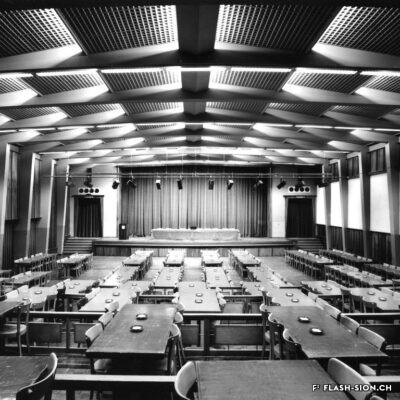
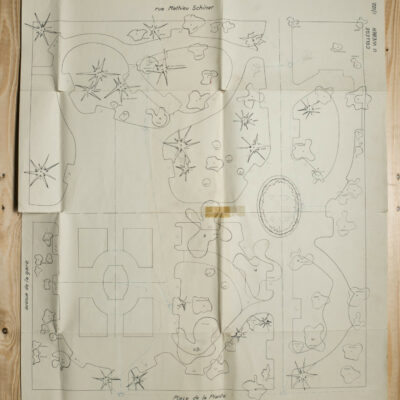
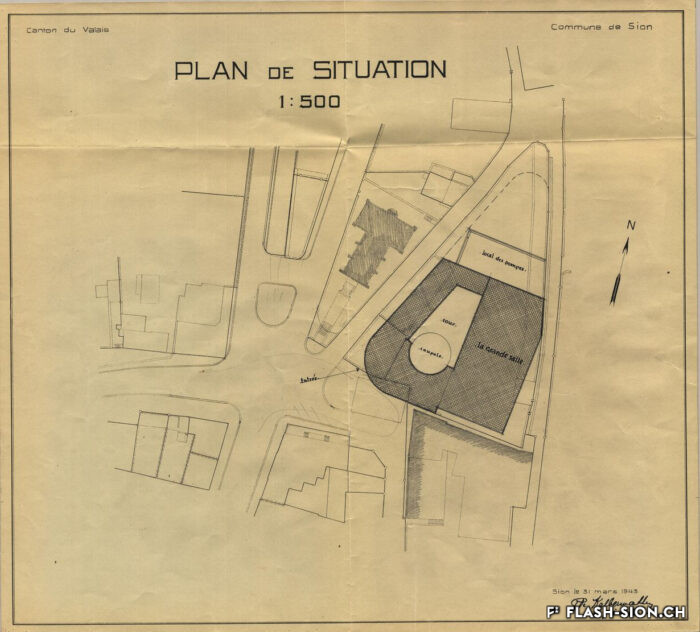
Au milieu des années 1950, le complexe de la Matze introduit une nouvelle échelle et manière de penser la ville dans un quartier encore marqué par des vergers. C’est le Groupement Artisanal, fondé par les frères Raymond, Marcel et Pierre Kamerzin et Armand Varone, qui porte et finance le projet dessiné par l’architecte Robert Tronchet. Avec ses 13 commerces de première nécessité, un hôtel, un restaurant-bar et 87 appartements à loyer modéré, il constitue jusqu’à sa démolition en 2014 une véritable petite cité à lui seul. La légendaire Salle de la Matze, avec ses 800 places assises, reste longtemps la plus grande salle de spectacle du canton. Elle ouvre en 1959, après d’âpres négociations qui ont conduit les promoteurs à accepter l’inscription d’une servitude en faveur de la Municipalité. Quant au premier dancing de plaine, perçu comme un lieu de « débauche dangereux » et refusé par la Ville, il reçoit finalement l’approbation de l’évêque… sous conditions de fermetures temporaires obligatoires durant les périodes de l’Avent et du Carême.
Verbotene Tänze in der Matze
Mitte der 1950er Jahre setzt die Grossüberbauung der Matze in einem von Obstgärten geprägten Quartier einen neuen Maßstab und Ansatz der Stadtplanung. Das Projekt des Architekten Robert Tronchet wird vom Groupement Artisanal der Gebrüder Raymond, Marcel und Pierre Kamerzin sowie Armand Varone getragen und finanziert. Mit seinen 13 Geschäften für den täglichen Bedarf, einem Hotel, einem Restaurant-Bar und 87 Wohnungen mit erschwinglichen Mieten bildet der Komplex bis zu seinem Abriss im Jahr 2014 eine kleine Stadt in sich. Der legendäre Saal der Matze mit seinen 800 Sitzplätzen bleibt lange Zeit der größte Veranstaltungssaal des Kantons. Er wird nach zähen Verhandlungen, in deren Verlauf die Bauherren zur Eintragung einer Grunddienstbarkeit zugunsten der Gemeinde verpflichtet werden, 1959 eröffnet. Das erste Tanzlokal in der Talebene hingegen wird als Ort “gefährlicher Ausschweifungen” wahrgenommen und von der Stadt vorerst abgelehnt. Schliesslich erhält das Lokal die Genehmigung des Bischofs … unter der Bedingung, dass das Dancing während der Advents- und Fastenzeit geschlossen bleibt.
Forbidden dancing at la Matze
By the mid-50’s, the building complex of la Matze was a pionneer reference in terms of scale and way of conceiving the town in an area still imprinted by orchards. The Raymond brothers together with Marcel and Pierre Kamerzin and Armand Varone founded the Groupement Artisanal (craftsmen union), which was supporting and funding the project drafted by the architect Robert Tronchet: 13 basic goods shops, a hotel, a bar-restaurant and 87 moderate rental price flats. Until 2014 -when it was pulled down- it stood as a shear little town per se. The legendary hall la Matze -with a capacity of 800 seats- remained the biggest hall of the canton for quite a while. Its was opened in 1959 following up fierce negociations, among which promoters came to agree upon a right of way in favour of the Municipality. As to the first dancing ever existing in the plain it was looked upon as a ‘‘dangerous’’ place of ‘‘debauchery’’. First turned down by the Town, it was finally approved by the bishop… under the conditions of temporarily and compulsorily closing down during the Advent and Lent.
Danze proibite alla Matze
A metà degli anni Cinquanta, il complesso della Matze introdusse una nuova scala e un modo di pensare la città in un quartiere ancora dominato dai frutteti. Fu il raggruppamento artigianale “Groupement Artisanal”, fondato dai fratelli Raymond, Marcel e Pierre Kamerzin e da Armand Varone, che sviluppa e finanzia il progetto dell’architetto Robert Tronchet. Con 13 commerci essenziali, un hotel, un ristorante-bar e 87 appartamenti a basso costo, costituiva una vera e propria piccola città a sé stante, fino alla sua demolizione nel 2014. La leggendaria Salle della Matze, con i suoi 800 posti a sedere, è rimasta a lungo la più grande sala da spettacolo del Cantone. Fu inaugurata nel 1959, dopo dure trattative che portarono i promotori ad accettare l’iscrizione di una servitù a favore del Comune. Quanto alla prima sala da ballo della pianura, percepita come luogo di “pericolosa dissolutezza” e rifiutata dalla città, riceve finalmente l’approvazione del vescovo… con l’obbligo di chiusura temporanea durante i periodi di Avvento e Quaresima.
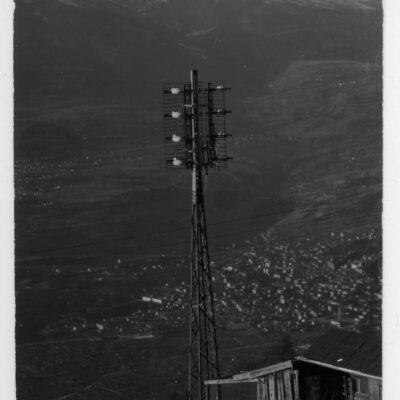
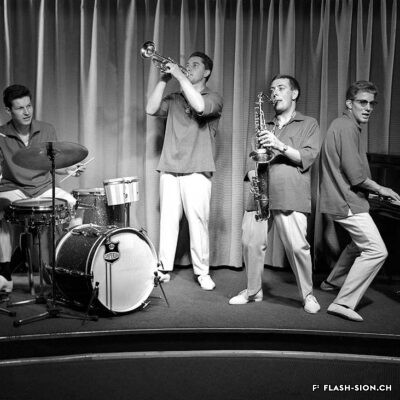
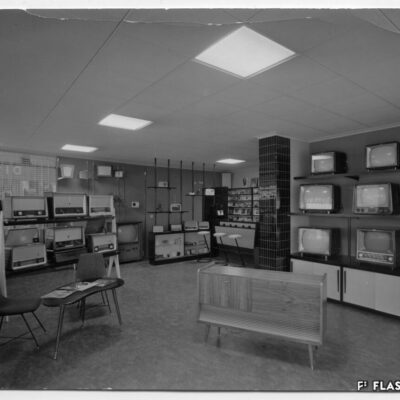
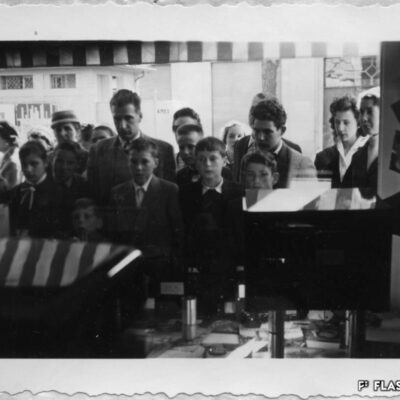
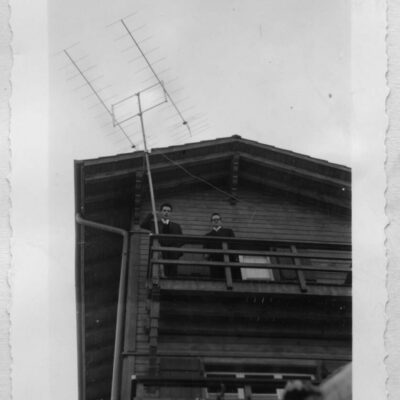
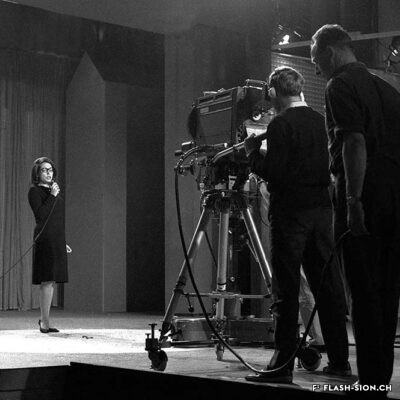
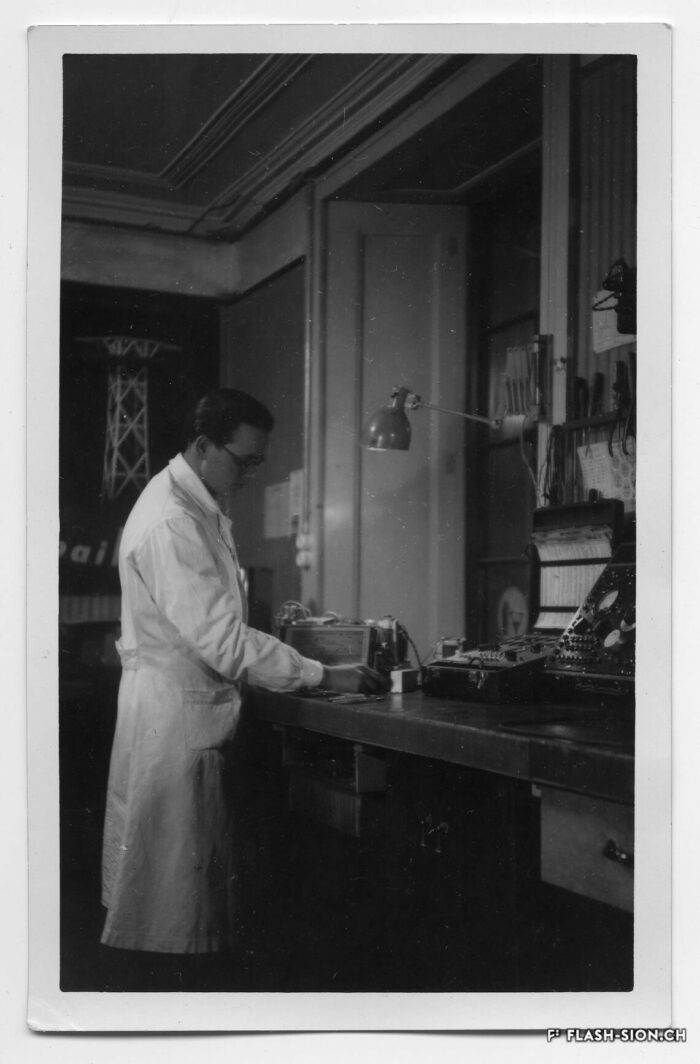
La télé dans le viseur
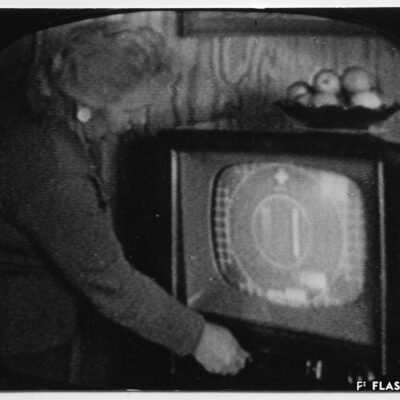
La télévision débarque à Sion pour la première fois en 1958, grâce à la pugnacité de l’ingénieur Serge Michelotti. Arrivé en Valais en 1944, cet inventeur jurassien spécialisé en radio-électricité s’indigne que le Valais n’ait pas encore accès au petit écran, la faute aux montagnes élevées. Afin de capter l’émetteur romand de la Dôle (VD), il installe une station relais sur les hauteurs de Veysonnaz. Il s’agit du premier réémetteur privé de Suisse. Les Valaisans découvrent avec joie la première émission officielle de la télévision le 17 avril, sur la centaine de postes installés dans les cafés de la région.
Den Fernseher im Auge
Das Fernsehen feiert 1958 seine Premiere in Sitten und ist der Beharrlichkeit des Ingenieurs Serge Michelotti zu verdanken. Der auf Radioelektrizität spezialisierte Tüftler aus dem Jura zieht 1944 ins Wallis. Er zeigt sich empört darüber, dass das Wallis wegen seiner geographischen Lage, umgeben von hohen Gebirgsketten, noch keinen Zugang zum Fernsehen hat. Um den welschen Sender auf dem La Dôle (VD) zu empfangen, installiert er eine Relaisstation oberhalb von Veysonnaz. Dabei handelt es sich um die erste private Sendestation der Schweiz. Am 17. April ist es soweit. Mit Begeisterung führen sich die Walliser die erste offizielle Fernsehsendung vor den rund hundert, in Gasthäusern der Region installierten Geräten zu Gemüte.
TV within reach
Television first arrived in Sion in 1958 thanks to the pugnacity of engineer Serge Michelotti. As he came to Valais in 1944, the Jurassian maker and specialist in radio electricity is outraged that Valais does not have access to the small screen yet, due to high mountains. In order to receive the romand transmitter of La Dôle (VD), he sets up a relay station on the heights of Veysonnaz. This is the first private retransmitter in Switzerland. The Valaisans people enthusiastically discover the first official television broadcast on April 17, on the hundreds of stations installed in local cafés.
La télé dans le viseur
La télévision débarque à Sion pour la première fois en 1958, grâce à la pugnacité de l’ingénieur Serge Michelotti. Arrivé en Valais en 1944, cet inventeur jurassien spécialisé en radio-électricité s’indigne que le Valais n’ait pas encore accès au petit écran, la faute aux montagnes élevées. Afin de capter l’émetteur romand de la Dôle (VD), il installe une station relais sur les hauteurs de Veysonnaz. Il s’agit du premier réémetteur privé de Suisse. Les Valaisans découvrent avec joie la première émission officielle de la télévision le 17 avril, sur la centaine de postes installés dans les cafés de la région.
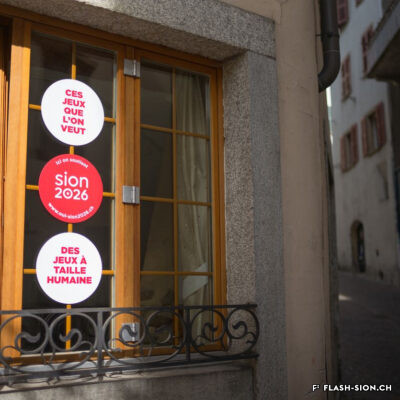
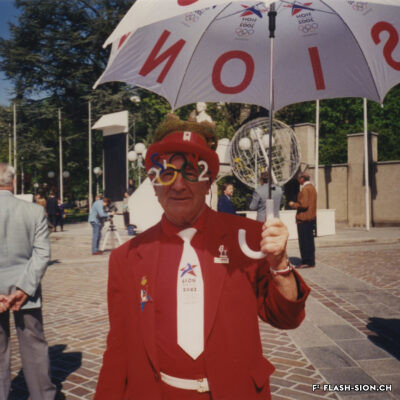
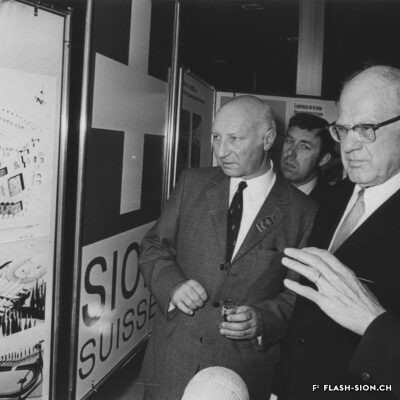
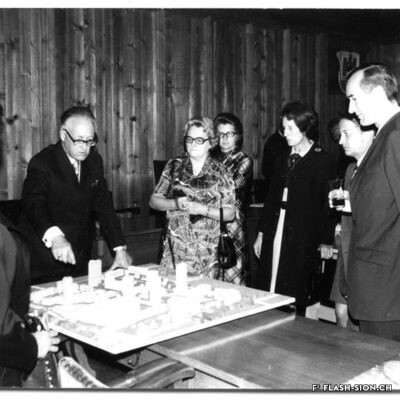
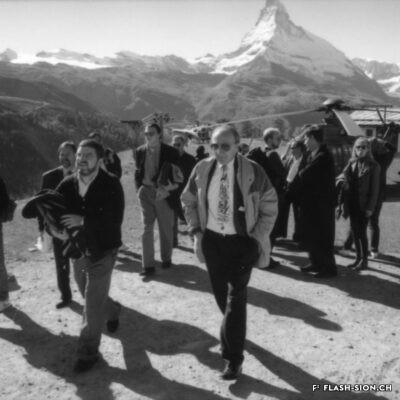
L’impossible histoire des JO à Sion ?
Printemps 1960, un comité étudie pour la première fois la possibilité d’accueillir les Jeux Olympiques d’hiver (JO) à Sion en 1968. La population vote pourtant en 1963 contre le crédit prévu pour cette entreprise. Malgré un premier échec, des candidatures sont officiellement lancées pour les JO 1976, 2002, 2006 et 2026. Le refus provient tantôt du Comité International Olympique (CIO), par ailleurs accusé de corruption, tantôt des autorités communales, refusant de porter le projet sans l’appui financier du Canton et de la Confédération. Les citoyens valaisans, pour leur part, indignés de voir l’argent public investi dans un tel projet et pas ailleurs, craignent de devoir éponger un éventuel déficit. Alors que les candidatures de 2002 et 2006 font rêver une majorité de Valaisans, celle de 2026 a plutôt suscité les dissensions et mis en lumière le décalage entre les ambitions des promoteurs du projet et les préoccupations écologistes grandissantes au sein de la population. Malgré tout, l’idée d’une candidature est émise pour 2030, mais n’aboutit pas. Sion poursuivra-t-elle son rêve olympique à l’heure d’une possible candidature suisse pour 2030 ?
Die unmögliche Geschichte der Olympischen Spiele in Sitten
Im Frühjahr 1960 prüft ein Komitee erstmals die Möglichkeit zur Austragung von Olympischen Winterspielen 1968 in Sitten. Die Bevölkerung lehnt den vorgesehenen Kredit für das Vorhaben jedoch 1963 ab. Trotz dieser Abfuhr werden 1976, 2002, 2006 und 2026 weitere Olympia-Kandidaturen lanciert. Die Ablehnung der Bewerbungen ist einmal auf das damals der Korruption bezichtigte Olympische Komitee (IOC) zurückzuführen, ein andermal auf die Gemeindebehörden, die das Projekt nicht ohne finanzielle Absicherung durch Kanton und Bund zu tragen bereit sind. Die Walliser Bevölkerung wiederum zeigt sich empört darüber, dass öffentliche Gelder nicht besser investiert werden, und befürchtet, dass der Ausgleich eines allfälligen Defizits auf sie zurückfällt. Während bei den Olympia-Kandidaturen von 2002 und 2006 noch eine Mehrheit der Walliser Bevölkerung mitfiebert, führt die Bewerbung für die Spiele von 2026 eher zu Meinungsverschiedenheiten und zeigt eine zunehmende Diskrepanz zwischen den Ambitionen der Befürwortenden und dem wachsenden ökologischen Bewusstsein in der Bevölkerung auf. Dennoch wird eine Walliser Kandidatur 2030 nochmals in Erwägung gezogen, bevor diese kurz darauf fallen gelassen wird. Ob sich Sittens Olympia-Traum über die aktuellen Bestrebungen für eine Schweizer Kandidatur 2030 doch noch verwirklichen lässt, bleibt dahingestellt.
The impossible tale of the Olympic Games in Sion?
In the spring of 1960, for the first time, a committee studied the possibility of hosting the 1968 Winter Olympic Games in Sion. However, in 1963, the population voted against funding this project. Despite this initial defeat, bids were officially submitted for the 1976, 2002, 2006 and 2026 Olympic Games. The opposition came either from the International Olympic Committee (IOC), incidentally accused of corruption or from the local authorities, who refused to support a project without the financial support of the Canton and the Confederation. The local population, outraged to see public money being invested in such a project and not elsewhere, feared that they would have to cover any potential deficit. While the 2002 and 2006 bids revealed a united and utopic Valais, the 2026 bid sparked divisions and highlighted the gap between the ambition of the promoters of the project and the growing environmental concerns of the population. The idea of another bid for 2030 has nonetheless been issued but did not come to fruition. Will Sion pursue its olympic ambition despite Switzerland becoming a potential candidate for 2030?
La storia impossibile dei Giochi Olimpici a Sion?
Nella primavera del 1960, un comitato studiò per la prima volta la possibilità di ospitare le Olimpiadi invernali a Sion del 1968. Tuttavia, nel 1963 la popolazione votò contro il credito previsto per questo progetto. Nonostante un iniziale insuccesso, furono lanciate ufficialmente le candidature per i Giochi Olimpici del 1976, 2002, 2006 e 2026. Il rifiuto arrivò sia dal Comitato Olimpico Internazionale (CIO), accusato inoltre di corruzione, e dalle autorità comunali, che si sono rifiutate di sostenere il progetto senza l’appoggio finanziario del Cantone e della Confederazione. I vallesani, dal canto loro, indignati nel vedere il denaro pubblico investito in un progetto del genere e non altrove, temono di dover coprire un eventuale deficit. Mentre le candidature del 2002 e del 2006 rappresentano il sogno della maggioranza dei vallesani, quella del 2026 è stata più che altro fonte di dissenso, evidenziando la discrepanza tra le ambizioni dei promotori del progetto e le crescenti preoccupazioni ecologiche della popolazione. Tuttavia, l’idea di una candidatura vallesana è stata avanzata per il 2030, ma non è stata realizzata. Sion perseguirà il suo sogno olimpico in vista di una possibile candidatura svizzera per il 2030?
Un escalier pas comme les autres
« Unique dans le canton, c’est « l’escalator », cet escalier infatigable qui monte et qui descend. » Pour finaliser leur nouvelle mue, les plus grands magasins valaisans s’offrent en 1962-1963 les premiers escalators du Valais. Résolument innovant pour l’époque, ces escaliers roulants aux dimensions imposantes apportent la dernière touche de modernisation aux nouveaux lieux de la Porte-Neuve, qui fêteront l’année suivante leurs cent ans d’existence.
Keine herkömmliche Treppe
“Sie ist einzigartig im Kanton, die Rolltreppe, welche unermüdlich auf- und absteigt.» Im Neubau der „Galeries du Midi“ von 1962/63, im damals grössten Kaufhaus des Kantons, waren diese imposanten, fahrenden Treppen eine Sensation. Sie verliehen dem neuen Gebäude bei der Porte-Neuve den letzten, modernen Schliff. Im darauffolgenden Jahr feierte das Unternehmen sein hundertjähriges Bestehen.
A highly unusual staircase
“It’s unique in the canton: the ‘escalator’, the staircase that never stops moving up and down.” To add the finishing touch to their new look, the largest shops in Valais installed the canton’s first escalators in 1962-1963. Back in those days, these immense moving staircases were a bold innovation – the last word in modern technology for the new premises of the Porte-Neuve shopping mall, which will celebrate its centenary next year.
Un escalier pas comme les autres
« Unique dans le canton, c’est « l’escalator », cet escalier infatigable qui monte et qui descend. » Pour finaliser leur nouvelle mue, les plus grands magasins valaisans s’offrent en 1962-1963 les premiers escalators du Valais. Résolument innovant pour l’époque, ces escaliers roulants aux dimensions imposantes apportent la dernière touche de modernisation aux nouveaux lieux de la Porte-Neuve, qui fêteront l’année suivante leurs cent ans d’existence.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Le « Boccalino » ouvre ses portes en 1968 à la rue de Conthey. Il est le premier établissement sédunois à mettre à l’honneur la pizza, plat symbole de toute une nation. Des épiceries aux noms italiens existaient par ailleurs en vieille ville dès le début du 20e siècle, tels que Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli ou encore Guido Nichini. Ce dernier, spécialisé dans la charcuterie et salaisons « exclusivement italiennes » avait à l’origine pignon sur la « via regia », une des appellations de l’actuelle rue de Conthey.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Das Restaurant “Boccalino” wurde 1968 in der Rue de Conthey eröffnet. Es war das erste Restaurant der Stadt, das sich ganz dem italienischen Nationalgericht, der Pizza, verschrieb. Seit Anfang des 20. Jahrhunderts sind in der Altstadt von Sitten auch Lebensmittelgeschäfte mit italienischen Namen wie Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli und Guido Nichini bekannt. Letzterer hatte sich insbesondere auf italienische Wurst- und Pökelwaren spezialisiert und führte seinen Feinkostladen ursprünglich an der “Via Regia”, wie die heutige Rue de Conthey ebenfalls genannt wurde.
Mangia che ti fa bene
The Boccalino opened on Rue de Conthey in 1968. It was the first restaurant in Sion to feature pizza – the iconic dish of an entire nation. Elsewhere in the old town, there had been grocery stores with Italian names such as Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli and Guido Nichini since the early 20th century. Nichini, which specialised in “exclusively Italian” cooked and cured meats, originally fronted onto the “via regia”, one of the names for the street now known as Rue de Conthey.
Mangia che ti fa bene
Il “Bocccalino” apre le sue porte nel 1968 nella “rue de Conthey”. È il primo stabilimento di Sion ad omaggiare la pizza, piatto simbolo di tutta una nazione. Botteghe con nomi italiani esistevano d’altronde nella città vecchia già all’inizio del 20° secolo, come Zoni&Schmidt, Zanoli oppure Guido Nichini. Quest’ultimo, specializzato in prodotti di salumeria e carni affumicate “esclusivamente italiane” possedeva un negozio nella “via regia”, uno dei nomi dell’attuale “rue de Conthey”.
La fuite des cerveaux ?
Dès le début des années 2000, la notion de fuite des cerveaux s’impose dans les médias et décrit, études à l’appui, un phénomène qui touche les cantons non universitaires : une majorité des étudiants expatriés ne reviennent pas au pays une fois leur diplôme en poche. Pour le Valais, le chiffre de 70% est articulé. Cet exode a des conséquences socio-économiques importantes et signale un manque d’emplois hautement qualifiés dans le tissu économique local. Est-ce la prise de conscience de cette problématique qui a fait évoluer le paysage de la formation tertiaire en Valais ? A Sion, la transformation du quartier sous-gare, en particulier la rue de l’Industrie, en pôle de formation et d’innovation concrétise ce changement de paradigme.
Braindrain ?
Anfang der 2000er-Jahre hat sich der Begriff Braindrain in den Medien durchgesetzt. Abgestützt auf Studien beschreibt dieser ein Phänomen, das nicht-universitäre Kantone betrifft: Die Mehrheit der Studierenden kehrt nach dem Abschluss an einer ausserkantonalen Bildungsstätte nicht in den Heimatkanton zurück. Im Wallis spricht man von einer Abwanderungsrate von 70%. Diese Abwanderung hat erhebliche sozioökonomische Folgen und deutet auf einen Mangel an hochqualifizierten Arbeitsplätzen in den lokalen Wirtschaftsstrukturen hin. Ist es das Bewusstsein für diese Problematik, das zur Förderung der Walliser Hochschullandschaft geführt hat? In Sitten zeugt die Umgestaltung des Quartiers Sous-Gare in ein Bildungs- und Innovationsstandort von diesem Paradigmenwechsel.
A brain drain?
In the early 2000s, the notion of brain drain made its way into the media and introduced, with studies to back it up, a phenomenon that affects non-university cantons: most expat students don’t return to their canton of origin once they have obtained their degree. For Valais it was estimated to be 70% of them. This exodus had important socio-economic consequences and implied a lack of highly qualified jobs in the local economy. Could it be that the awareness of this problem has helped to change the landscape of tertiary education in Valais? A concrete example of this paradigm shift is the transformation of the district situated “under the train station”, in particular the ‘Industrie’ Street, into a training and innovation centre.
La fuga di cervelli ?
Dall’inizio degli anni 2000 la nozione di fuga di cervelli s’impone nei media e descrive, basandosi su studi, un fenomeno che riguarda i cantoni non universitari: la maggioranza degli studenti espatriati una volta diplomati non ritornano più nel loro cantone. Per il Vallese questo fenomeno tocca il 70%. L’esodo ha delle conseguenze socio-economiche importanti e indica una mancanza d’impieghi altamente qualificati nell’ambito economico locale. È la consapevolezza di questo problema che ha fatto evolvere il panorama della formazione terziaria in Vallese? A Sion, la trasformazione del quartiere sotto la stazione, in particolare la Rue de l’Industrie, in un polo di formazione e d’innovazione concretizza questo cambiamento di paradigma.
La convivialité dans le panier
Dès le Moyen Age, les foires annuelles et concours de bétail animent la cité. Rythmant les saisons au gré des marchandises, les marchés des 19e et 20e siècles drainent un public varié et reconnectent la plaine à la montagne, ainsi que les clients aux producteurs et aux marchands. Qualité, prix et poids des marchandises sont contrôlés et les stands réglementés. Situé au cœur de la ville, le marché est alors un acteur principal de l’économie locale. Après un désintérêt progressif dès la seconde moitié du 20e siècle, le marché renaît en 2003, à l’initiative de l’Association des habitants de la vieille ville. Renouant avec la tradition, l’événement hebdomadaire très fréquenté atteste de sa grande attractivité. Devenu incontournable, le marché de la vieille ville s’affirme aujourd’hui comme lieu de rencontre et de convivialité.
Ein Marktkorb voller Geselligkeit
Seit dem Mittelalter beleben Jahrmärkte und Viehschauen die Stadt. Das rein saisonale Angebot auf den Wochenmärkten des 19. und 20. Jahrhunderts veranschaulicht den Lauf der Jahreszeiten, zieht ein vielfältiges Publikum an, verbindet die Seitentäler mit der Rhoneebene, sowie die Käufer mit den Produzenten und Händlern. Qualität, Preis und Gewicht der Waren werden kontrolliert und die Stände sind reglementiert. Mitten in der Stadt angesiedelt, entwickelt sich der Wochenmarkt zu einem der wichtigsten Zweige der lokalen Wirtschaft. In der zweiten Hälfte des 20. Jahrhunderts verliert der Markt zusehends an Bedeutung, bis er 2003 auf Initiative des Altstadt-Quartiervereins schliesslich wieder auflebt. Heute knüpft der Wochenmarkt gebührend an seine Tradition an und die vielen Besucherinnen und Besucher zeugen von seiner Attraktivität. Die Veranstaltung ist zu einem wöchentlichen Treffpunkt geworden, wo das gesellige Beisammensein im Vordergrund steht.
Conviviality in the basket
Since the Middle Ages, annual fairs and livestock competitions have brought life to the city. Throughout the seasons and their related produce, the markets of the 19th and 20th centuries attracted a varied public and connected the plain to the mountains, as well as customers to producers and merchants. The quality, price and weight of the goods were controlled, and the stalls were regulated. Situated in the heart of the city, the market became a major player in the local economy. After a gradual loss of interest in the second half of the 20th century, the market was revived in 2003 thanks to the initiative of the Association of the inhabitants in the old town. The weekly event, which is very well attended, is a revival of tradition and has become a major attraction. The market in the old town has become a must and is now a place where people meet and socialise.
Convivialità nel carrello
Fin dal Medioevo, le fiere annuali e i concorsi di bestiame hanno animato la città. Le stagioni erano scandite dalle merci proposte, i mercati del XIX e XX secolo hanno portato un pubblico variegato e hanno ricollegato la pianura alla montagna, nonché i clienti ai produttori e ai commercianti. La qualità, il prezzo e il peso delle merci erano controllati e gli stand regolamentati. Situato nel cuore della città, il mercato divenne un attore importante dell’economia locale. Dopo una graduale perdita di interesse nella seconda metà del XX secolo, il mercato è stato rilanciato nel 2003 su iniziativa dell’Association des habitants de la vieille ville (Associazione degli abitanti del centro storico). L’evento settimanale, molto frequentato, è un ritorno alla tradizione e testimonia la sua grande
On mange à la Médiathèque !
Innovant, le centre culturel des Arsenaux l’est assurément ! L’ouverture du restaurant « Le Trait d’Union », à l’intérieur de la Médiathèque de Sion en 2014, fut une première en Suisse. Ce concept inédit a été imaginé dans le cadre d’un vaste chantier visant à regrouper sous le même toit plusieurs services et institutions liés à la culture. Cet espace, géré par l’Organisation romande d’intégration et de formation professionnelle (ORIF), permet à environ 10 jeunes adultes de se former au quotidien face à une réelle clientèle.
Die Mediathek bittet zu Tisch!
Innovativ ist das Zentrum für Kultur und Wissen in den ehemaligen Zeughäusern auf jeden Fall! Die Eröffnung des Restaurants „Le Trait d’Union“ in der Mediathek Sitten im Jahre 2014 stellt eine Premiere in der Schweiz dar. Das einzigartige Konzept, verschiedene, kulturbezogene Dienstleistungen und Institutionen unter einem Dach zusammenzuführen, wurde im Rahmen der umfassenden Bauarbeiten umgesetzt. In dem von der westschweizer Organisation für Integration und Berufsausbildung (ORIF) geführten Gastbetrieb sammeln täglich etwa 10 junge Erwachsene wichtige Berufserfahrungen.
Let's eat at the Médiathèque!
Innovative – that’s certainly the word for Sion’s Les Arsenaux Cultural Centre! The opening of “Le Trait d’Union” restaurant inside the Sion Médiathèque in 2014 marked a first for Switzerland. This novel concept is realised in the setting of a huge worksite that aims to bring multiple culture-related services and institutions together under one roof. This venue, managed by the Organisation for Professional Integration and Training of French-speaking Switzerland (ORIF), offers training for about 10 young adults as they deal with real customers on a daily basis.
On mange à la Médiathèque !
Innovant, le centre culturel des Arsenaux l’est assurément ! L’ouverture du restaurant « Le Trait d’Union », à l’intérieur de la Médiathèque de Sion en 2014, fut une première en Suisse. Ce concept inédit a été imaginé dans le cadre d’un vaste chantier visant à regrouper sous le même toit plusieurs services et institutions liés à la culture. Cet espace, géré par l’Organisation romande d’intégration et de formation professionnelle (ORIF), permet à environ 10 jeunes adultes de se former au quotidien face à une réelle clientèle.